Leaving the Buska Lodge, we turned east to cross the rugged Humu Range. Our eventual destination in three days’ time was Addis Ababa, but today we had one last tribe to visit: the Arbore tribe, whose ancestral homeland extends to the Weito River and Lake Chew Bahir.
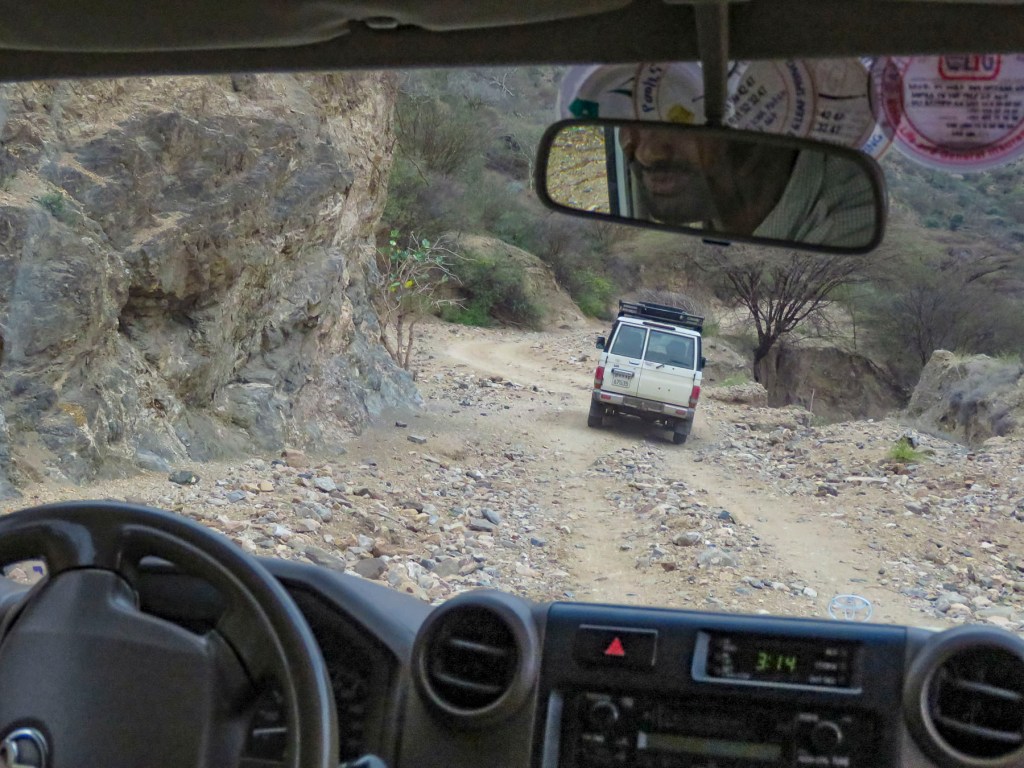

Not far from the lodge, the compacted dirt road deteriorated into a rock-strewn obstacle course, the result of a recent rockslide caused by torrential rains earlier in August. We coined the phrase “rattled tourist syndrome” here – after a couple of hours on this road, we felt like we had suffered brain damage! Rounding a bend, we got our first glimpse of Lake Chew in the distance, before the road descended to a dry riverbed which we followed out of a canyon to the flood plain along the western shore of the lake.

When the shallow lake is full, its water covers an area 40 miles long by 15 miles wide and extends into northern Kenya. It’s been drying up slowly for more than a century, and today it is mostly a papyrus-filled marshland. Its fertile shoreland is now farmed, and the papyrus reeds are cut from it by the Arbore to construct their huts. Plots of land along the lake are redistributed yearly by the elders of the tribe, so no one family always has the best parcel.

A short while later, under a threatening gray sky, we entered a small village. Here and there, women were involved in daily chores. Off to the side some children were tasked with rounding up a few young goats scampering about, while the married women of the village were attending to various chores in front of their huts.
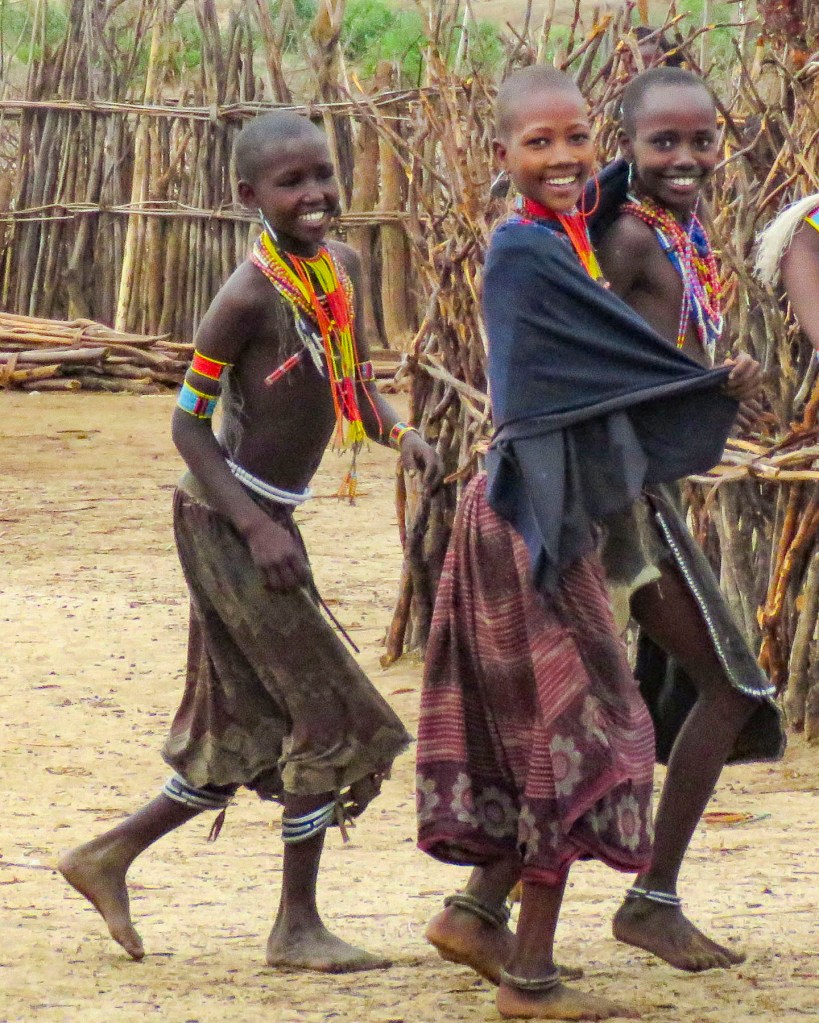



The young, unmarried women of the clan were recognizable by the black cloth, a symbol of virginity, they draped over their shaven heads to protect themselves from the sun. Cattle-centric like most of the Omo Valley tribes the Arbore, which means land of the bulls, add a new dimension to it with the men joining the names of their favorite cows to their wives’ names.
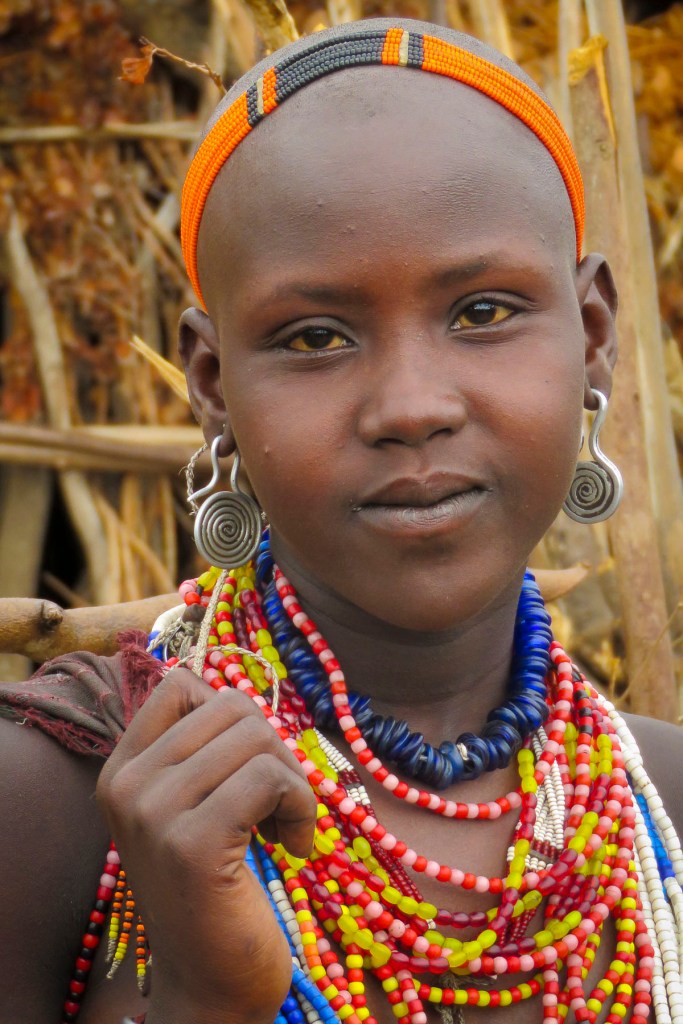



The Arbore are well respected by the surrounding tribes, the result of an ancient enduring legend in which the tribe defeated the devil in a battle. Consequently, they have a centuries’ old “don’t mess with us” reputation that ensures a peaceful coexistence with their neighbors and fosters inter-tribal marriages and sharing of grazing lands when there are droughts.



With the onslaught of the expected rain we were invited into a tribeswoman’s hut. It was larger than some made by other tribes, with a second room where two small children were asleep on goat skins. The front was roomy enough to shelter three of us and five villagers, sitting and standing, from the downpour outside. It was a dark but dry enclosure. The colorful beads the women wore were illuminated by the only light source, the short entryway to the hut.


There are not any convenient alternate routes between points in the Omo Valley which meant we backtracked on roads previously driven as we worked our way towards Konso and Arba Minch. We arrived late in the day to the Paradise Lodge, and the view from their terrace was spectacular as the sunny sky brightened the verdant jungle that separated Lake Abaya from Lake Chamo in the distance.

“The next time you come, we will go to the Bridge of God. It’s on the peak of that mountain that separates the two lakes. There is a wonderful track through the jungle that takes you there,” our guide promised.
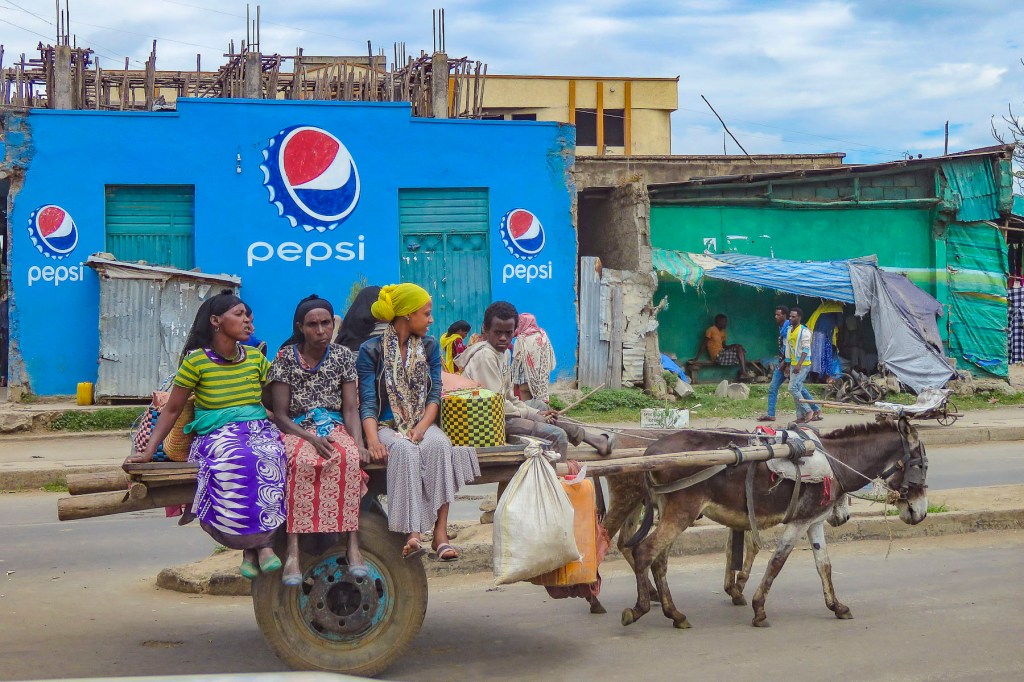

