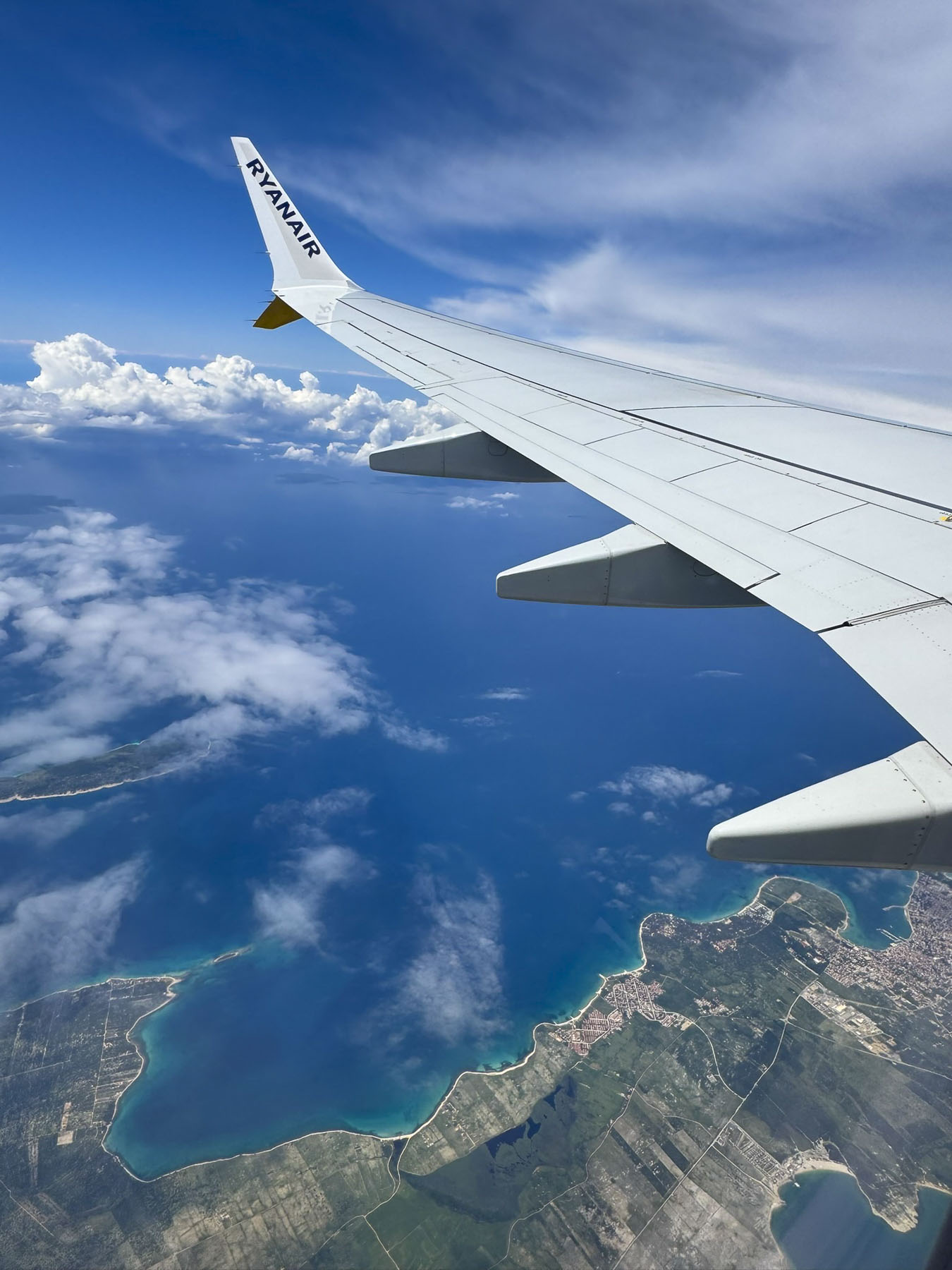
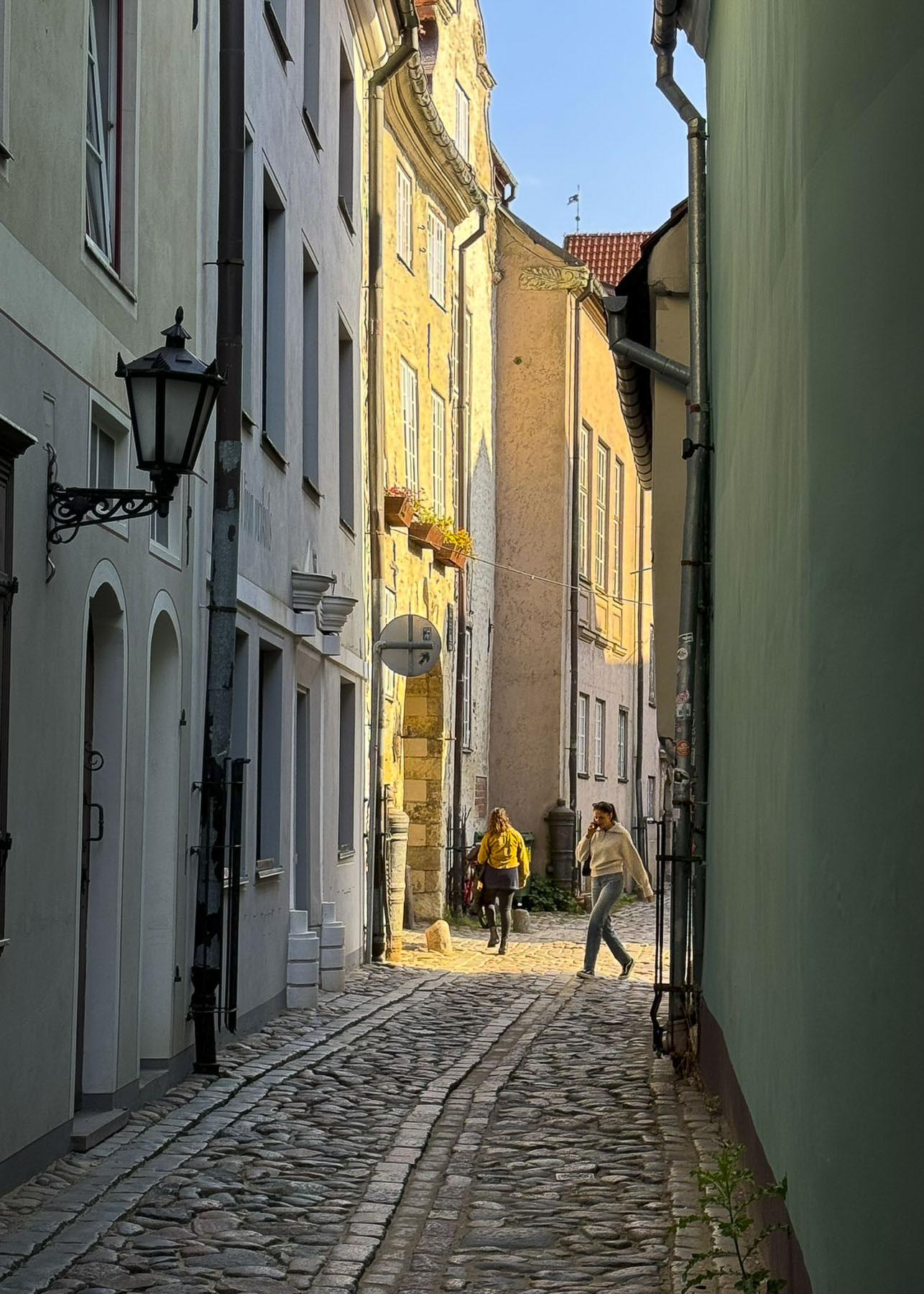Peering down at the shimmering cobalt and turquoise blue water of the Adriatic Sea relieved the previous day’s anxiety of nearly missed connections. We encountered a long delay at passport control in Paris, before catching our connecting early morning flight to Zadar.

This temporary reprieve was short lived though, as we were confronted with a shuttered rental car window at the Sicily By Car booth, directly across from the small Zadar terminal. It was a Sunday morning – maybe the service at church ran long, or the coffee and pastries at the café were particularly delicious; nevertheless, the other passengers on our early morning flight who had rented with other agencies were long gone. At the terminal’s outdoor café we sipped coffee, waited, and discussed whether or not to cancel our existing reservation. An hour passed before a car parked behind the booth, and the shuttered window was noisily cranked open. A pleasant young woman greeted us, and the morning’s delay was forgotten. Years ago, we began the habit of asking attendants at the rental car counters for suggestions to non-touristy places to eat. It appears it’s an unusual request from a customer, but folks seem pleased that we sincerely ask for their opinion. “Let me think on that, and by the time paperwork is done and I show you the car, my colleague and I will have some ideas for you.” With the names of three restaurants and a patisserie, “you should definitely try,” we headed off to see waterfalls at Skradinski Buk National Park in a nearly new small SUV, an upgrade from what we had reserved. The park was our first stop on our three-week long Croatian road trip, before our late afternoon check-in at an apartment rental in old town Zadar later.