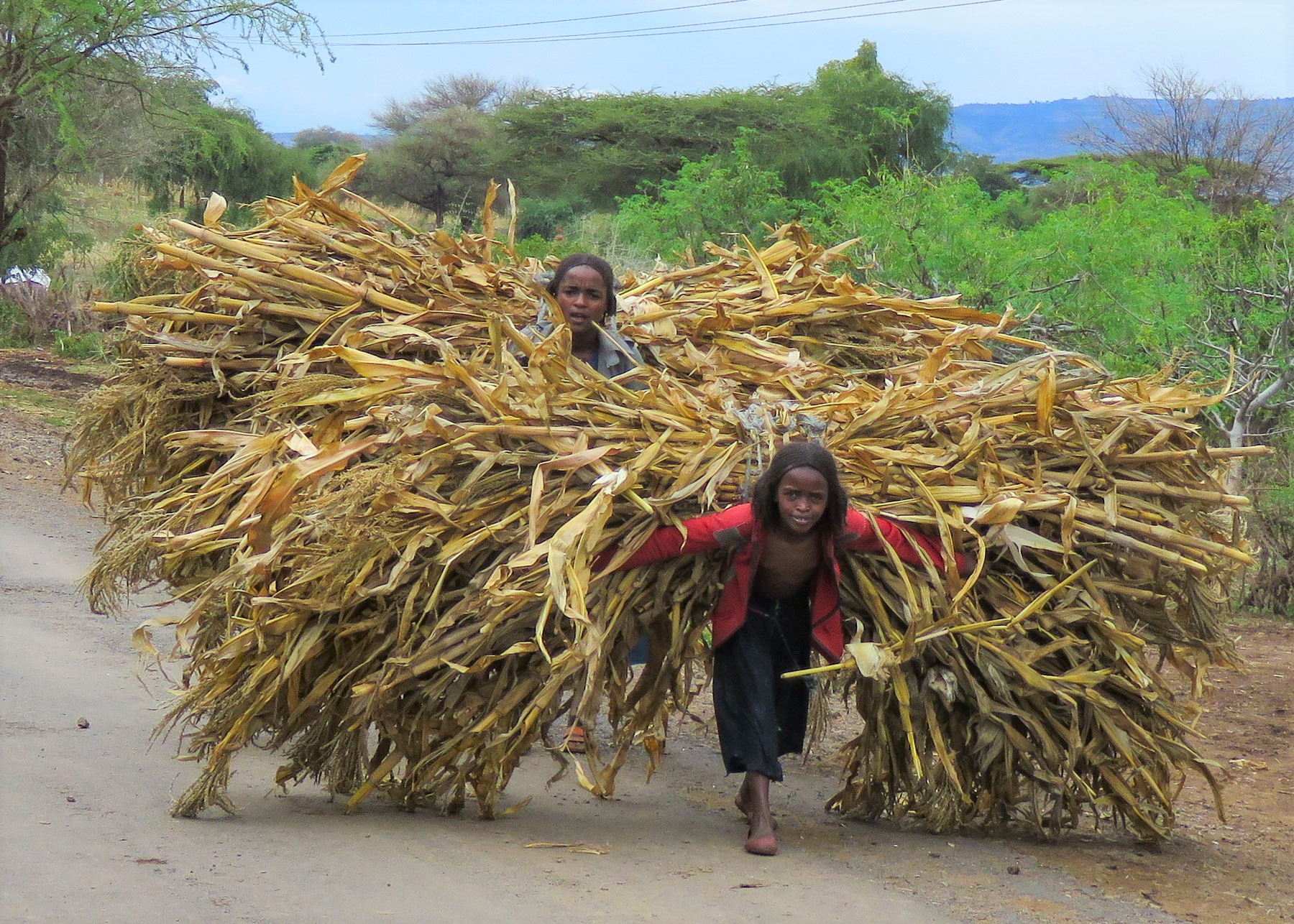
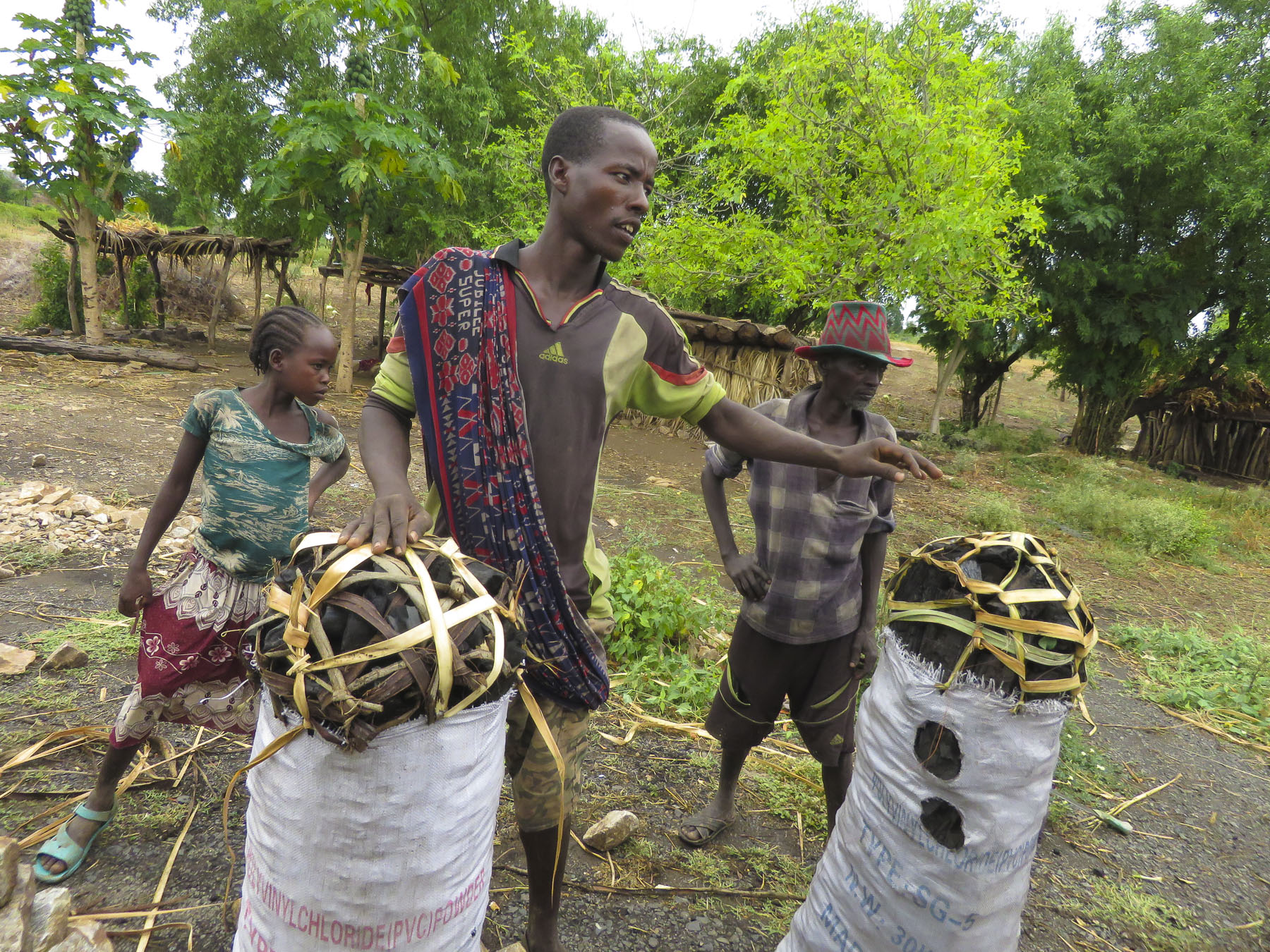
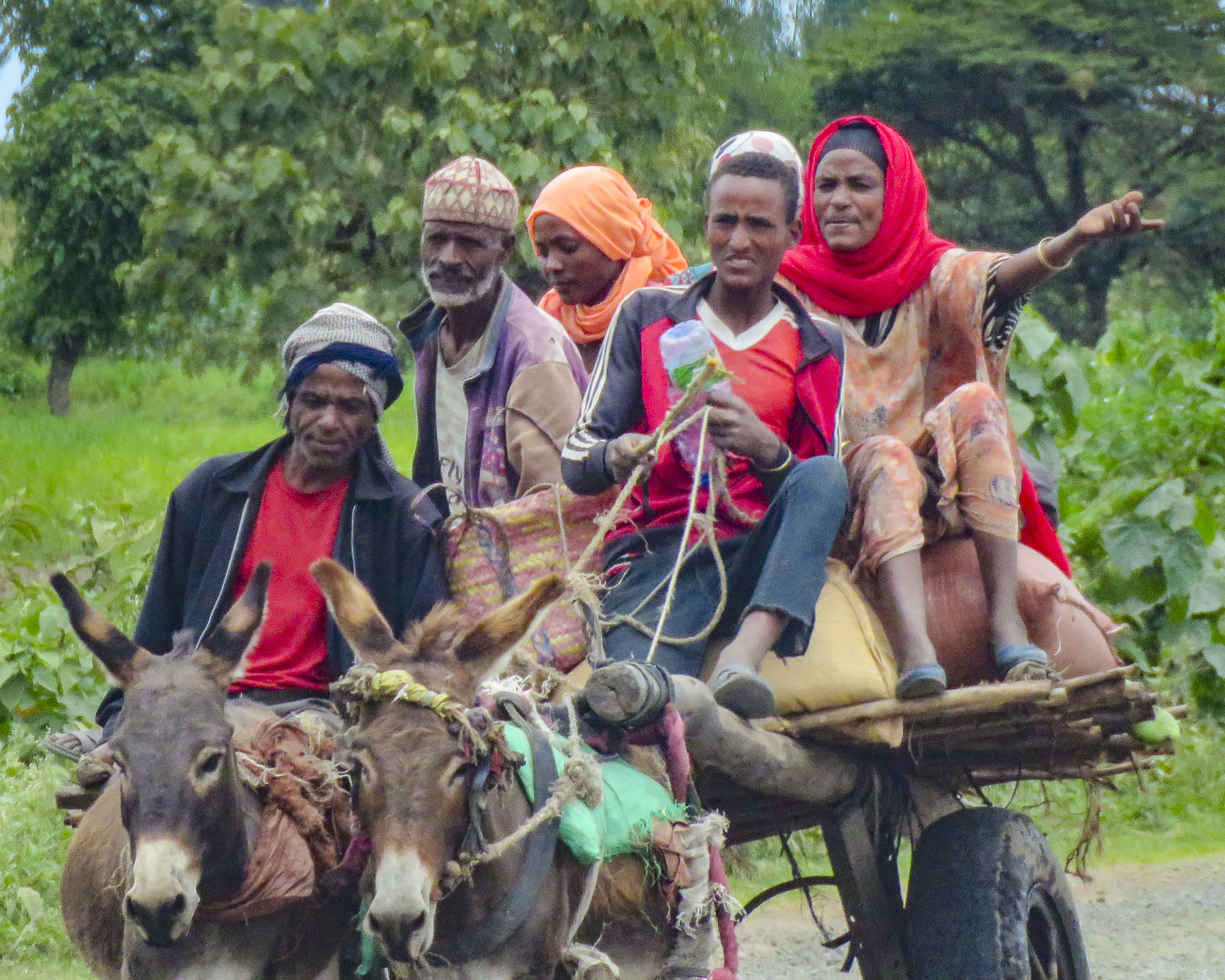
In the morning we set north to Lake Awassa, and the route was humming with activity. Folks walking, charcoal and dried chili vendors, tuk-tuks, donkey carts, herds of cattle and buses all jostled peacefully for space on this artery of commerce.





Before spending the night in Awassa, we detoured into the Senkele Wildlife Sanctuary, a 13,000-acre reserve established to protect a herd of 700 Swayne’s hartebeests, an endangered antelope.

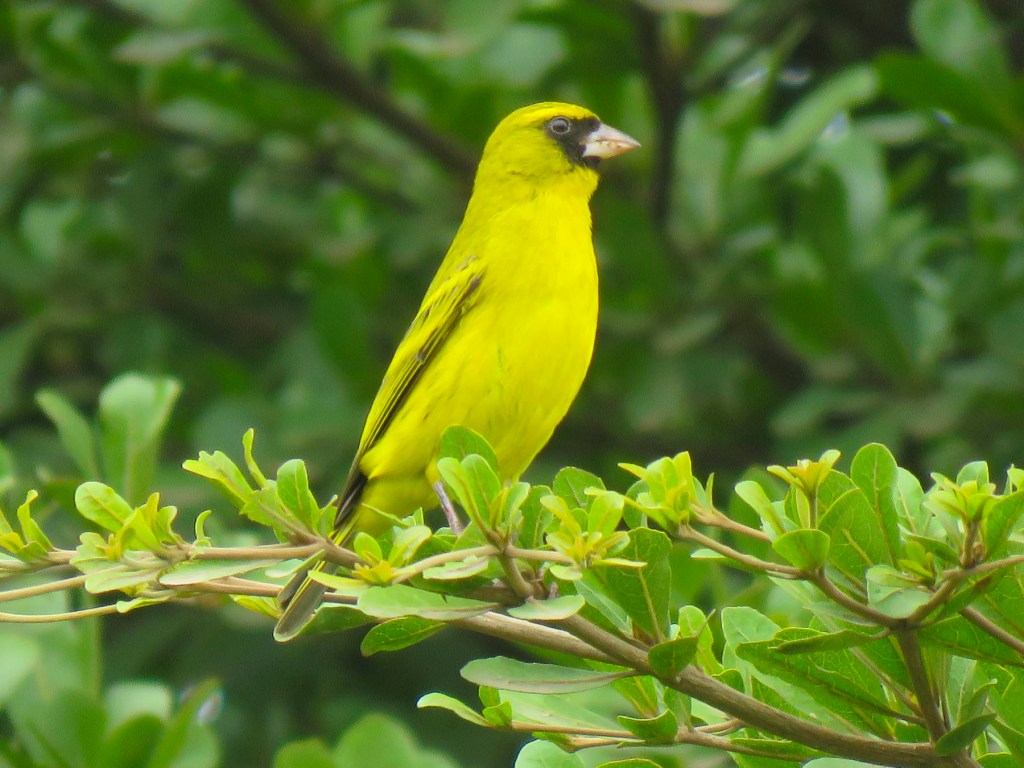
At the ranger station we parked our truck next to a large acacia tree, where to our delight a colony of weaver birds were frantically darting to and fro, constructing their intricate hanging nests.


The guide drove us deep into the surrounding grasslands until he spotted a herd, and then encouraged us to walk across the plain with him. Just exiting the vehicle made a huge difference in our appreciation of this gently rolling, beautiful landscape.



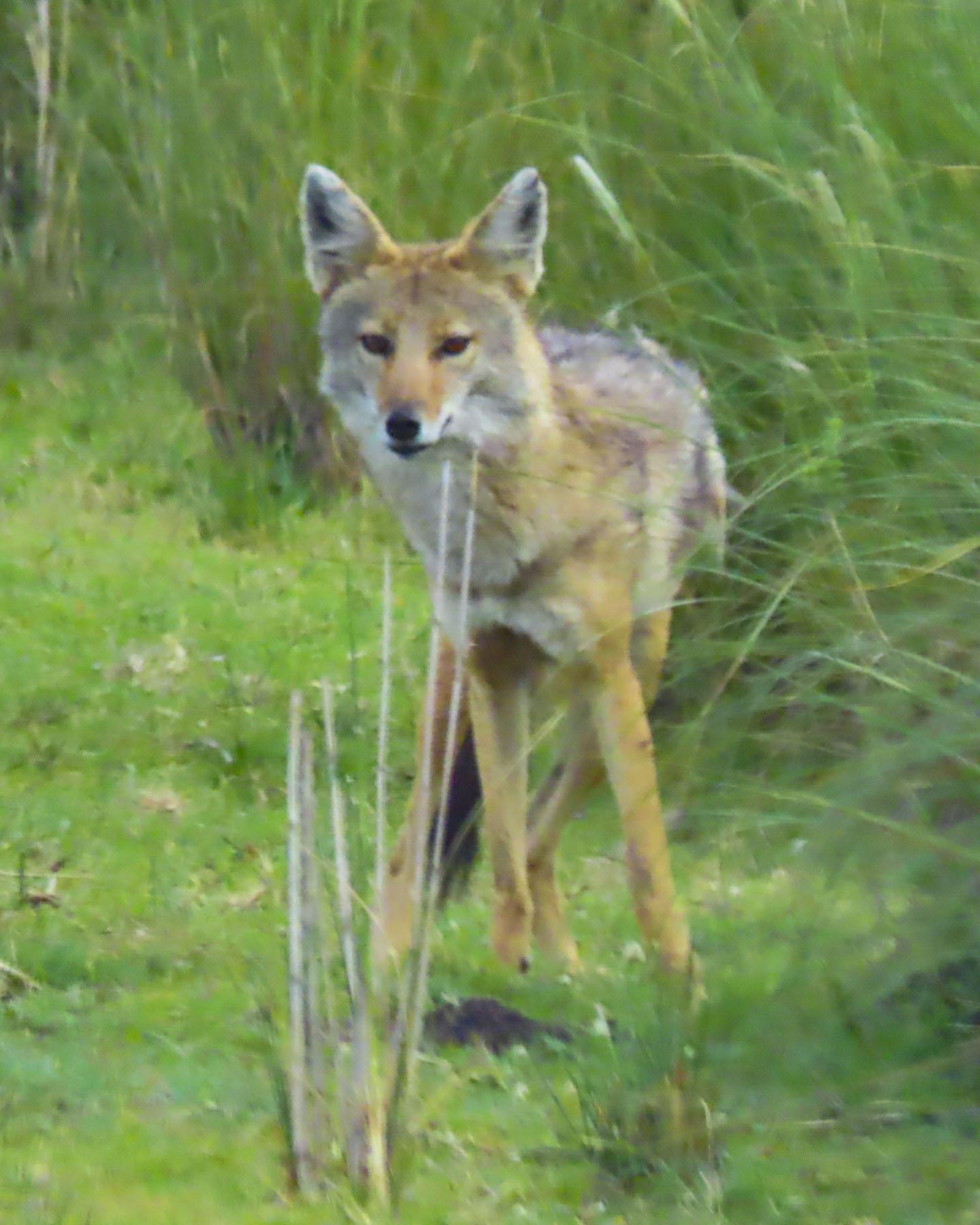
The air was fresh, and an earthy aroma rose from the ground. Farther down the track the ranger turned a blind eye to a young herder quickly moving some cattle through the reserve. And to everyone’s surprise we spotted a rare Ethiopian wolf, which was stealthily shadowing a dik-dik.