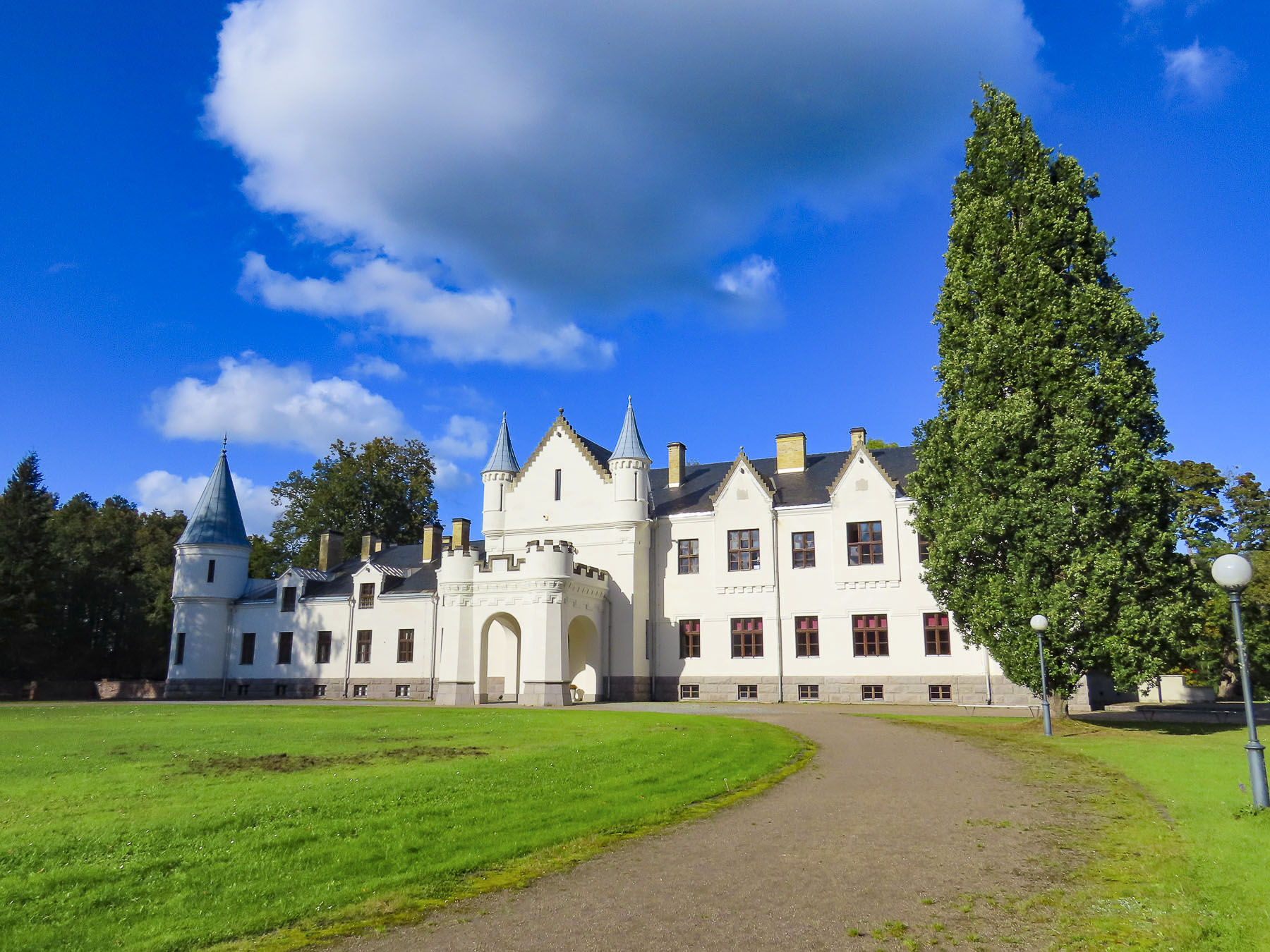
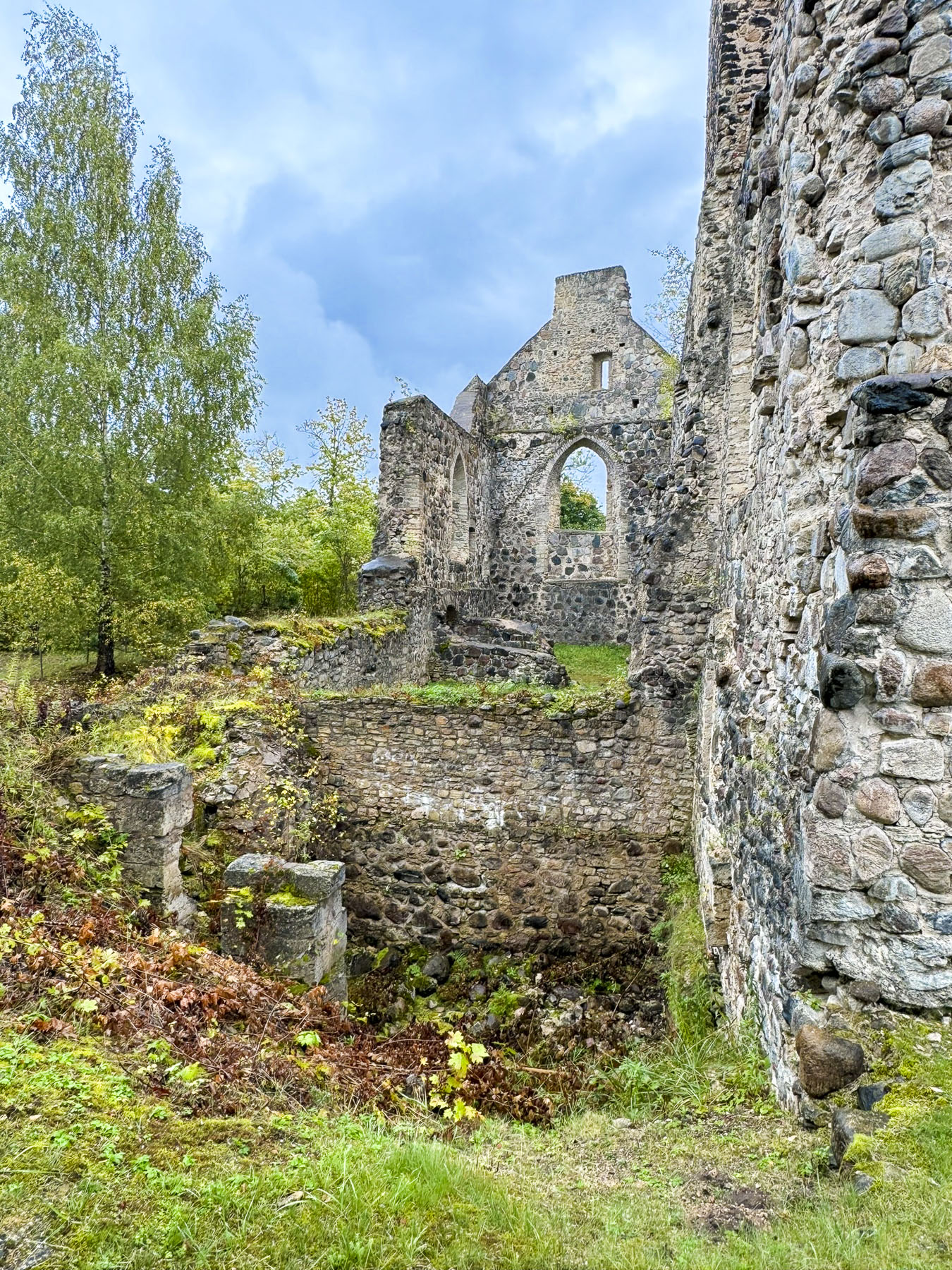
The sunny April morning was now overcast as we drove into the small village of Benković to see its hilltop castle, and indulge our “drive a little, then café,” philosophy. Unfortunately, the castle was closed and the town seemed deserted in the pre-tourist season. Down the lane from the castle fig trees were setting their fruit and the first flowers of Spring were blooming. The café remained an unfulfilled desire.



We love traveling during the shoulder seasons to avoid the crowds of summer. But one of the drawbacks is fewer, if any, restaurants/cafes are open, especially in the more rural areas.