Our destination the next morning was the Hawassa fish market, next to Amora Gedel, the smallest national park in Ethiopia. The market is a daily open-air event where fishermen paddle anything that floats, in order to eke out a living from the over-fished lake and its dwindling stock of tilapia, catfish, and Nile perch.

It was a colorful, chaotic affair as the fishermen gutted and filleted the freshly caught fish on the ground as soon as the nets were emptied. It attracted a huge number of birds ready to swoop in to scavenge the scraps when the activity died down.
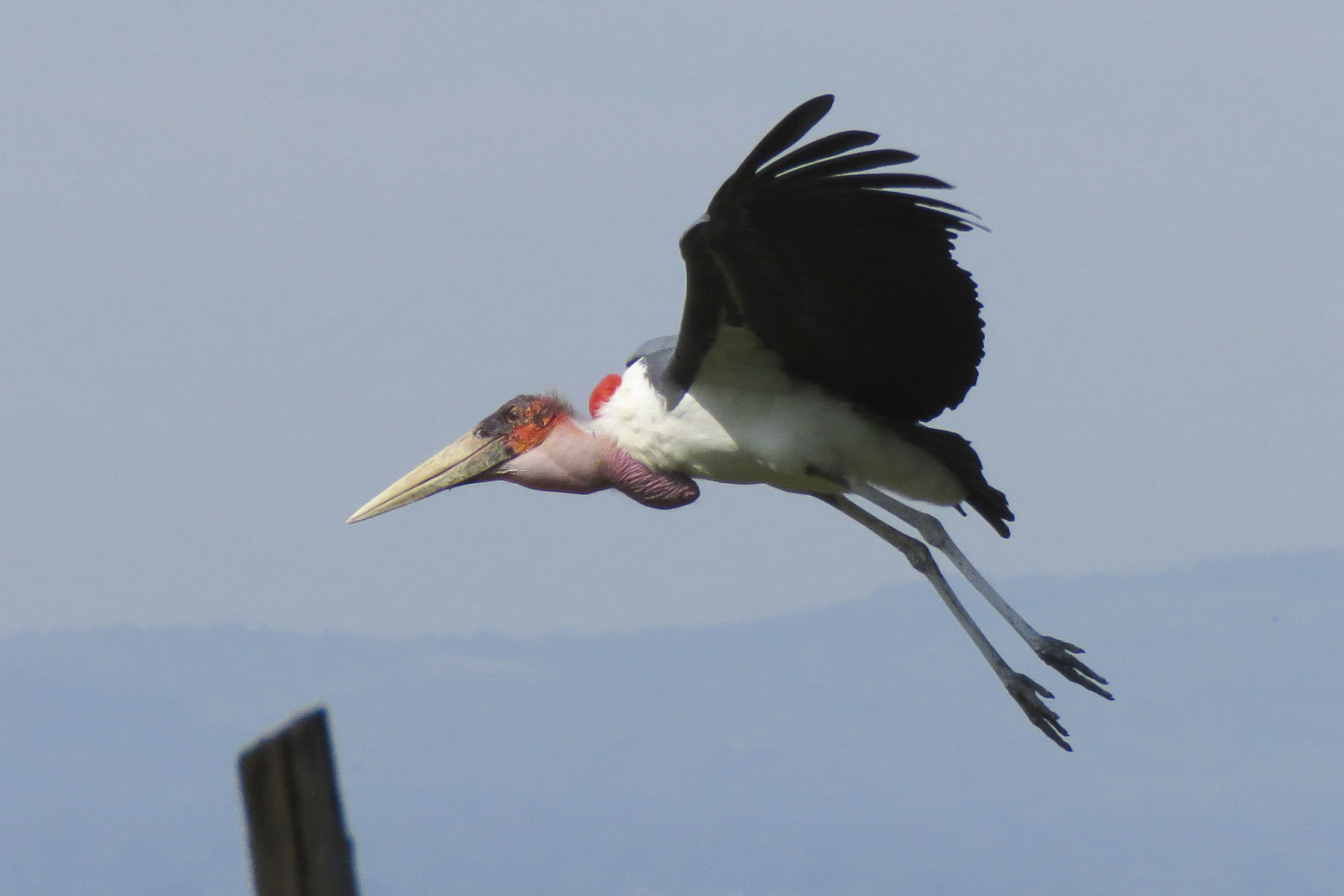


There were a large number of ugly marabou storks, with their peculiar scaly heads, but we also saw hamerkop, ibis, pelicans and cormorants waiting patiently. Ringing the parking lot, there were food shacks that prepared fried fish and a fish soup that is popular locally for breakfast.





Afterwards we headed to Abidjatta-Shalla National Park, which is known for its two large alkaline lakes surrounded by hot springs and flocks of flamingos, as well as a vast variety of bird life that favors the encompassing savanna. We hired a ranger at the main gate and followed him along an unmarked path through the open woodland.
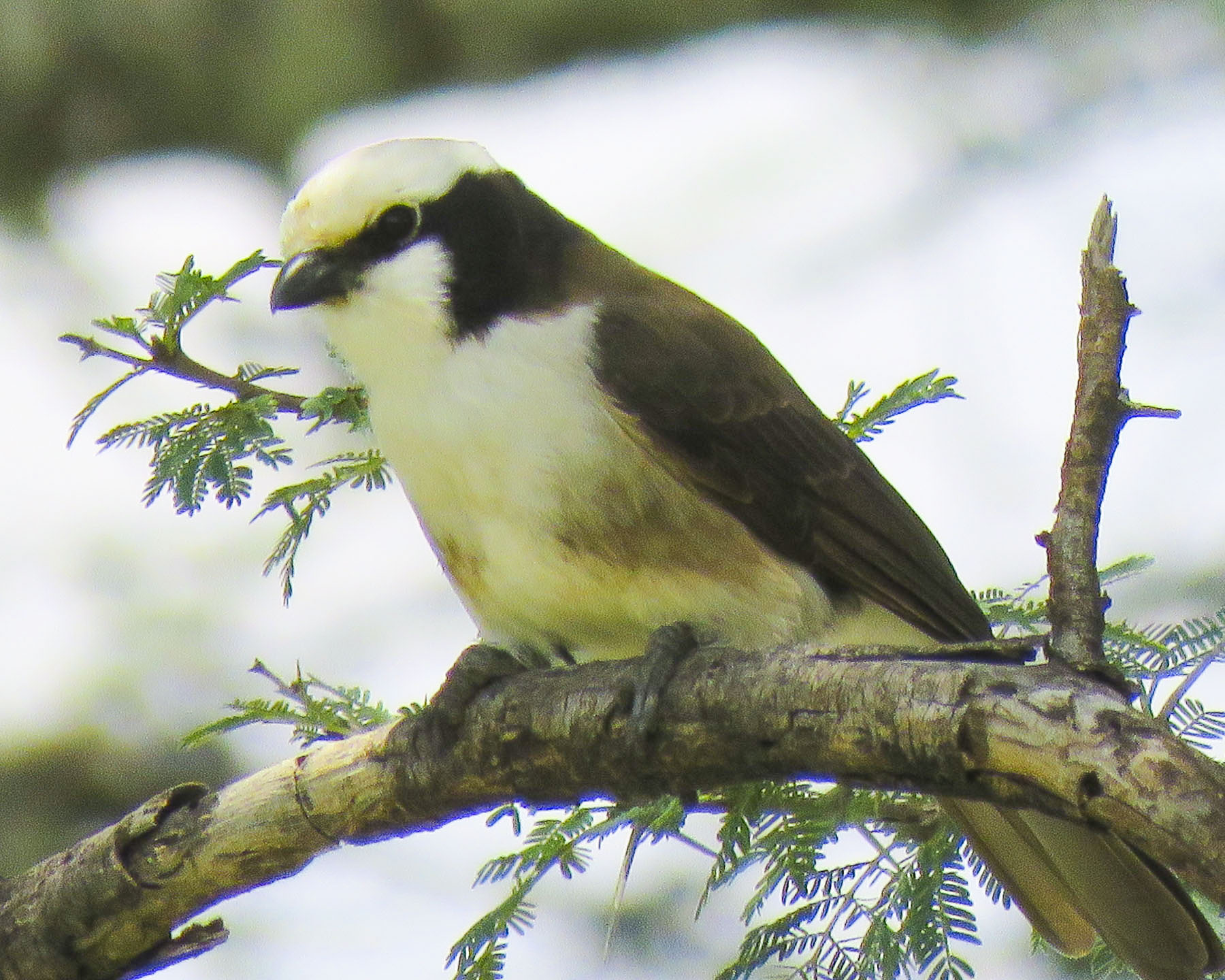





Soon we spotted a go away bird, warthogs and our favorite blue-eared glossy starlings. Farther on we crept slowly up to a dominant male ostrich watching over a small flock. Our guide wanted us to go home with spectacular photos, so he instructed my wife to give him her camera, and to approach the large ostrich.


“It will be good photo,” he said in his broken English. “Closer, closer, closer.” My wife eyed the massive claws and muscular legs of the beast, and uncomfortably crept closer to the ostrich than she thought wise to do, the guide motioning her on all the while. “Stop!” the guide suddenly whisper-screeched and began snapping. He was right – they were pretty dramatic photos. Seconds later the ostriches were spooked by an unexpected antelope bounding through, and trotted off.
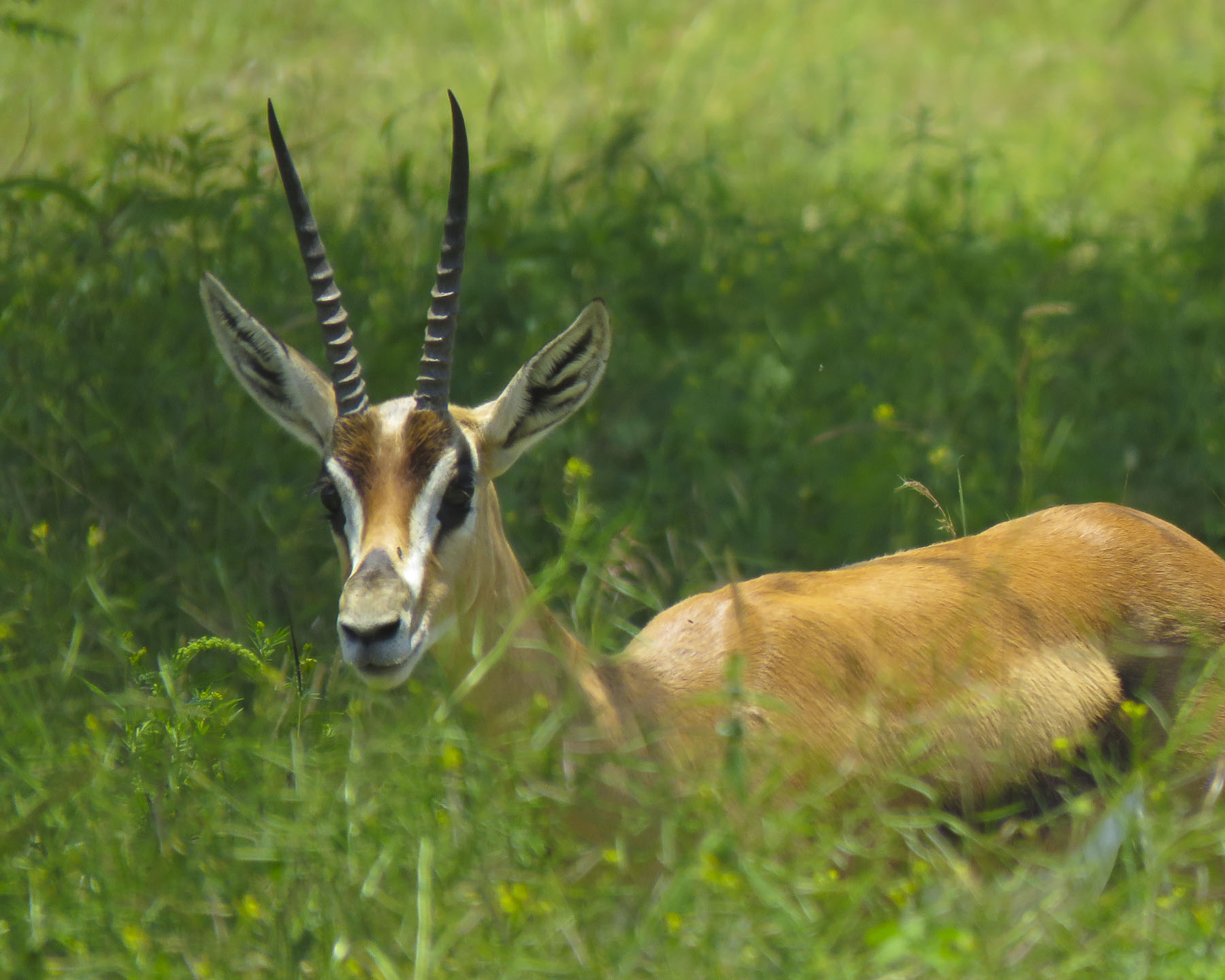


Back in the truck, our ranger guided us across the park to the shore of Shala Lake where we observed lesser flamingos feeding on cyanobacteria, abundant in the lakes’ alkaline water.

After cresting a small ridge, we were overlooking a hot spring that bubbled up through the earth in a gully several hundred yards from the lake shore. Surprisingly, there was a good size makeshift camp around it, supporting folks doing laundry and cooking food in the hot water. Farther downstream people were bathing in ever cooler pools before the water emptied into the lake.