The drive to the park along Rt56 was semi-desolate, but pretty in an austere way, and passed through Croatia’s garigue shrublands, olive groves, and pine forests. From the road as we drove past Skradin, we could see large charter yachts at their winter moorings on the Krka River, two miles from the sea, sheltering there from fierce Adriatic storms, as they waited for the warmer cruising season to start. Across the river the road zigged and zagged up the mountainside before leveling off on a high plateau.
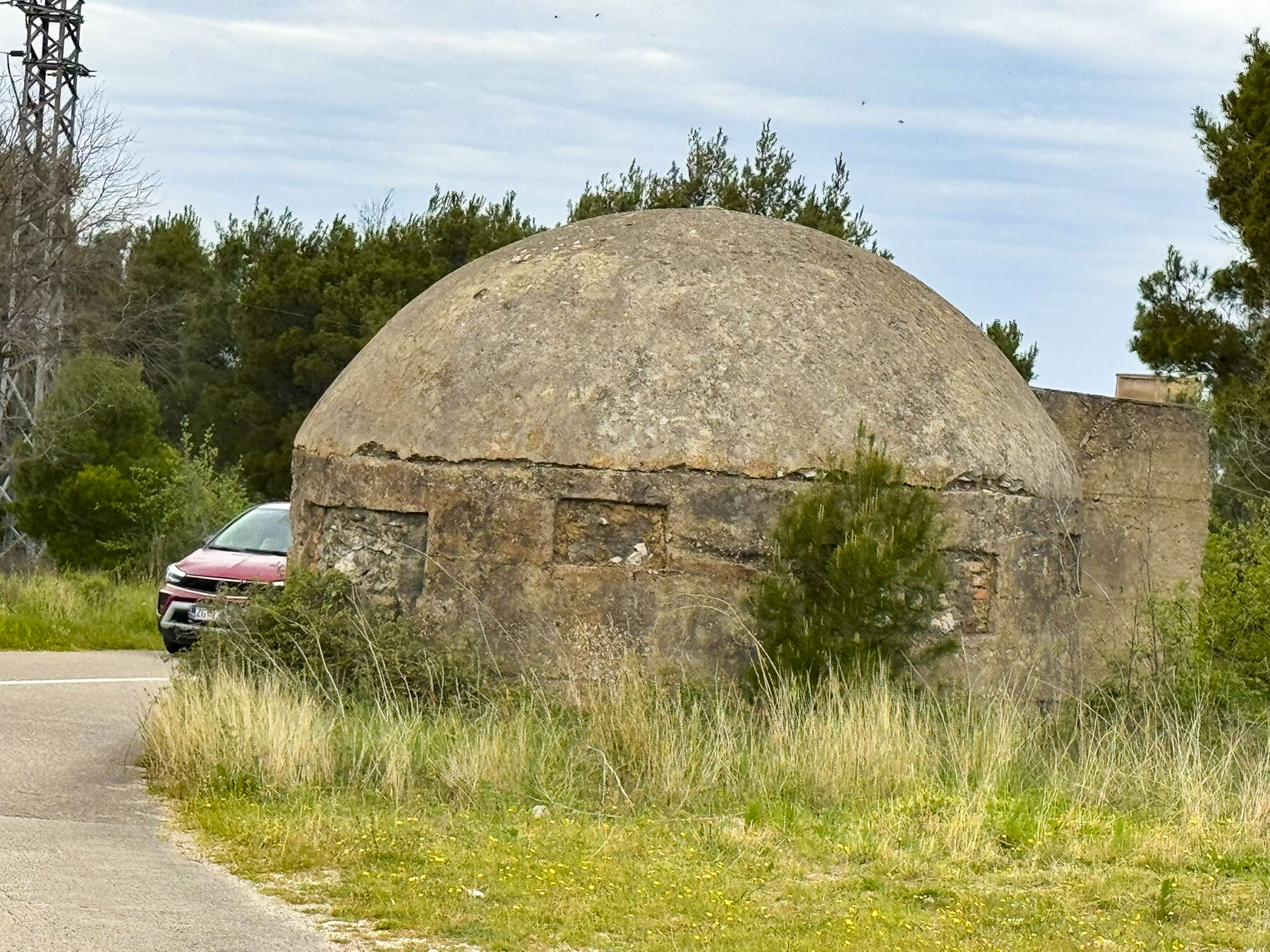


Following the signs to the national park we drove down a side road which passed a sprawling abandoned factory site, fronted with several concrete military bunkers. They were relics from the Cold War era like the ones that dot the landscape in Albania. Built in the 1930s, the IVANAL d.o.o. plant was the Balkans region’s first state-of-the-art aluminum processing complex that employed 400 people. It was confiscated by Czechoslovakia’s communist regime in the 1940’s and never upgraded or maintained. Over the decades production fell until the plant was closed after Croatia’s independence in 1991.
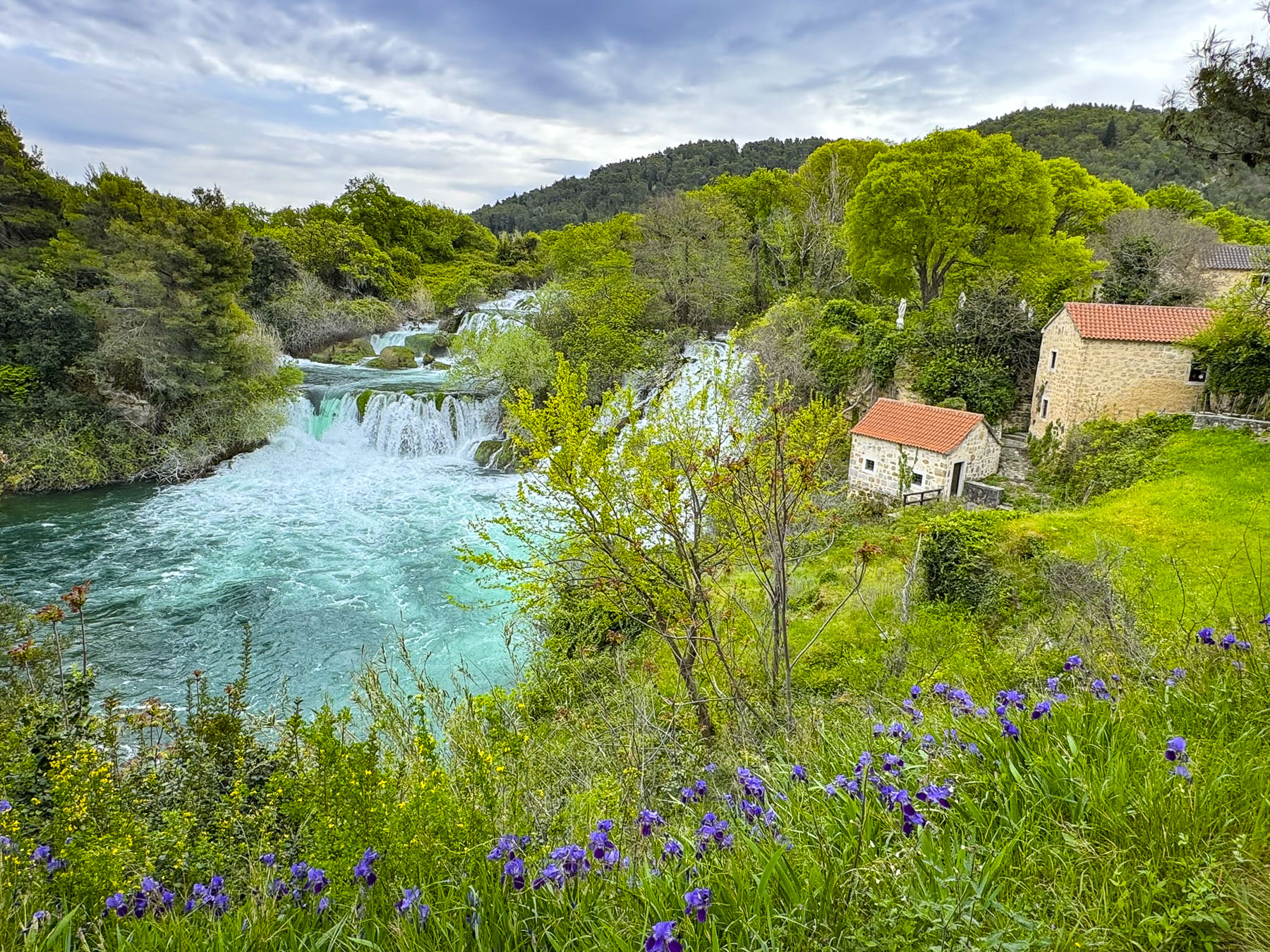

The parking lot at the national park was very full, considering it was a chilly Spring Sunday, but the queue at the ticket booth moved quickly. While the falls are quite a distance downhill from the entrance to the park, some folks chose to walk a route through the forest to forage for the wild asparagus that sprouts along its path from March to May.

We opted for a ticket that included a shuttle bus ride to the largest waterfall, Skradinski Buk, at the bottom of a series of equally impressive waterfalls on the Krka River, then a walk back upstream along the waterway to another shuttlebus stop for a return ride to the top of the park entrance plateau. During the summer months the national park also offers a scenic twenty-minute boat ride from the harbor in Skradin,to the base of Skradinski Buk.

The overcast day was actually the perfect weather condition to photograph the waterfalls without heavy shadows or bright highlights, and the falls were thundering, foaming with the snowmelt from the Dinaric Alps, which run through the coastal Balkans region.
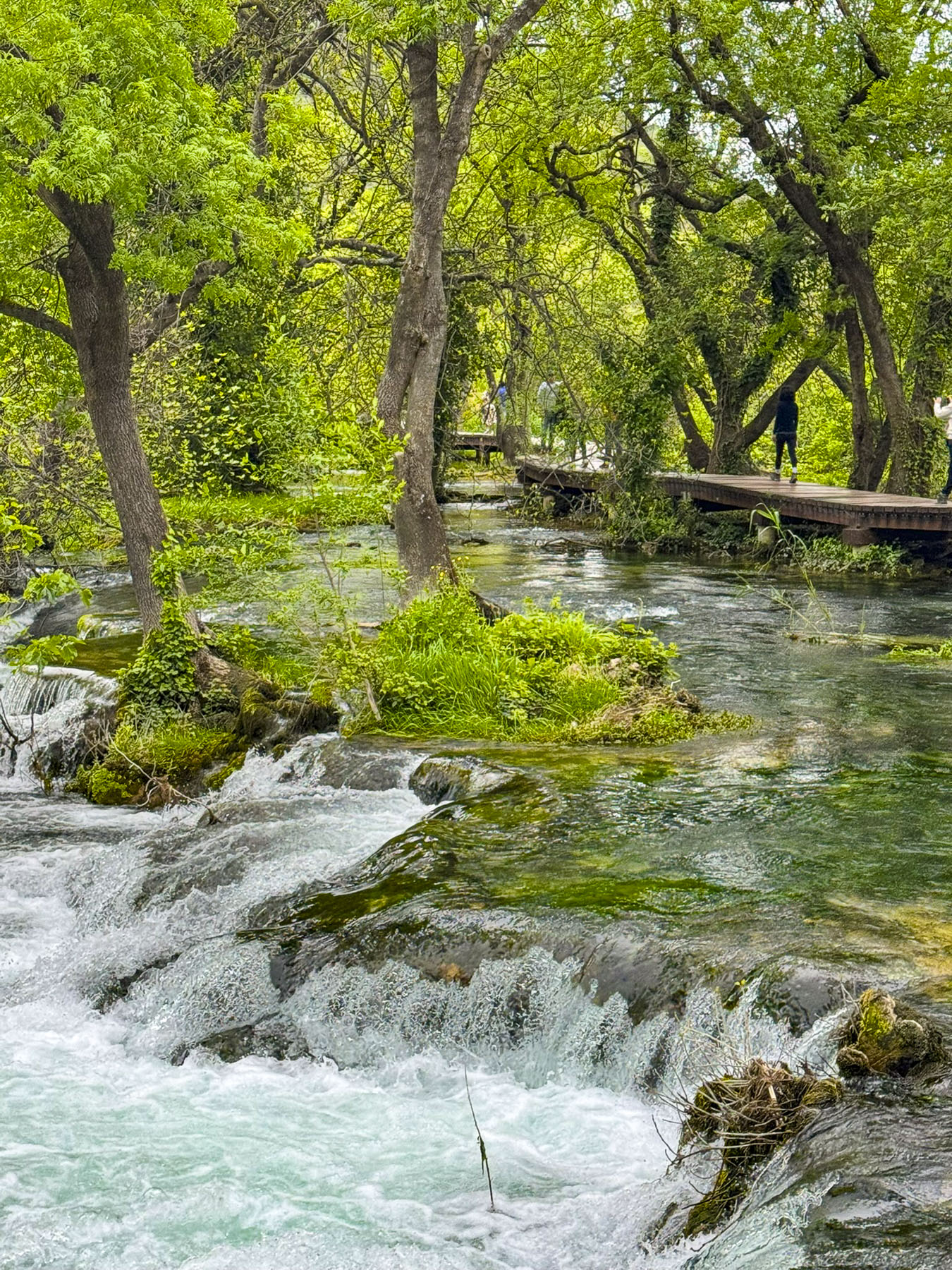
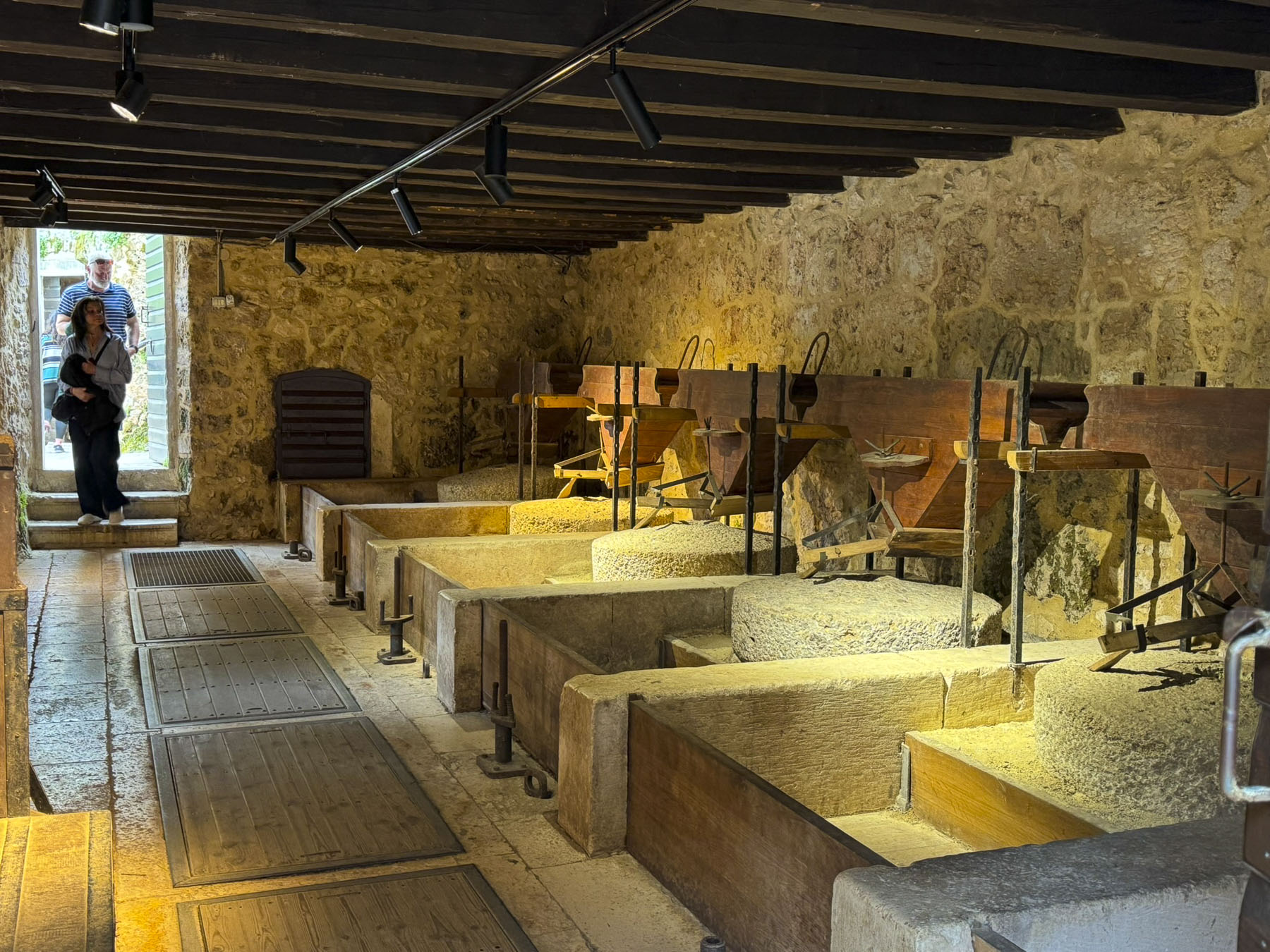



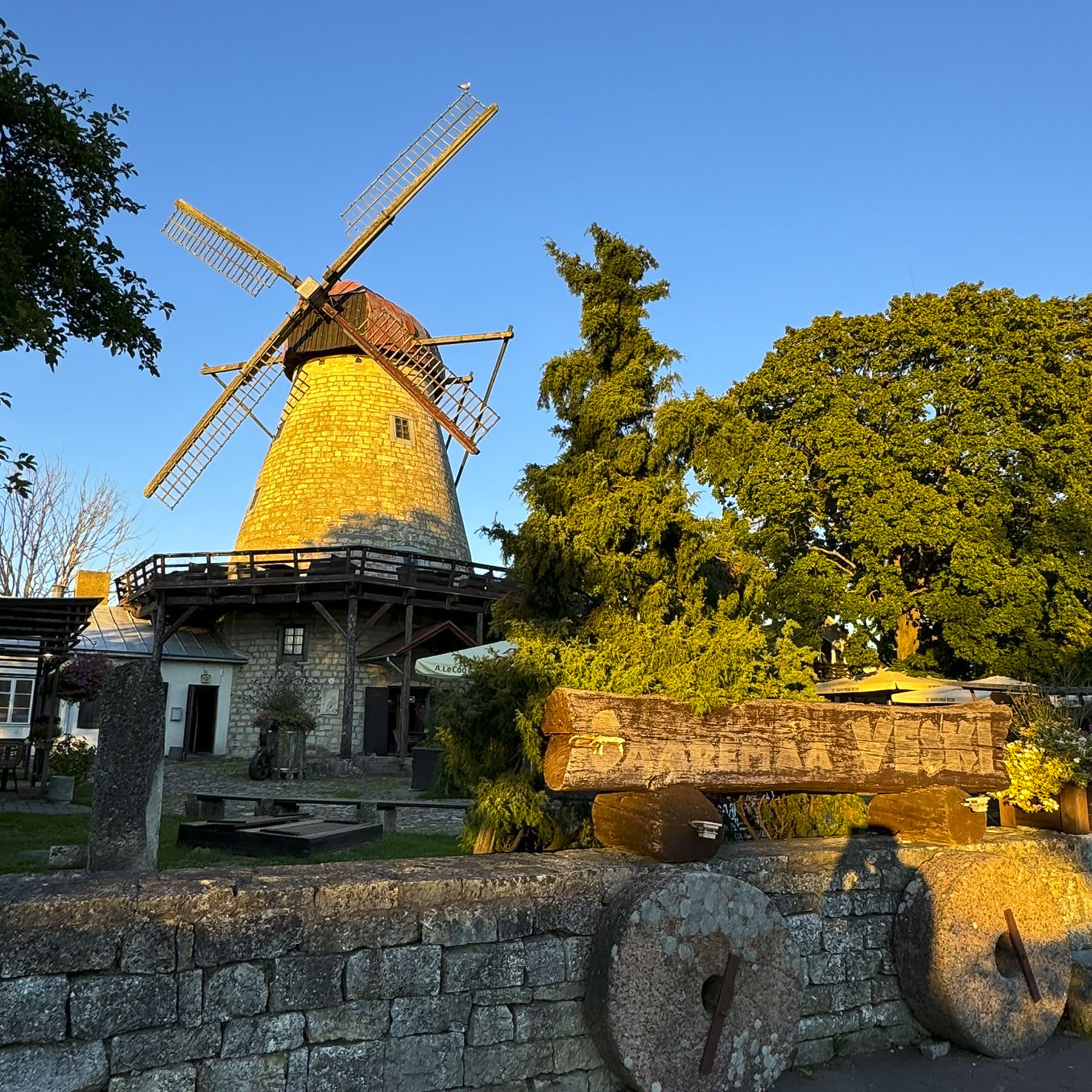
Along the way, we stopped at several restored watermills, with their mill races still intact. They were used primarily to grind locally harvested grain into flour, and to wash processed wool. A blacksmith shop also used a waterwheel to drive its furnace bellows to keep the fire hot enough to work the iron, and to power the heavy trip hammers the smith used to shape tools.