After soaking our feet in a suitable pool, it was time to return to Addis Ababa for our own day of laundry and rest before the next part of our Ethiopian journey, the rock churches of Lalibela.
Till next time, Craig & Donna




 Often overshadowed in recent decades by its East African neighbors recognized for their safaris, Ethiopia has been known to Western culture for millennia. It was first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, around 1000 BC (3,000 years ago!), when the Queen of Sheba, hearing of “Solomon’s great wisdom and the glory of his kingdom,” journeyed from Ethiopia with a caravan of treasure as tribute. Unbeknownst to Solomon their union produced a son, Menilek, (meaning son of the wise man). Years later, wearing a signet ring given to him by his mother, Menilek visited Jerusalem to meet Solomon and stayed for several years to study Hebrew. When his son desired to return home, Solomon gifted the Ark of the Covenant to Menilek for safe keeping in Ethiopia, and to this day it is said to reside in the Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion, in Aksum, where only a select few of the Ethiopian Orthodox church can see it.
Often overshadowed in recent decades by its East African neighbors recognized for their safaris, Ethiopia has been known to Western culture for millennia. It was first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, around 1000 BC (3,000 years ago!), when the Queen of Sheba, hearing of “Solomon’s great wisdom and the glory of his kingdom,” journeyed from Ethiopia with a caravan of treasure as tribute. Unbeknownst to Solomon their union produced a son, Menilek, (meaning son of the wise man). Years later, wearing a signet ring given to him by his mother, Menilek visited Jerusalem to meet Solomon and stayed for several years to study Hebrew. When his son desired to return home, Solomon gifted the Ark of the Covenant to Menilek for safe keeping in Ethiopia, and to this day it is said to reside in the Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion, in Aksum, where only a select few of the Ethiopian Orthodox church can see it.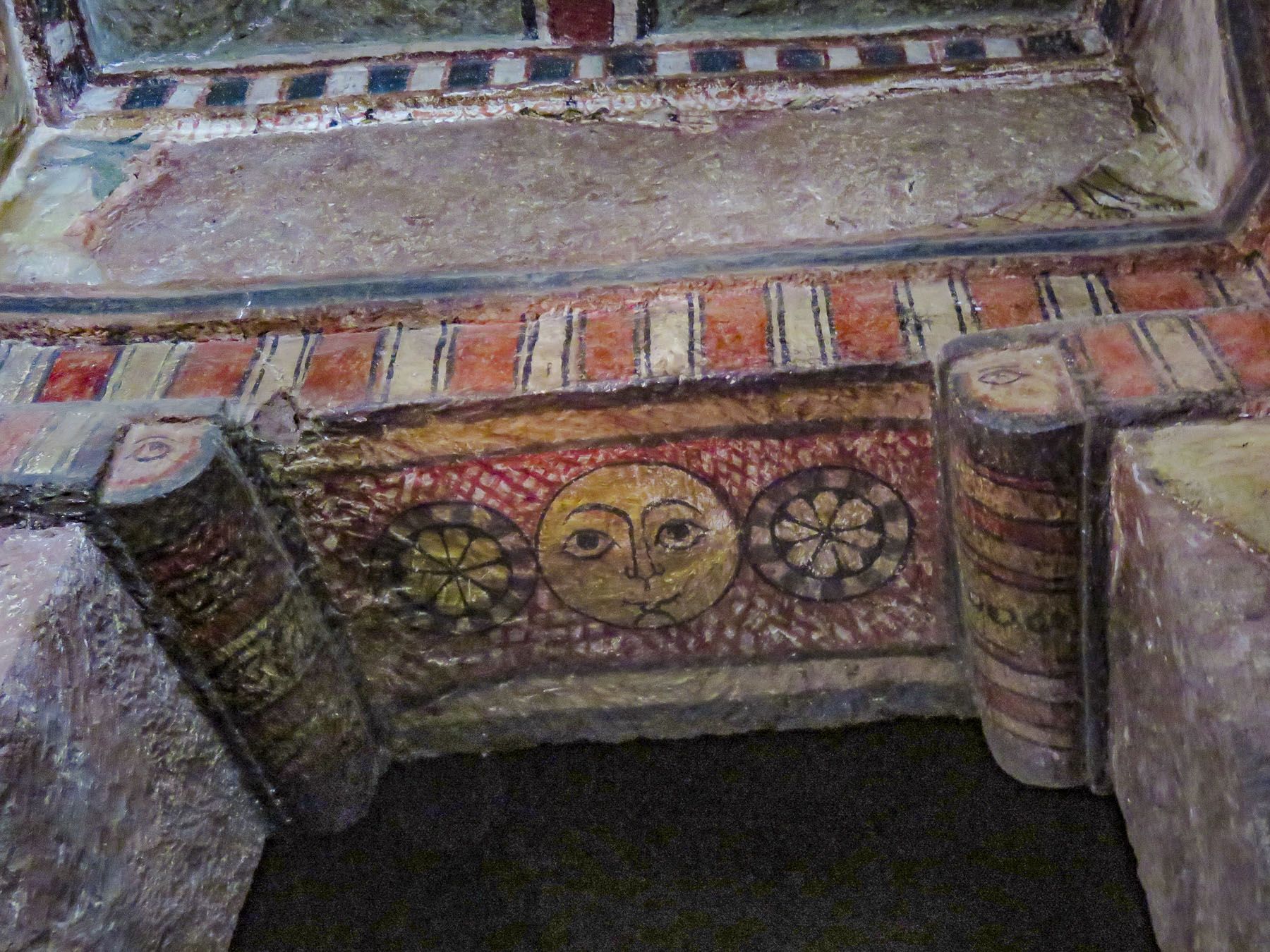








 With the Ethiopian Orthodox Church having a site in Jerusalem since the sixth century, Ethiopian pilgrimages to the Holy Land, which took six months, were common until the route was blocked by Muslim conquests in 1100s and the journey became too hazardous. As it became surrounded further by Muslim territories, the country sank into isolation from Europe. Ethiopia’s early history and its connection to Judaism and Christianity is a twisting tale, like caravan tracks across the desert, meeting then disappearing behind sand dunes, the story buried by the blowing sands of time.
With the Ethiopian Orthodox Church having a site in Jerusalem since the sixth century, Ethiopian pilgrimages to the Holy Land, which took six months, were common until the route was blocked by Muslim conquests in 1100s and the journey became too hazardous. As it became surrounded further by Muslim territories, the country sank into isolation from Europe. Ethiopia’s early history and its connection to Judaism and Christianity is a twisting tale, like caravan tracks across the desert, meeting then disappearing behind sand dunes, the story buried by the blowing sands of time. Distraught by this, King Lalibela commissioned eleven architecturally perfect churches, to be hewn from solid rock, to serve as a New Jerusalem complete with a River Jordan for pilgrims to visit. He based the designs on memories of holy sites from his own pilgrimage to the Holy Land as a young man.
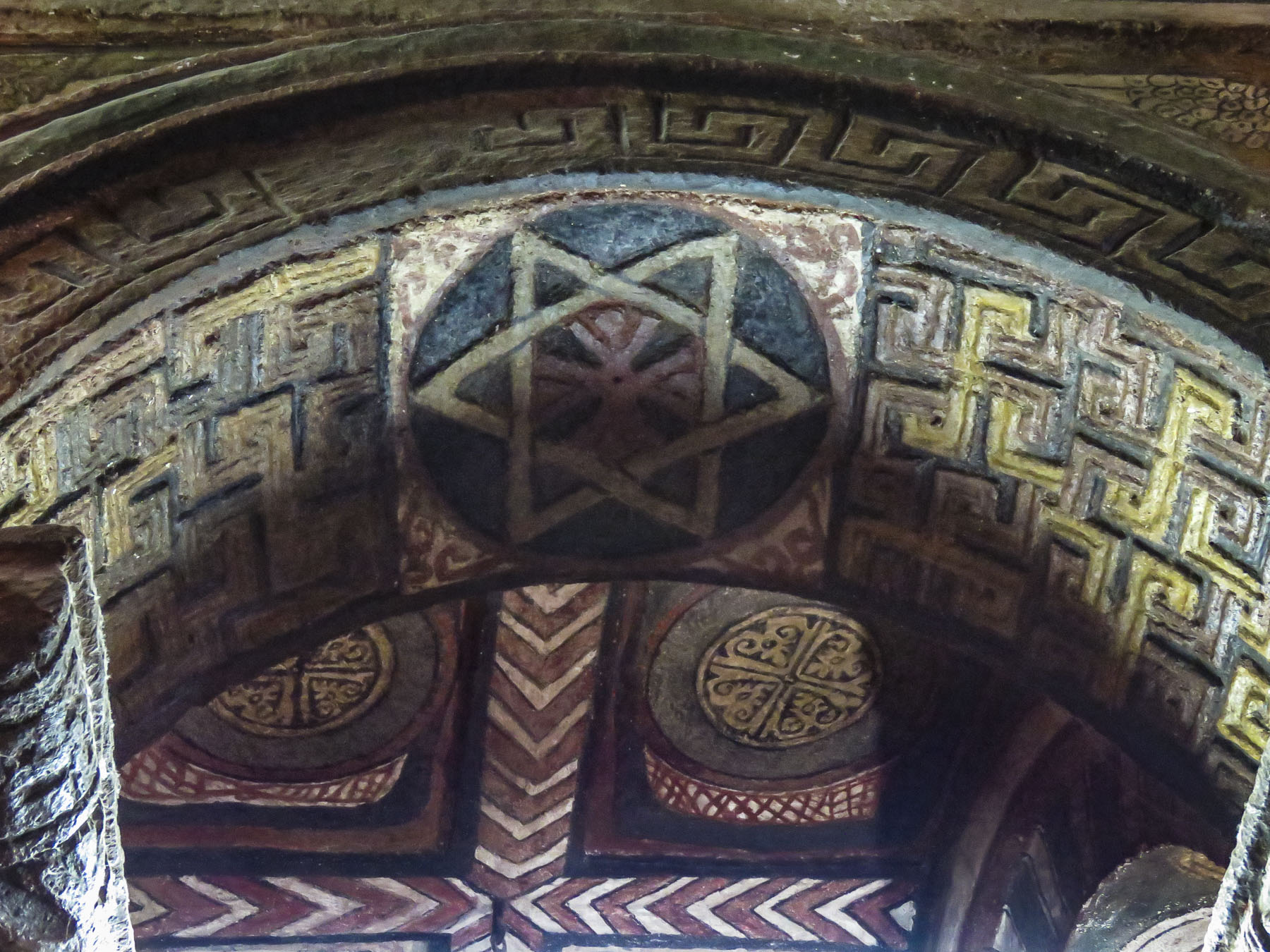
Distraught by this, King Lalibela commissioned eleven architecturally perfect churches, to be hewn from solid rock, to serve as a New Jerusalem complete with a River Jordan for pilgrims to visit. He based the designs on memories of holy sites from his own pilgrimage to the Holy Land as a young man.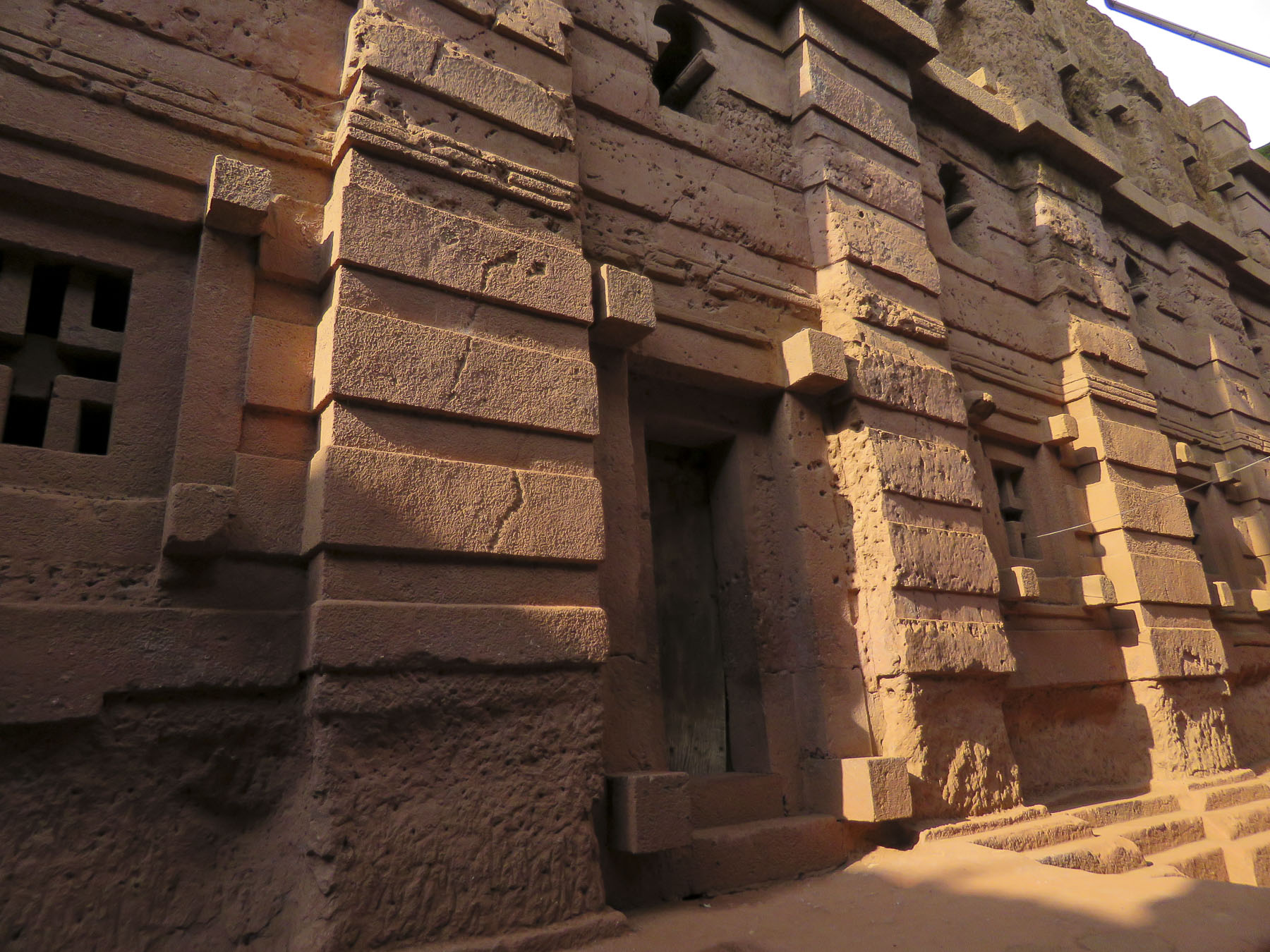 Considering the limited availability of tools in the 1100s, I can’t imagine what a daunting task this must have been. I’m sure the chief architect said, “you have to be kidding.” It’s believed that 40,000 men, assisted by angels at night, labored for 24 years to create this testament to their faith. Masons outlined the shape of these churches on top of monolithic rocks, then excavated straight down forty feet to create a courtyard around this solid block. Doors would then be chiseled into the block and the creation of the church would continue from the inside, often in near total darkness.
Considering the limited availability of tools in the 1100s, I can’t imagine what a daunting task this must have been. I’m sure the chief architect said, “you have to be kidding.” It’s believed that 40,000 men, assisted by angels at night, labored for 24 years to create this testament to their faith. Masons outlined the shape of these churches on top of monolithic rocks, then excavated straight down forty feet to create a courtyard around this solid block. Doors would then be chiseled into the block and the creation of the church would continue from the inside, often in near total darkness.