A serpentine elevated wooden walkway, without guardrails, twisted through groves of flooded forest, and kept us dry as the spring runoff rushed below us. It’s important to be aware of your footing in these circumstances, and we always waited at a wider part of the walkway for other folks to pass when the boardwalk was too narrow, to avoid fulfilling my mental image of being swept away down the rapids.
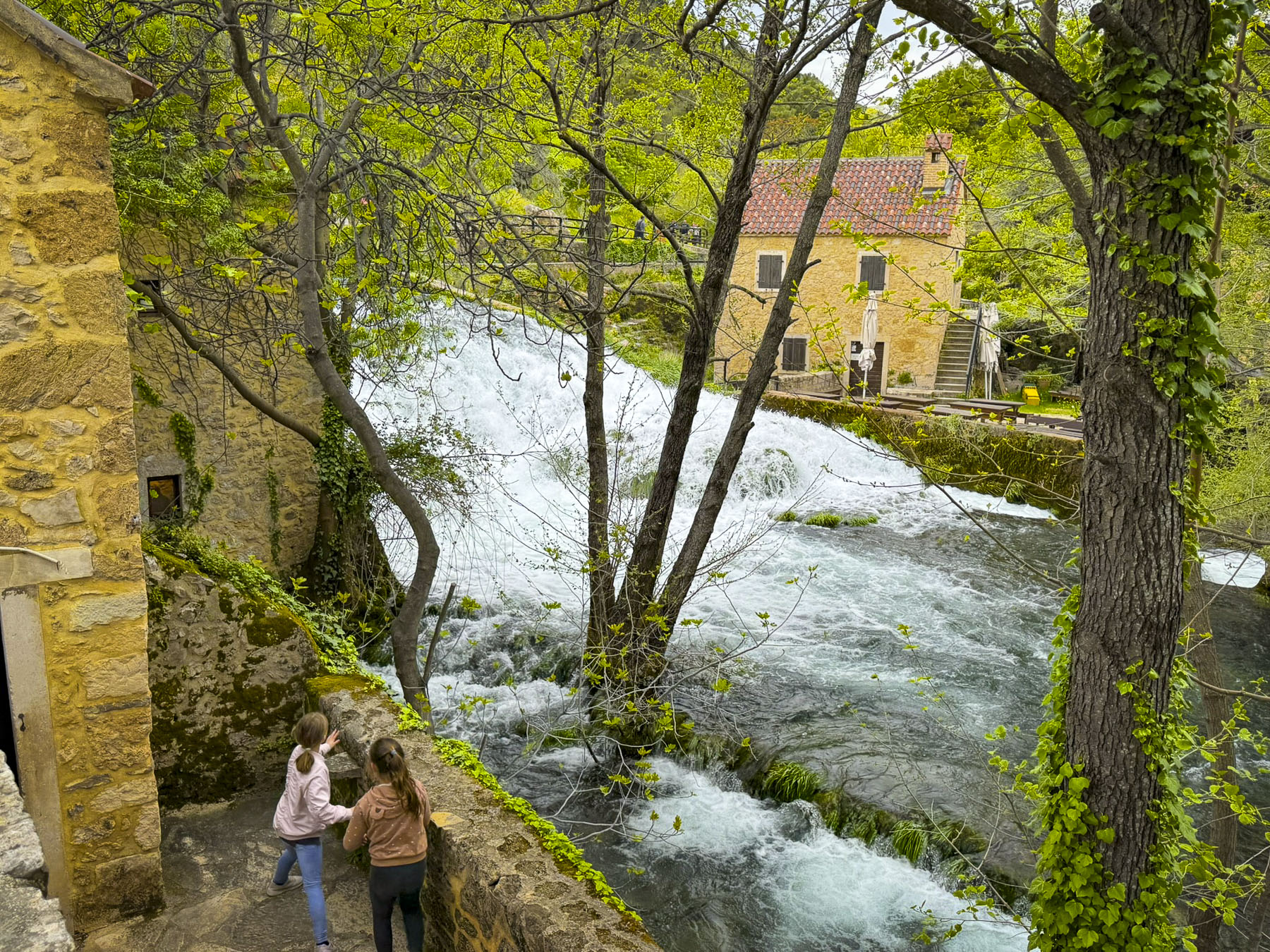

Unlike tourist sites in the United States, where everything is fenced to protect us from injury, in Europe you are expected to be responsible for yourself, and aware of your surroundings to guard against mishaps. We thoroughly enjoyed the waterfalls. We don’t see them in the coastal area at home, since we live nearly at sea level.

Zadar protrudes into the Adriatic, on a small peninsula, like a thumbs up sign, its once rough coastline now manicured with a sidewalk that follows its waterfront. Parking was challenging, but after circling the old town twice, we found a metered space near the Apartments Donat, our base for three nights. The rooms in the restored 700-year-old building were small. But the location, on a small lane overlooking the Cathedral of St. Anastasia and the Church of St. Donatus, was very convenient.


The manager of the building, who didn’t live on site, kindly made his parking space, next to the building, available to us for the duration of our stay. While having a rental car provides a lot of freedom, the typical 20 euro daily expense of parking in Europe can quickly add up. It’s not always possible, but we try to stay in hotels that provide free parking when we can.

Later that day we walked along the waterfront to Obala Petra Krešimira, a jetty that was being battered by whipping winds and crashing waves, which lifted large sprays of water over anyone brave or foolish enough to venture out onto it.
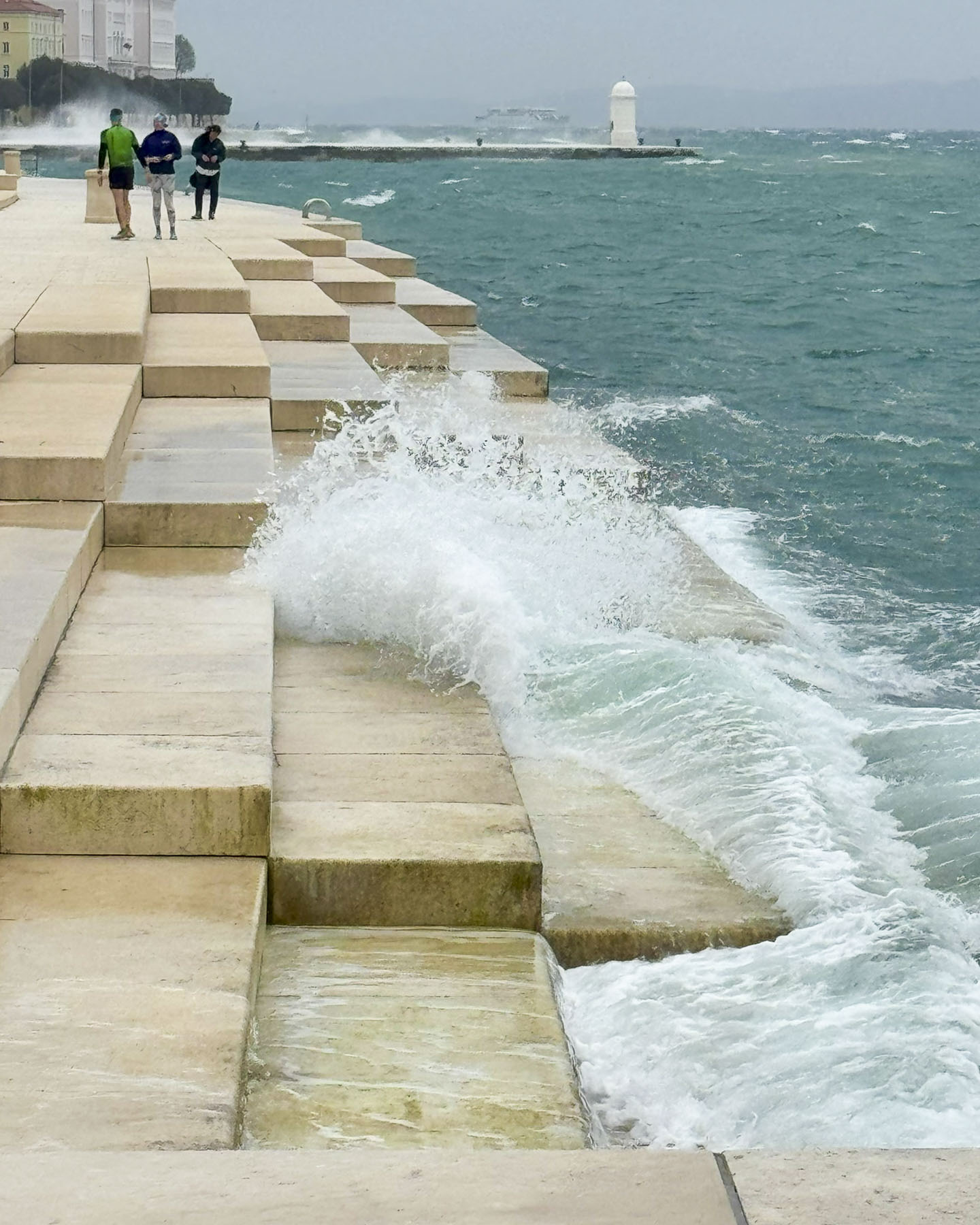