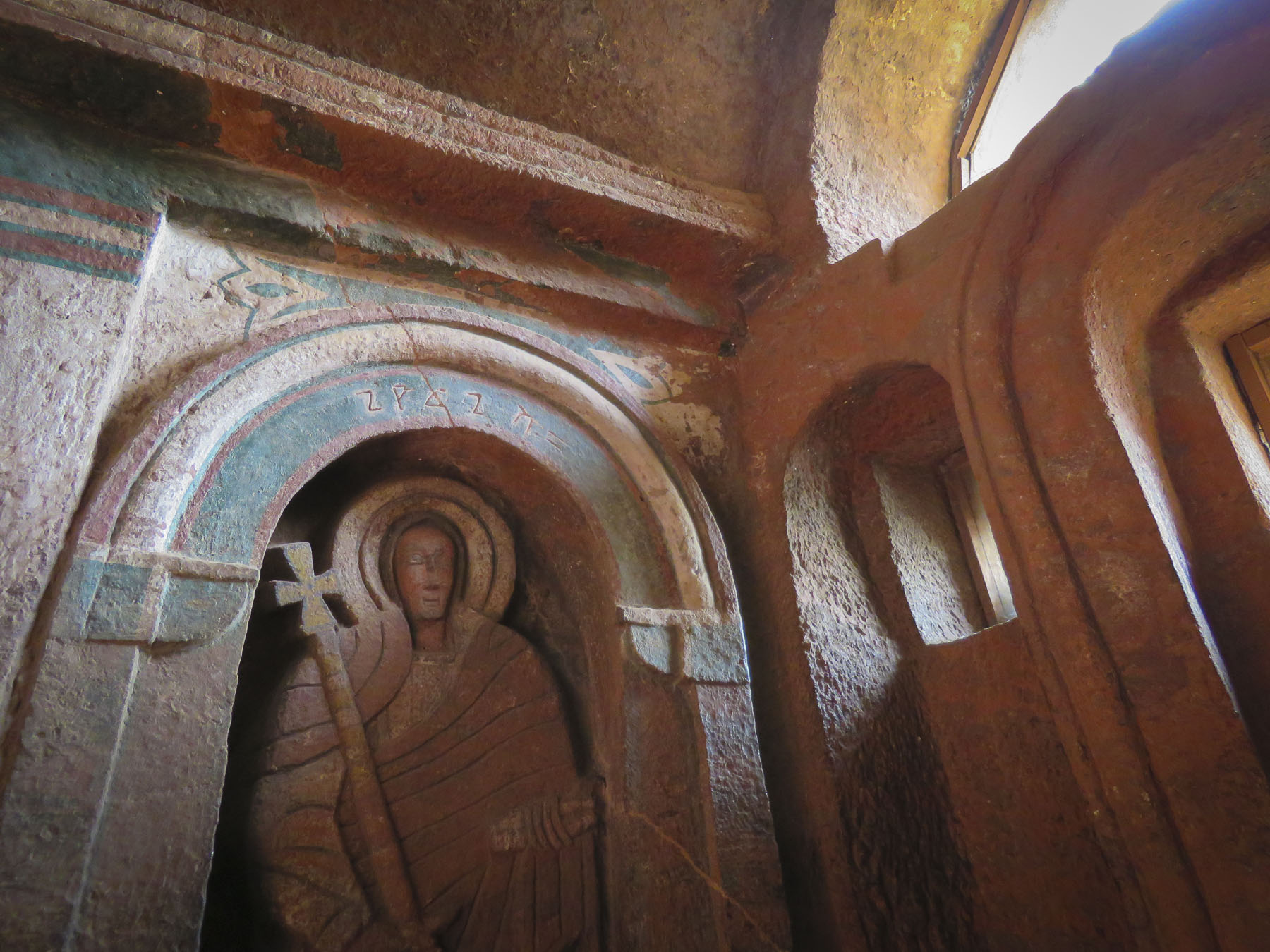
 Women worshippers traditionally enter through a separate door and pray apart from the men. Inside, thirty-eight stone columns form four aisles and support a stone ceiling that soars overhead. After walking for days or weeks to reach Lalibela, often fasting the entire time, the journey ends here for many pilgrims, in hopes of receiving a blessing or cure from touching the Lalibela Cross and offering prayers.
Women worshippers traditionally enter through a separate door and pray apart from the men. Inside, thirty-eight stone columns form four aisles and support a stone ceiling that soars overhead. After walking for days or weeks to reach Lalibela, often fasting the entire time, the journey ends here for many pilgrims, in hopes of receiving a blessing or cure from touching the Lalibela Cross and offering prayers.
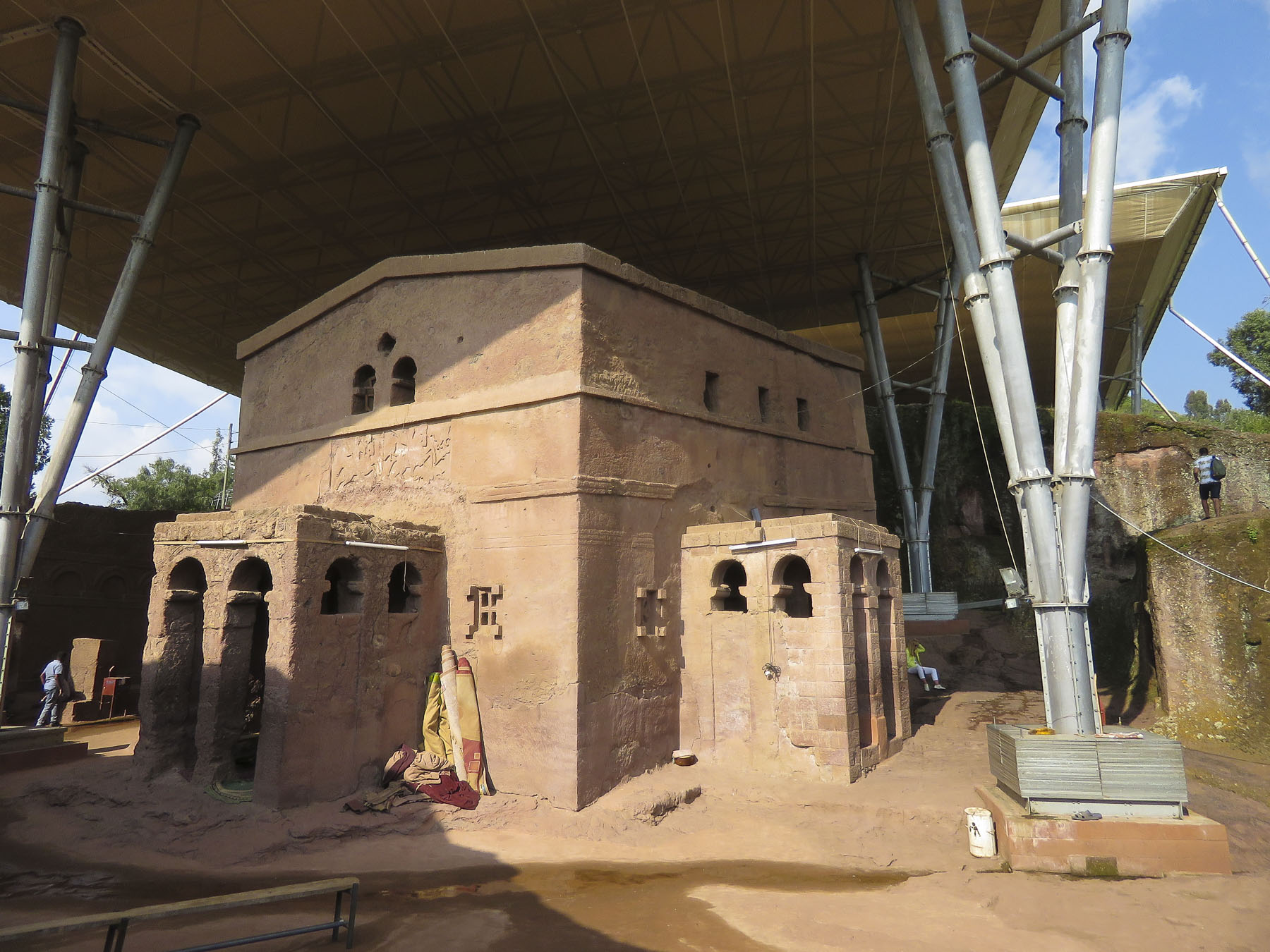



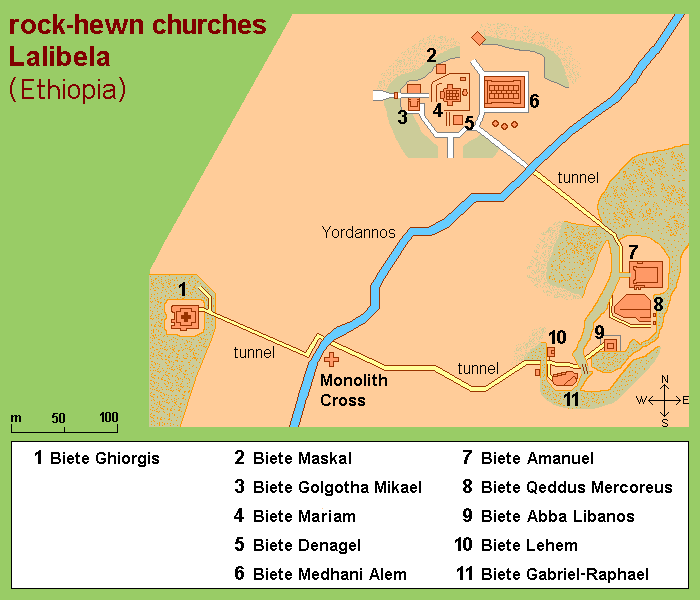


 The next morning, we completed our tour of the cluster of the southern of the rock churches: Beta Emmanuel (Church of Emmanuel), Beta Abba Libanos (Church of Father Libanos), Beta Merkurios (Church of Mercurius) and Beta Gabriel and Beta Rafa’el (the twin churches of Gabriel and Raphael.)
The next morning, we completed our tour of the cluster of the southern of the rock churches: Beta Emmanuel (Church of Emmanuel), Beta Abba Libanos (Church of Father Libanos), Beta Merkurios (Church of Mercurius) and Beta Gabriel and Beta Rafa’el (the twin churches of Gabriel and Raphael.)

 It’s important to remember that this is not a museum with ancient artifacts and manuscripts in glass cases, but an active holy site where the ancient manuscripts are still used daily, and it is home to a large community of priests and nuns. It has been a destination for Ethiopian Orthodox pilgrims in the northern highlands (elevation 8,200’) for the last 900 years and continues to be visited by tens of thousands of pilgrims annually.
It’s important to remember that this is not a museum with ancient artifacts and manuscripts in glass cases, but an active holy site where the ancient manuscripts are still used daily, and it is home to a large community of priests and nuns. It has been a destination for Ethiopian Orthodox pilgrims in the northern highlands (elevation 8,200’) for the last 900 years and continues to be visited by tens of thousands of pilgrims annually. Leaving the churches behind, we walked through an area of ancient two story, round houses called Lasta Tukuls, or bee huts, built from local, quarried red stone. Abandoned now for preservation, they looked sturdy, their stone construction distinctive from the other homes in the area that use an adobe method.
Leaving the churches behind, we walked through an area of ancient two story, round houses called Lasta Tukuls, or bee huts, built from local, quarried red stone. Abandoned now for preservation, they looked sturdy, their stone construction distinctive from the other homes in the area that use an adobe method. Today roughly 100,000 foreign tourists, in addition to Ethiopian pilgrims, visit Lalibela annually, a far cry from its near obscurity 140 years ago. Located four hundred miles from Addis Ababa, it is still far enough off the usual tourist circuits to make it a unique and inspiring destination.
Today roughly 100,000 foreign tourists, in addition to Ethiopian pilgrims, visit Lalibela annually, a far cry from its near obscurity 140 years ago. Located four hundred miles from Addis Ababa, it is still far enough off the usual tourist circuits to make it a unique and inspiring destination.



 We would have been terribly dissappointed if this had happened to us and we missed visiting the Mursi tribe. (Note to self – don’t leave important events to the last day.) Curious children made their way amidst the tourist vehicles, looking through the windows and asking for soap, shampoo, pens, pencils, caramels, and empty water bottles. The kids would have been happy with anything anyone gave them. Some pointed to the clothes we were wearing, hoping we would donate them. Folks make do with very little here and wear things until they are threadbare, out of necessity. Often, we saw older children wearing infant onesies with the feet of the garment cut off. We are not criticizing; it’s all they had. It saddened us and we wished we had brought an extra suitcase of clothes along to donate to a village. Eventually there was a burst of activity with rumbling engines at the front of the line and folks running back to their rides.
We would have been terribly dissappointed if this had happened to us and we missed visiting the Mursi tribe. (Note to self – don’t leave important events to the last day.) Curious children made their way amidst the tourist vehicles, looking through the windows and asking for soap, shampoo, pens, pencils, caramels, and empty water bottles. The kids would have been happy with anything anyone gave them. Some pointed to the clothes we were wearing, hoping we would donate them. Folks make do with very little here and wear things until they are threadbare, out of necessity. Often, we saw older children wearing infant onesies with the feet of the garment cut off. We are not criticizing; it’s all they had. It saddened us and we wished we had brought an extra suitcase of clothes along to donate to a village. Eventually there was a burst of activity with rumbling engines at the front of the line and folks running back to their rides.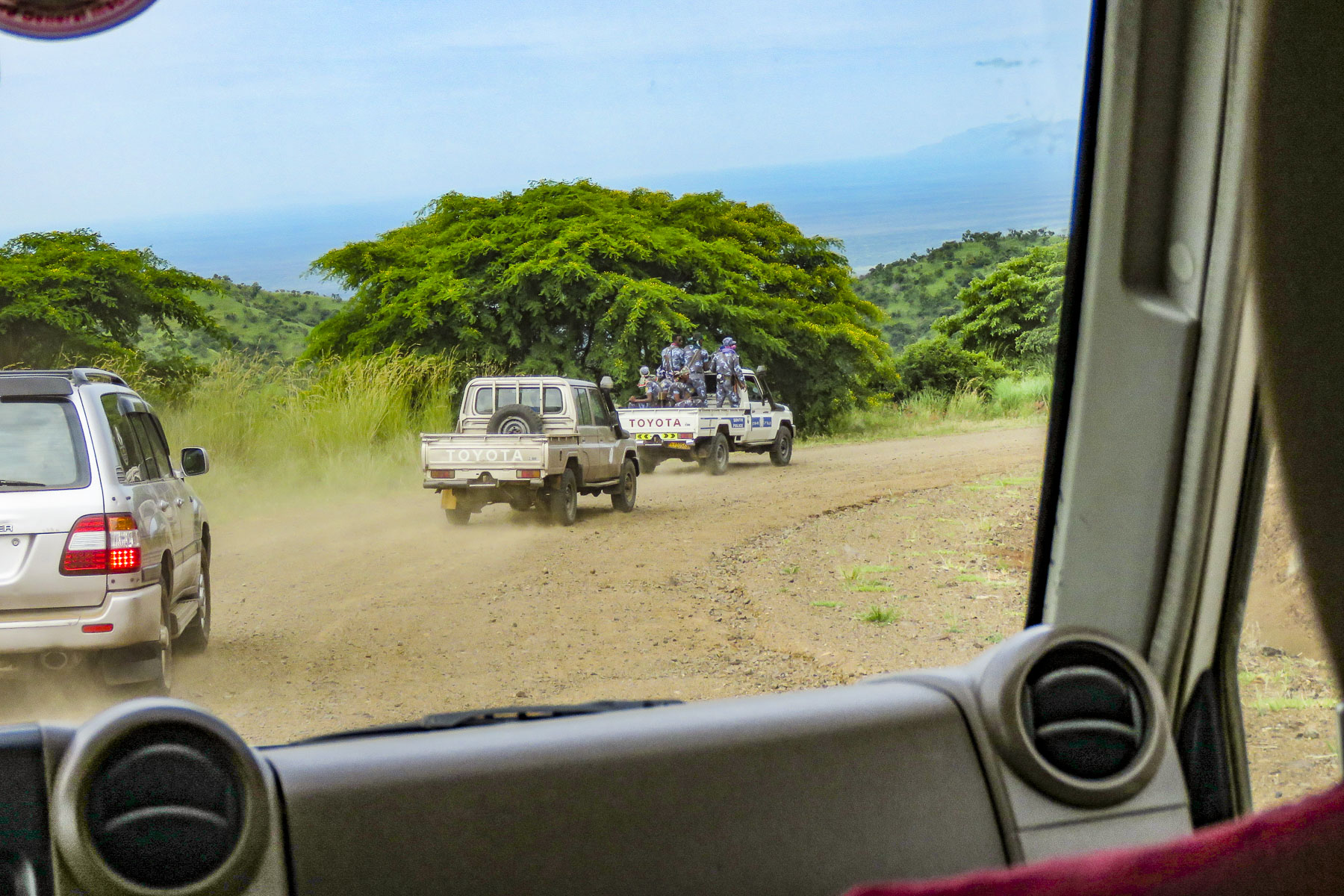  We were the third car in a group of five that was being led by a pickup truck full of armed paramilitary policemen. Many of the incidents that have occurred are related to the increase in truck and bus traffic roaring through Mursi territory on the way to new cotton and sugarcane plantations along the banks of the Omo River.
We were the third car in a group of five that was being led by a pickup truck full of armed paramilitary policemen. Many of the incidents that have occurred are related to the increase in truck and bus traffic roaring through Mursi territory on the way to new cotton and sugarcane plantations along the banks of the Omo River.  Cattle are very often herded down the roads and sometimes are struck and killed, along with their herders. Often drivers do not stop to take responsibility. In the eyes of the villagers, the local authorities have not resolved the situation. As a result, tribespeople will set roadblocks to rob buses carrying plantation workers and extract revenge on truckers. A while later we stopped and were assigned an armed escort, with an AK-47, who accompanied us for the duration of our visit. He was euphemistically called a scout.
Cattle are very often herded down the roads and sometimes are struck and killed, along with their herders. Often drivers do not stop to take responsibility. In the eyes of the villagers, the local authorities have not resolved the situation. As a result, tribespeople will set roadblocks to rob buses carrying plantation workers and extract revenge on truckers. A while later we stopped and were assigned an armed escort, with an AK-47, who accompanied us for the duration of our visit. He was euphemistically called a scout. Turning off the dirt road, branches scratched against the side of the truck as we followed a narrow dirt track through the savanna to a clearing where a small group of thatched huts stood. Soon the women of the village stopped what they were doing to greet us.
Turning off the dirt road, branches scratched against the side of the truck as we followed a narrow dirt track through the savanna to a clearing where a small group of thatched huts stood. Soon the women of the village stopped what they were doing to greet us.