Nearby, in front of Zadar’s City Hall was Morske Orgulje, the Sea Organ, an experimental architectural sound installation designed by the architect Nikola Bašić and completed in 2005 to refurbish Zadar’s waterfront which had been neglected since the end of World War Two. The design incorporates polyethylene organ pipes under the marble stairs that lead down to the water. The motion of the waves continuously forces air through these pipes to create a “harmonic symphony crested by the wind, waves, and tides,” that is vented through the rise of the steps. Visually it’s a flat surface, but as we walked across the plaza the ethereal music faded in and out moodily with the motion of the turbulent sea.

The Greeting to the Sun, a solar-powered light installation also designed by Bašić, was a short distance away, closer to the tip of the peninsula. It’s a 22m (72ft) wide disc composed of 300 multi-layered glass plates, embedded into the plaza, which you can walk across. The panels absorb solar energy during the day to turn the disk into a colorful light display in the evening.

We hoped the storm clouds would begin to break apart so we could catch a scene from the spot that “Alfred Hitchcock once declared during a 1964 visit to the city as having “the most beautiful sunsets in the world.” Alas, during our stay in Zadar the mornings were sunny, the afternoons cloudy, and our sunsets stormy and grey.
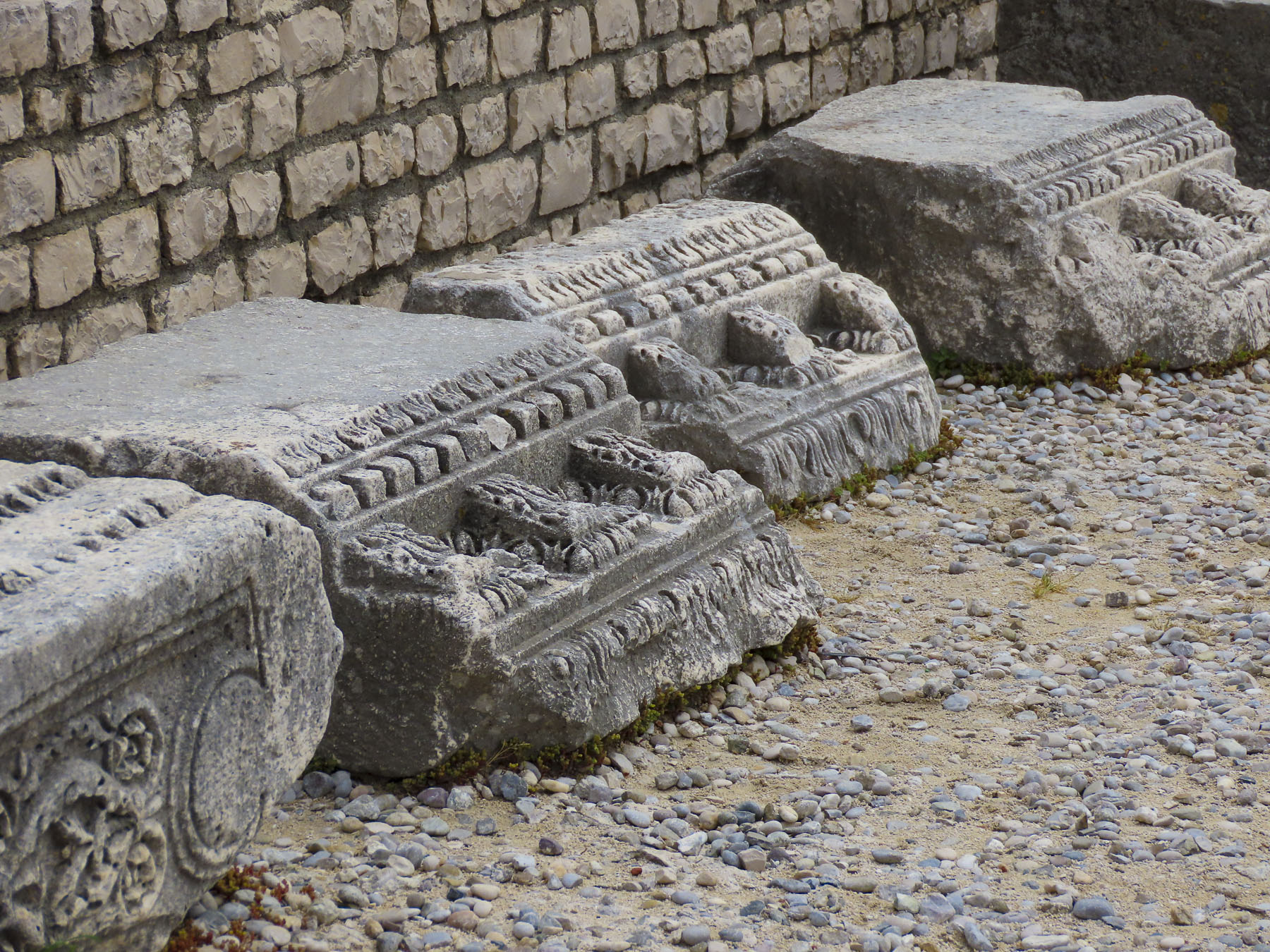



The next morning, we set out to properly explore the town, first stopping at the Roman Effigies, a collection of column sections and decorated capitals from the ancient Roman Forum, which stood in the area of Piazza Papa Giovanni Paolo (Pope John Paul II Square). The plaza itself was built over Zadar’s 16th century water cistern.
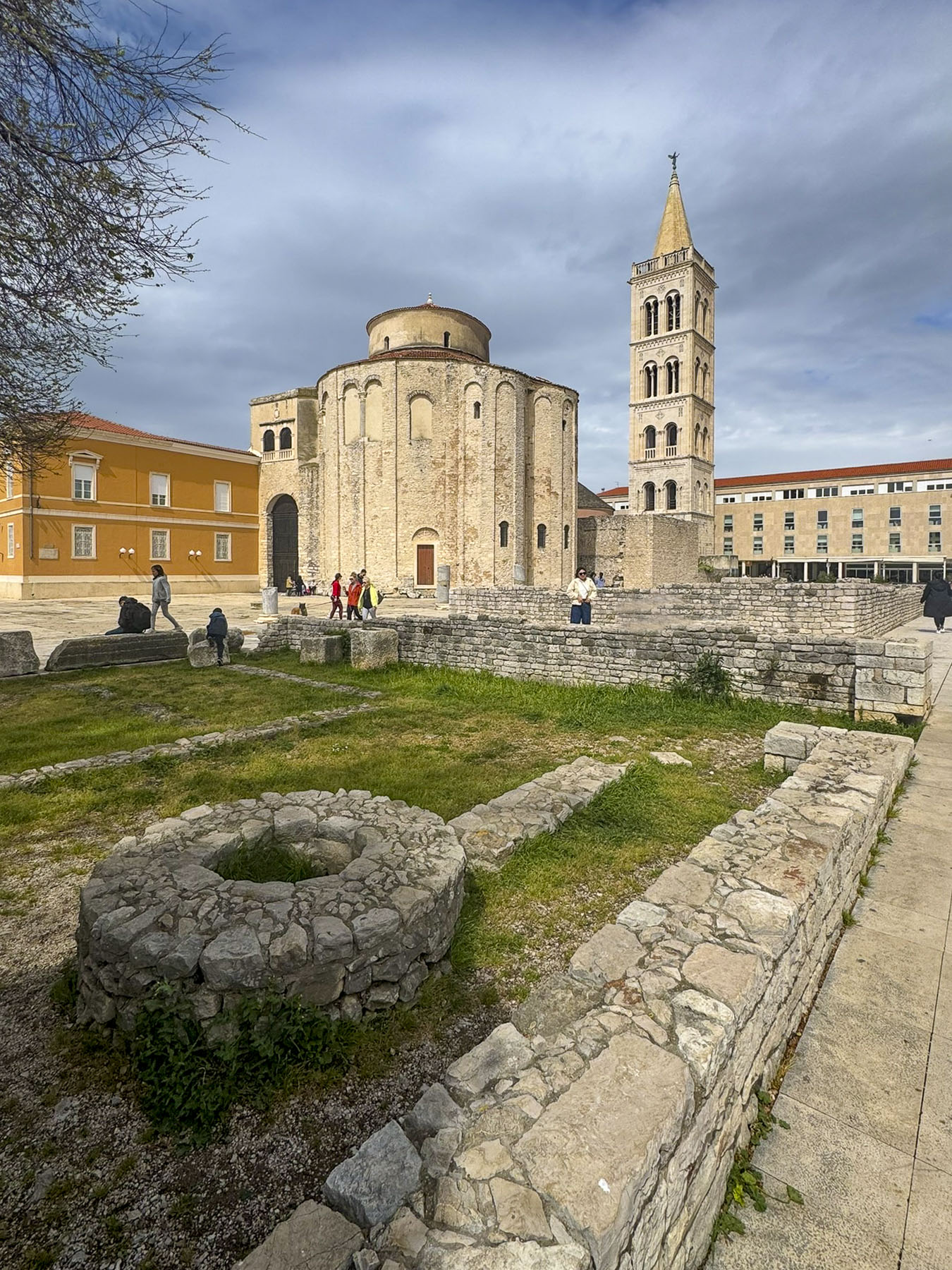