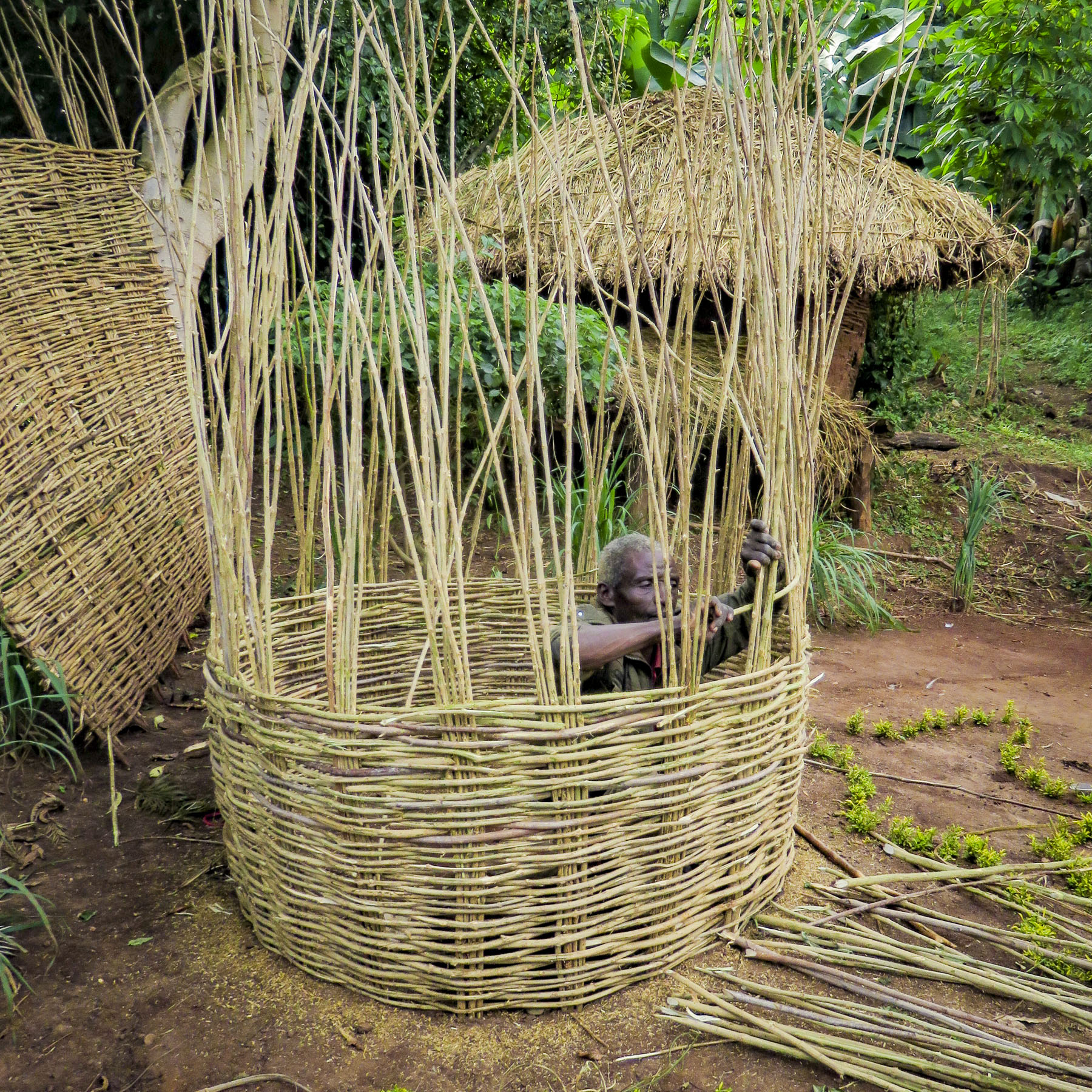
 It was a steep walk up a trail through a forest of false banana, enset, to a well-kept sturdy hut with a medicinal herb garden.
It was a steep walk up a trail through a forest of false banana, enset, to a well-kept sturdy hut with a medicinal herb garden.  Outside two women were pinching clay into bowls and teapots that would later be sold at a weekly market.
Outside two women were pinching clay into bowls and teapots that would later be sold at a weekly market.


 With sunlight shining through a canopy of giant enset leaves above her, a tribeswoman prepared kocho, a traditional Ethiopian flatbread, over an open smoky fire as we sat and watched. Behind us children giggled as they playfully rolled an old bicycle rim down the path.
With sunlight shining through a canopy of giant enset leaves above her, a tribeswoman prepared kocho, a traditional Ethiopian flatbread, over an open smoky fire as we sat and watched. Behind us children giggled as they playfully rolled an old bicycle rim down the path.
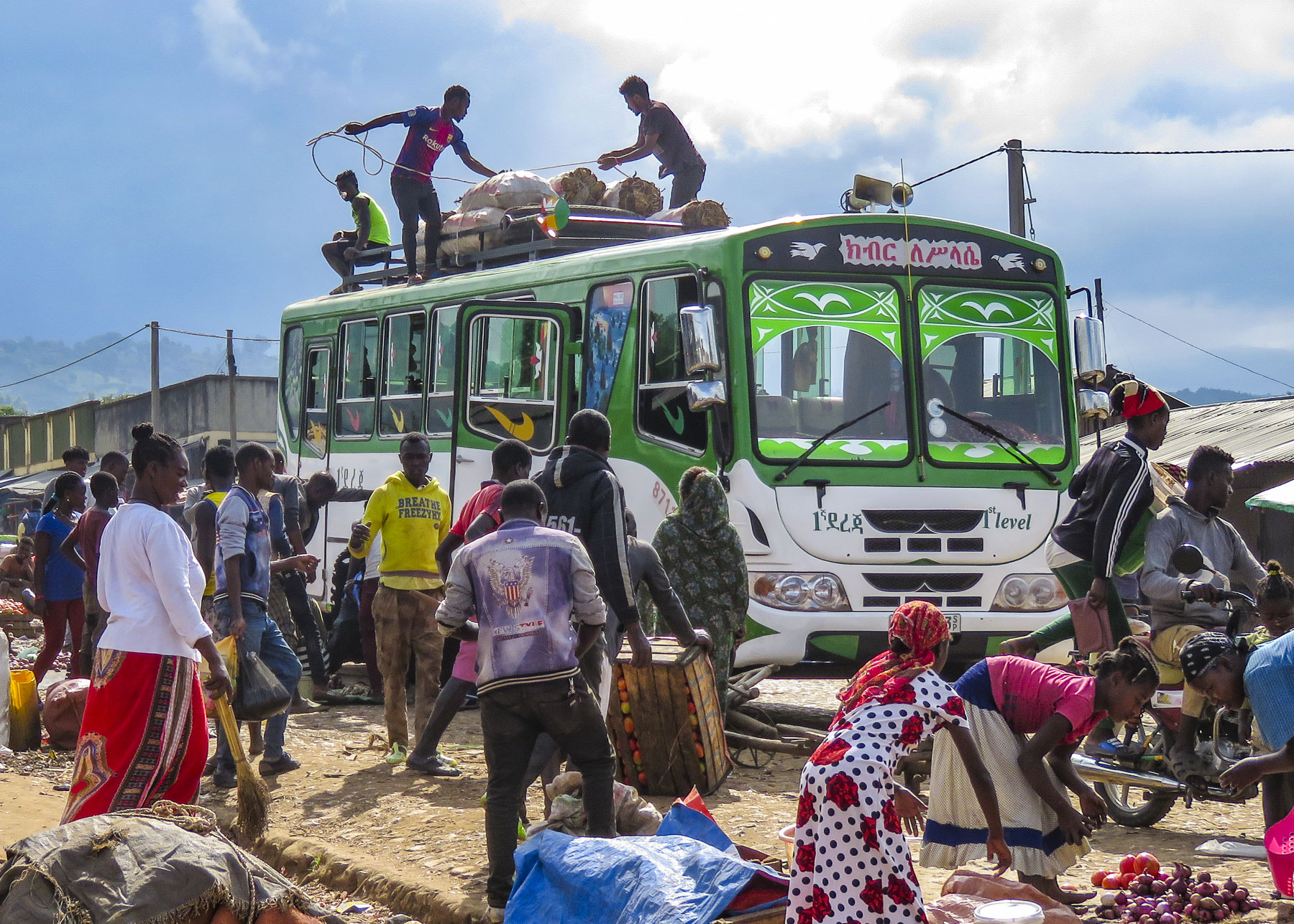


 There was a lively commotion of activity by the buses as porters brought over bundles to be tossed up onto the roofs and tied down before heading back to outlying villages.
There was a lively commotion of activity by the buses as porters brought over bundles to be tossed up onto the roofs and tied down before heading back to outlying villages.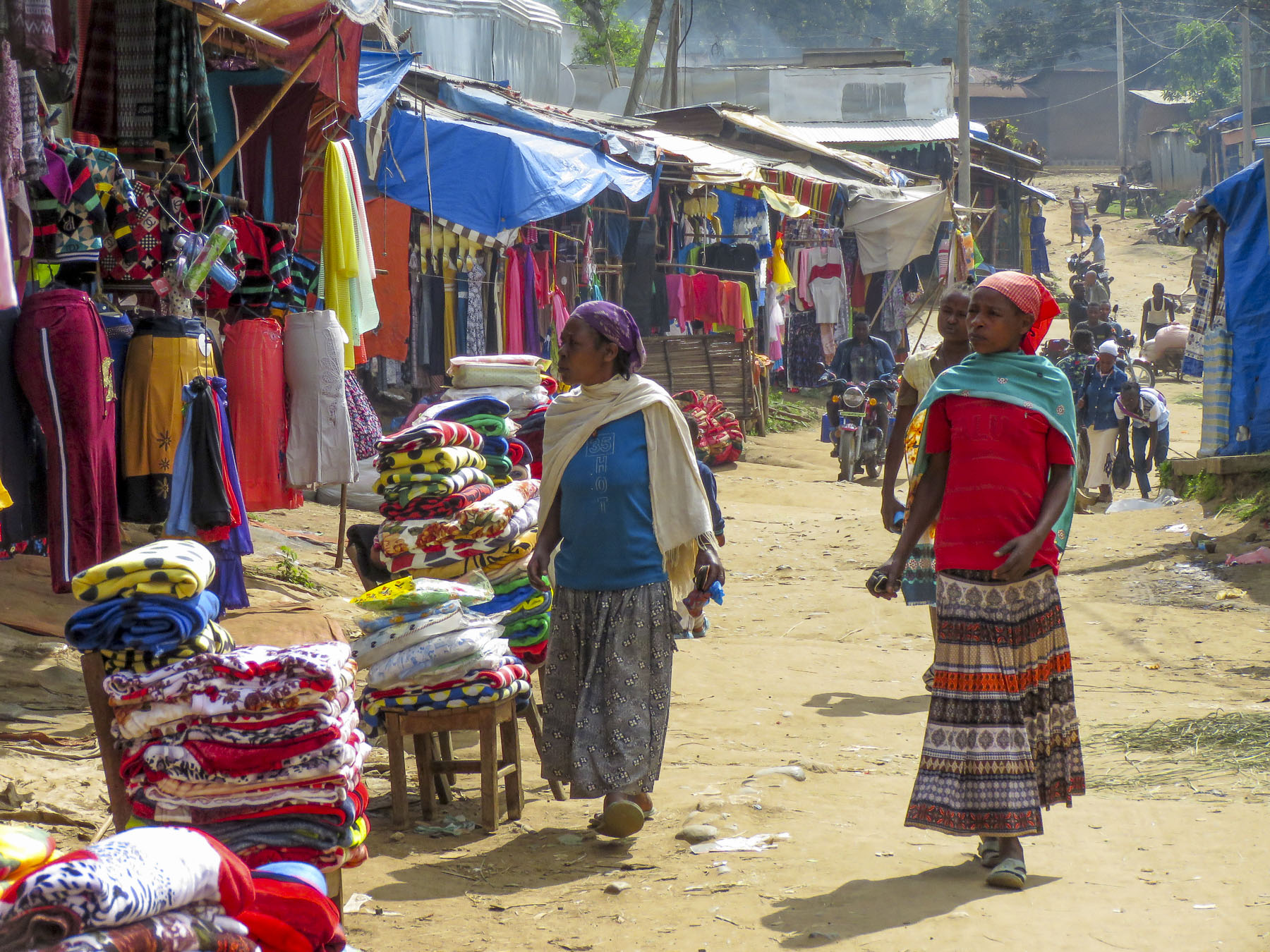  Goats, cows and children were left to wander about freely while small piles of detritus burned slowly in the streets as vendors cleaned up at the end of the day. The earthy smell of dung and smoke lightly scented the air. It was chaotic.
Goats, cows and children were left to wander about freely while small piles of detritus burned slowly in the streets as vendors cleaned up at the end of the day. The earthy smell of dung and smoke lightly scented the air. It was chaotic.