The piazza located next to the 9th-century Church of St. Donatus and the 11th-century Benedictine Monastery of St. Maria is the center point for the northern end of Zadar. The historic buildings did not open until later in the morning, so we continued down Zadar’s narrow lanes, enjoying the fragrance of orange blossoms while we strolled to Pekara Dalmatinka – Old Town Bakery, a recommendation from our friend at the car rental agency.


On the way, something piqued our curiosity down a narrower side alley and we detoured. There in a small workshop a craftsman was applying gold leaf to a frame. We appreciate old-world talents like this, and I asked in English, and gestured with my cell phone, if I could take a photo of him working. All was lost in translation and the man suddenly walked out, only to return a few minutes with his son who spoke English, and we chatted for a minute. Apparently, few tourists ever poked their heads into the workshop; the frame he was gilding was for a church, and his dad is a busy man, but it is okay to take his picture.
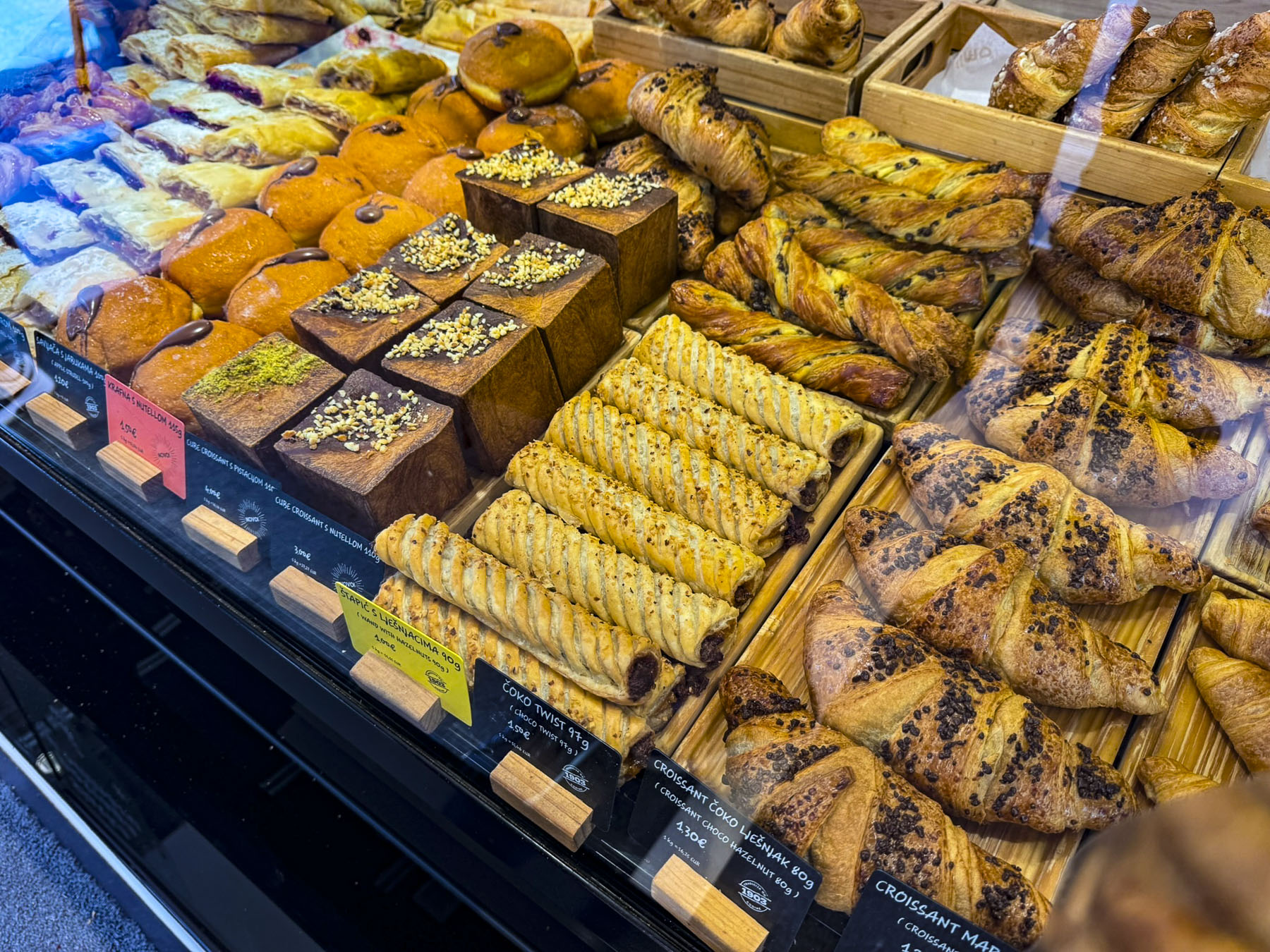


It’s a mistake to arrive hungry to a bakery that confronts you with a display case featuring mouthwatering Croatian pastries. We drooled over Kremšnita, custard cream cake; Madarica, a layered chocolate cake; Makovnjača & Orehnjača, a rolled dough pastry filled with walnuts or poppy seeds; Princes Krafne, a doughnut stuffed with luscious cream; Splitska Torta, a cake with layers of meringue, cream, almonds and figs; and of course Börek, a delicious, coiled phyllo dough pastry filled with feta cheese or spinach.