 The highlands area is home to the Konso people who are renowned for their ringed hilltop villages, fortified with stone walls. They have developed terraced farming techniques to survive in a semi-arid, rock strewn and hilly territory for almost seven-hundred years.
The highlands area is home to the Konso people who are renowned for their ringed hilltop villages, fortified with stone walls. They have developed terraced farming techniques to survive in a semi-arid, rock strewn and hilly territory for almost seven-hundred years.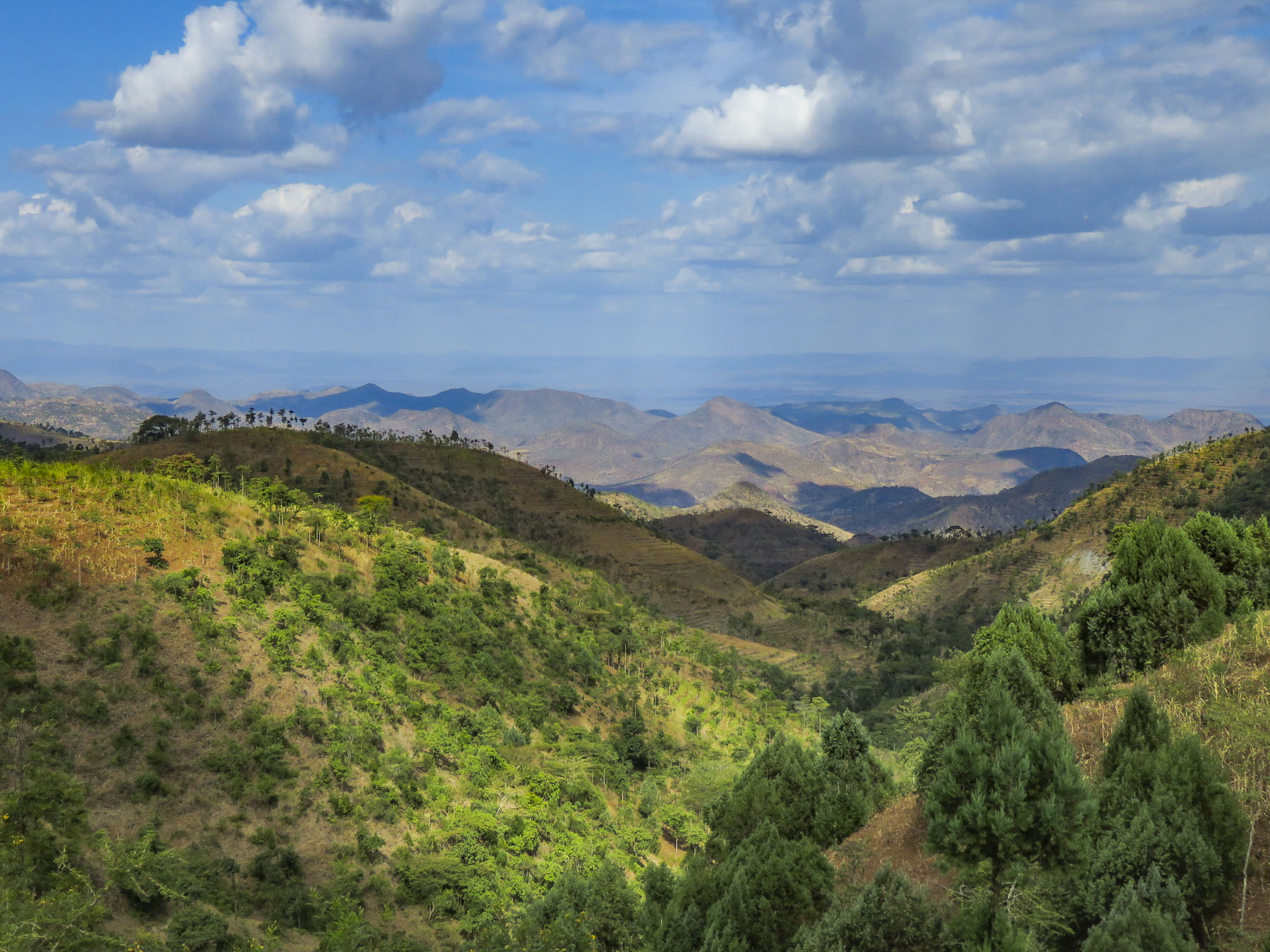 As we entered the town of Konso, bundles of candles miraculously appeared from under our guide’s seat and we stopped to donate them to a young man collecting offerings in front of his Ethiopian church. This was the guide’s ritual when we changed territories and it continued throughout our trip. It was a common sight to see small groups of parishioners walking along the road holding up a picture of a beloved saint and umbrellas for shade.
As we entered the town of Konso, bundles of candles miraculously appeared from under our guide’s seat and we stopped to donate them to a young man collecting offerings in front of his Ethiopian church. This was the guide’s ritual when we changed territories and it continued throughout our trip. It was a common sight to see small groups of parishioners walking along the road holding up a picture of a beloved saint and umbrellas for shade.



 As we walked to the center of the village young children following us jumped from rock to rock, along the tops of the tall walls built to protect the village, as we made our way along the path below.
As we walked to the center of the village young children following us jumped from rock to rock, along the tops of the tall walls built to protect the village, as we made our way along the path below.

 Each ring also has a community area called a mora; this is a large thatched roof structure with an open lower level and an enclosed upper platform where the married men and bachelors of the village sleep.
Each ring also has a community area called a mora; this is a large thatched roof structure with an open lower level and an enclosed upper platform where the married men and bachelors of the village sleep. More importantly it provides a shaded meeting place where men play gebeta. It’s considered the oldest board game in the world and is played simply with stones, beans or seeds being moved around holes in a board with the goal to capture as many of your opponent’s pieces as possible. Each village is also divided into two zones and a man born in one zone must always have his homestead in that zone.
More importantly it provides a shaded meeting place where men play gebeta. It’s considered the oldest board game in the world and is played simply with stones, beans or seeds being moved around holes in a board with the goal to capture as many of your opponent’s pieces as possible. Each village is also divided into two zones and a man born in one zone must always have his homestead in that zone. The Konso also erect generation poles, called olahita, which are raised every eighteen years. The olahita are made of cedar trees taken from the kala, a sacred forest. Gamule village had eighteen olahita which dates the village to be nearly 400 hundred years old. Sadly, the oldest central poles have succumbed to termite damage and rot over the centuries. The oldest village in the Konso region is Dokatu which has 43 olahita. Near the olahita was the village ceremonial daga, a large rock, that teenage boys lift over their heads to prove their manhood and eligibility for marriage. The Konso also carve waka, grave makers, in rough likeness of the deceased. These were originally placed at the grave sites in the sacred forest, but have now all been brought back into the village to deter looting. Each village is surrounded by a dina, or grove of trees, which acts as a buffer between the village and agricultural terraces. This buffer of trees was meant to inhibit attack on the village and provide an area close to the settlement where folks could forage for firewood. There are 36 paletas, with populations ranging from 1,500 to 3,000 in each village, scattered across the Konso territory.
The Konso also erect generation poles, called olahita, which are raised every eighteen years. The olahita are made of cedar trees taken from the kala, a sacred forest. Gamule village had eighteen olahita which dates the village to be nearly 400 hundred years old. Sadly, the oldest central poles have succumbed to termite damage and rot over the centuries. The oldest village in the Konso region is Dokatu which has 43 olahita. Near the olahita was the village ceremonial daga, a large rock, that teenage boys lift over their heads to prove their manhood and eligibility for marriage. The Konso also carve waka, grave makers, in rough likeness of the deceased. These were originally placed at the grave sites in the sacred forest, but have now all been brought back into the village to deter looting. Each village is surrounded by a dina, or grove of trees, which acts as a buffer between the village and agricultural terraces. This buffer of trees was meant to inhibit attack on the village and provide an area close to the settlement where folks could forage for firewood. There are 36 paletas, with populations ranging from 1,500 to 3,000 in each village, scattered across the Konso territory.
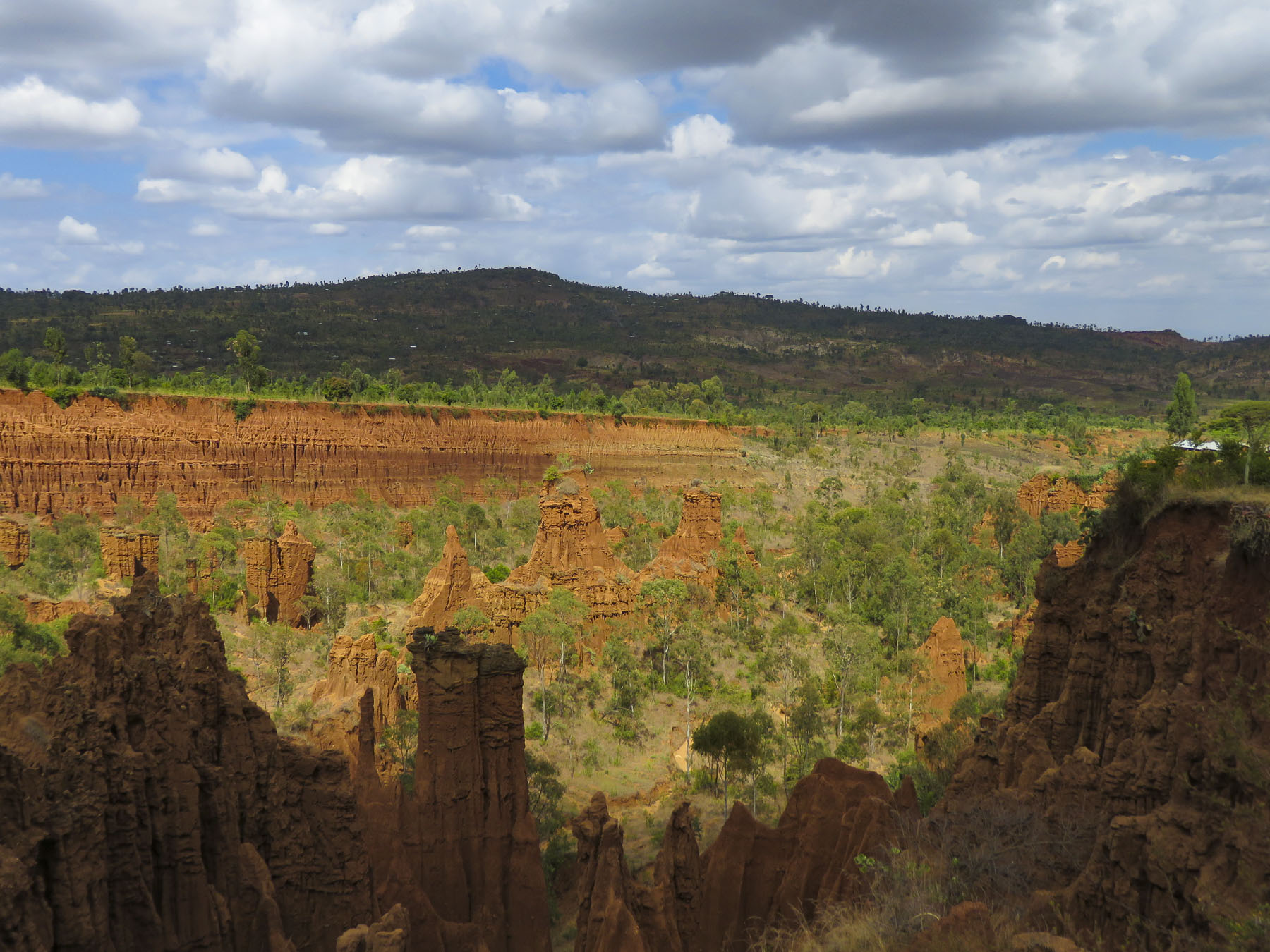
 We didn’t really see the NYC comparison, but the landscape was interesting in that it contrasted sharply from the surrounding terrain. And the encompassing territory is beautiful with vistas of rolling hills. Driving away a group of young men were perched on a lone boulder, just passing time.
We didn’t really see the NYC comparison, but the landscape was interesting in that it contrasted sharply from the surrounding terrain. And the encompassing territory is beautiful with vistas of rolling hills. Driving away a group of young men were perched on a lone boulder, just passing time.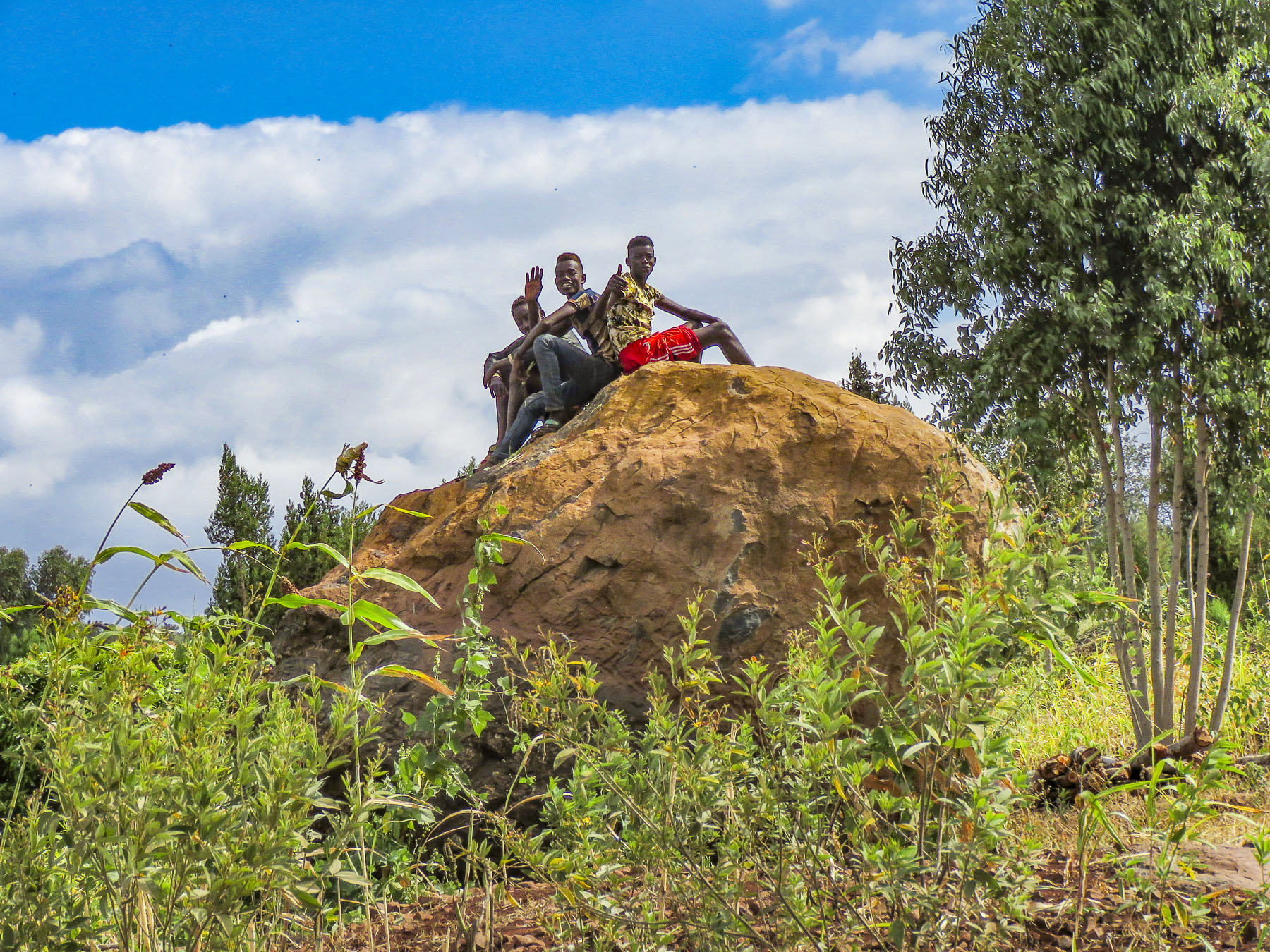 We arrived late in the afternoon to the Konso Korebta Lodge, situated high on a hill. It was a relatively new complex with attractive, circular stone huts topped with steep thatched roofs and beautiful plantings of bougainvillea. Desperately needing showers, we were flummoxed when the tap was dry and headed to reception to see what was up. Unbeknownst to us it’s common practice at hotels throughout the countryside to only turn on the electricity and water between 6:00 – 9:00 in the morning and 6:30 – 10:00 in the evening to conserve resources.
We arrived late in the afternoon to the Konso Korebta Lodge, situated high on a hill. It was a relatively new complex with attractive, circular stone huts topped with steep thatched roofs and beautiful plantings of bougainvillea. Desperately needing showers, we were flummoxed when the tap was dry and headed to reception to see what was up. Unbeknownst to us it’s common practice at hotels throughout the countryside to only turn on the electricity and water between 6:00 – 9:00 in the morning and 6:30 – 10:00 in the evening to conserve resources.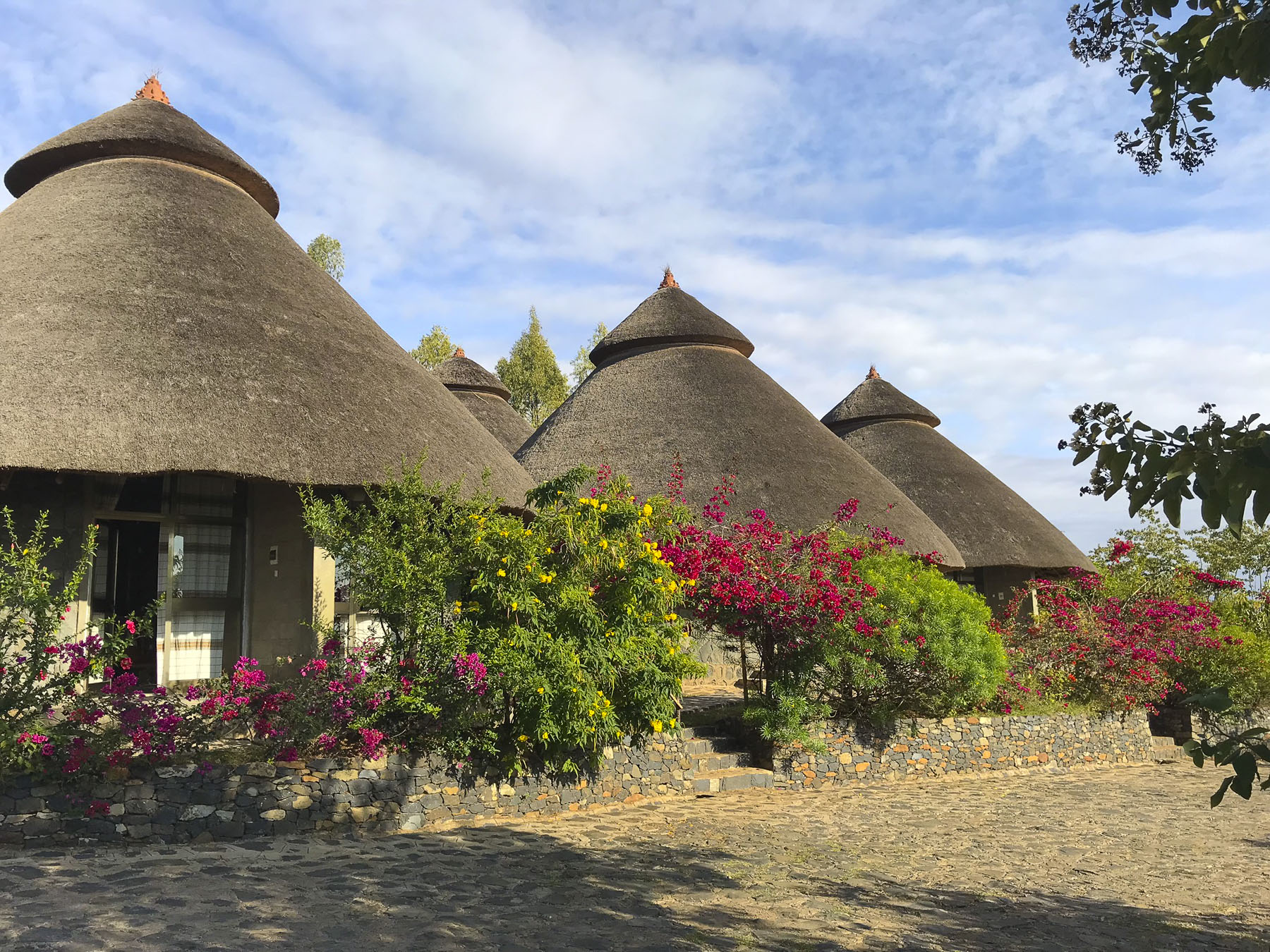 Thankfully, the staff called the owner to get permission to start the generator early for us. Back seat driver that I am I thought our driver drove fast, safely but fast to cover the great distances we had to travel. So, we were surprised the next afternoon when he was tootling along very slowly to get back to the hotel. Evidently the hotel owner made it very clear to our guide that he would not turn on the generator early again.
Thankfully, the staff called the owner to get permission to start the generator early for us. Back seat driver that I am I thought our driver drove fast, safely but fast to cover the great distances we had to travel. So, we were surprised the next afternoon when he was tootling along very slowly to get back to the hotel. Evidently the hotel owner made it very clear to our guide that he would not turn on the generator early again.

 Market days are huge events in the rural areas and folks from various tribes travel for miles to attend them.
Market days are huge events in the rural areas and folks from various tribes travel for miles to attend them.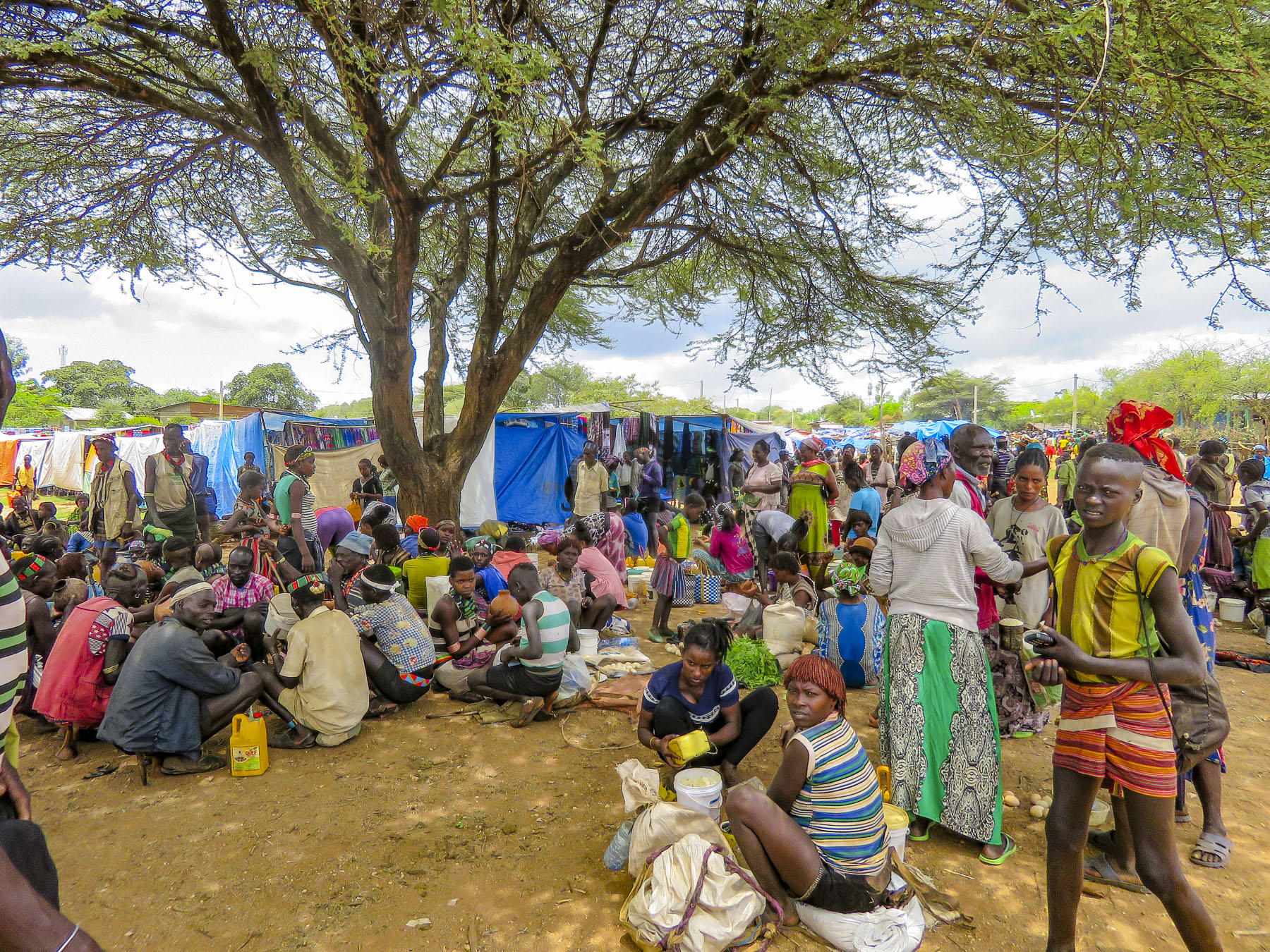  Not just to buy or trade supplies; it’s also a cherished opportunity for men and women to socialize with friends and extended family from other villages, often in raucous beer halls which could be in a makeshift shed or more often a spot under a large shade tree that serves a local brew.
Not just to buy or trade supplies; it’s also a cherished opportunity for men and women to socialize with friends and extended family from other villages, often in raucous beer halls which could be in a makeshift shed or more often a spot under a large shade tree that serves a local brew.
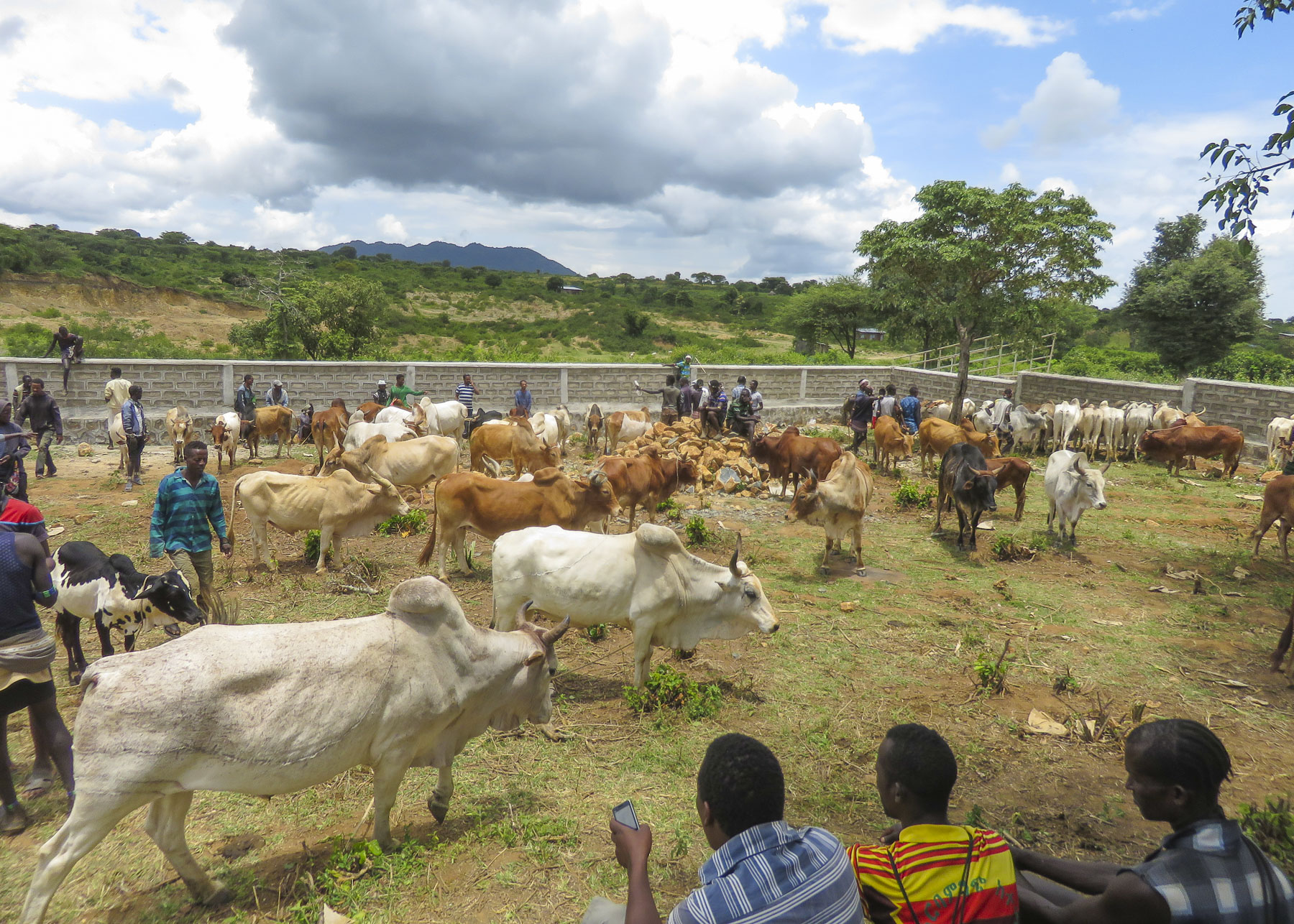

 We were able to take many candid photos as we followed our guide through the market to its various parts. Ceramic pots, handmade tools, ropes and leather goods produced by different tribespeople were available as were pots, pans, cloth and sandals produced in China.
We were able to take many candid photos as we followed our guide through the market to its various parts. Ceramic pots, handmade tools, ropes and leather goods produced by different tribespeople were available as were pots, pans, cloth and sandals produced in China.



 Many folks were very receptive to this and our guide would negotiate a fee. And even though we paid for the privilege to take their photo, they seemed pleased that we admired their style. A few, however, angrily waved us away.
Many folks were very receptive to this and our guide would negotiate a fee. And even though we paid for the privilege to take their photo, they seemed pleased that we admired their style. A few, however, angrily waved us away.






 Pulling over occasionally to take photos from scenic overlooks along this isolated track, we were always surprised when, in the middle of nowhere, a young man selling souvenirs would emerge from the shade. Later we would come across an enterprising group of young stilt walkers urging tourists to stop for photos – and of course we did.
Pulling over occasionally to take photos from scenic overlooks along this isolated track, we were always surprised when, in the middle of nowhere, a young man selling souvenirs would emerge from the shade. Later we would come across an enterprising group of young stilt walkers urging tourists to stop for photos – and of course we did. Entering Jinka, we noticed signage for the International Airport (BCO, though we are pretty sure you can only fly in from Addis Abba.) We might have arranged our trip differently if we had known this previously as it would have eliminated two eight-hour drives from and to the capital. Note: if you fly into Ethiopia on a ticketed Ethiopian Airways flight you are able to purchase
Entering Jinka, we noticed signage for the International Airport (BCO, though we are pretty sure you can only fly in from Addis Abba.) We might have arranged our trip differently if we had known this previously as it would have eliminated two eight-hour drives from and to the capital. Note: if you fly into Ethiopia on a ticketed Ethiopian Airways flight you are able to purchase 