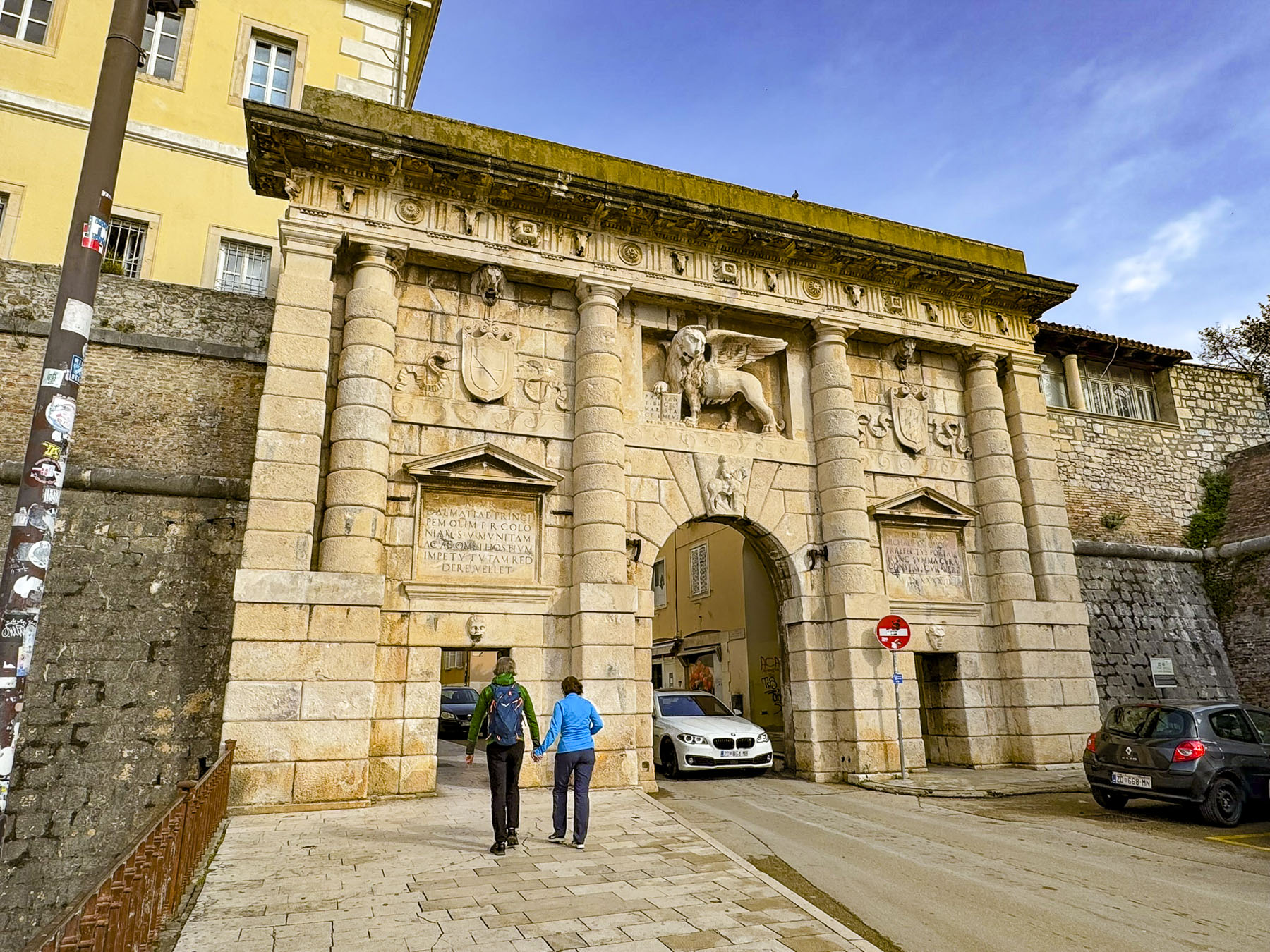
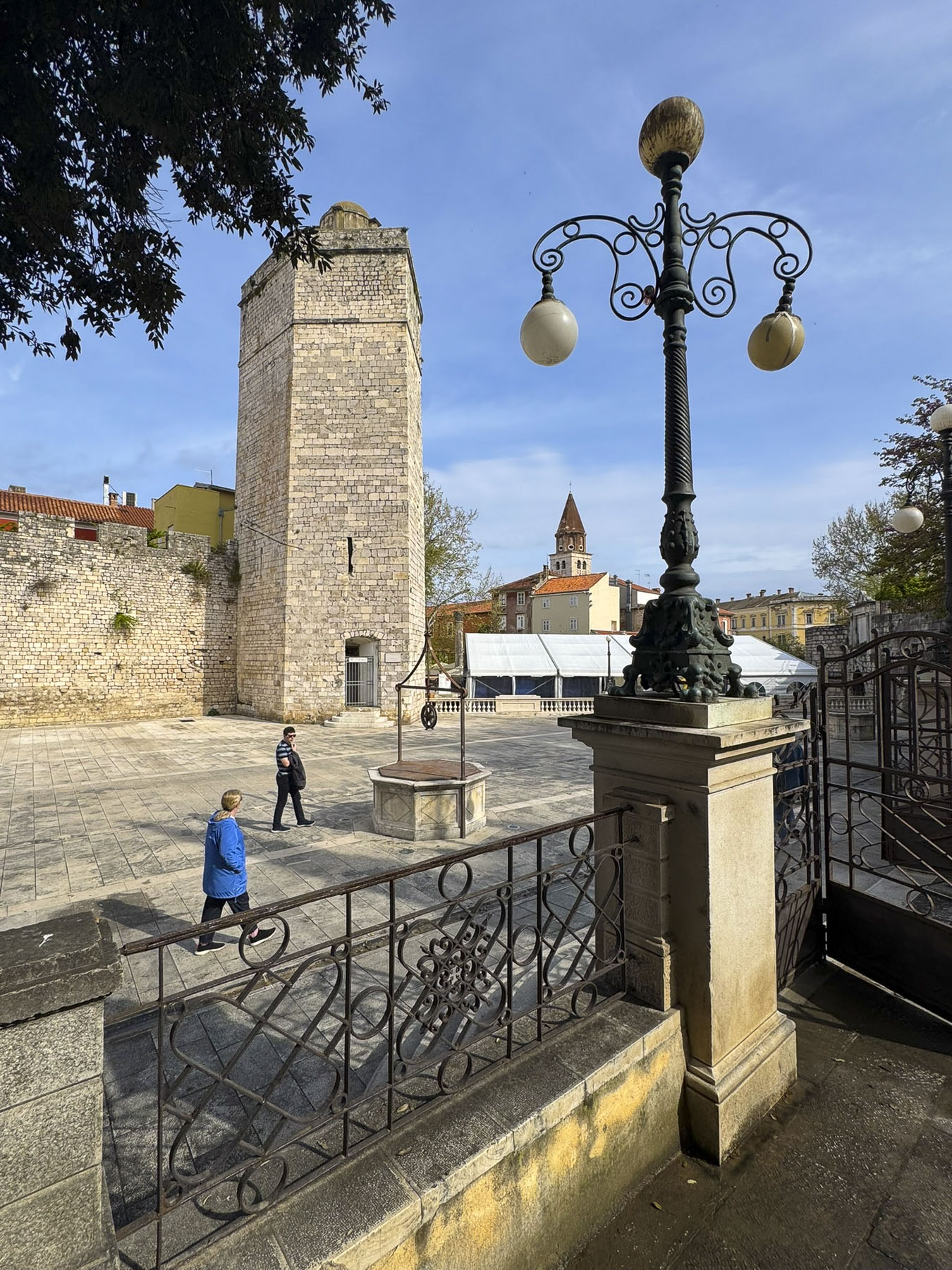
We planned to walk off our over-indulgence, and headed through Trg Pet Bunara, the Five Wells Square, to find a bench in Queen Jelena Madijevka Park. Tree branches laden with purple flowers hung over the decorative railing at the entrance to the park, which sits atop the city’s old bastion, next to the ancient Venetian Land Gate, and was the perfect spot for a morning picnic. Built in 1573, it replaced an old Roman gate, and featured a relief of the Winged Lion of St. Mark, the symbol of the Venetian Empire, to celebrate a naval victory over the Turks. From our bench we watched a boat enter the small harbor in front of Zadar’s ancient defensive wall, a continuous activity since Zadar’s founding.
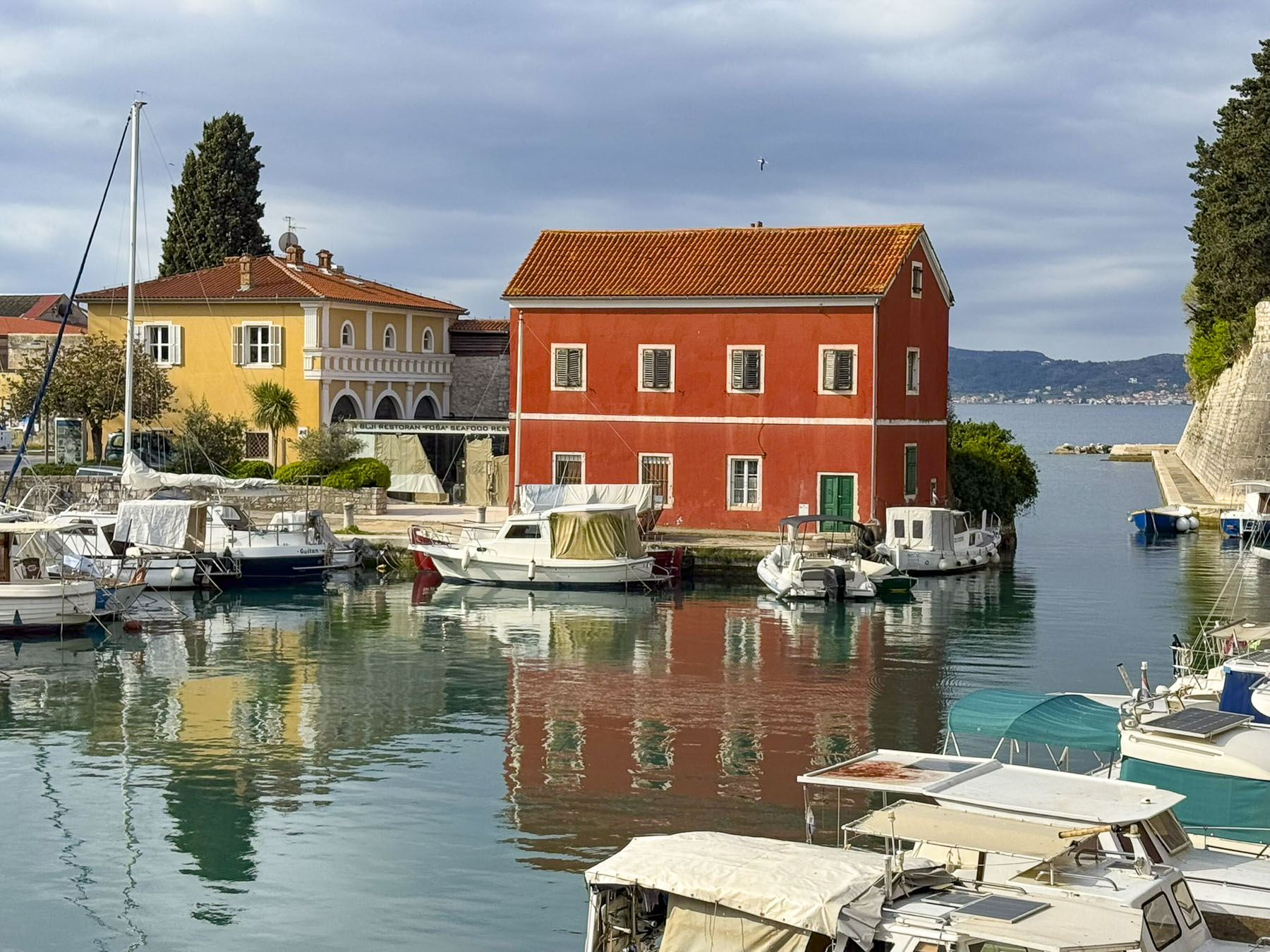


The ancient walls and gates around the city were first built by the Romans and then expanded upon by the Venetians in the 16th and 17th centuries, to defend the city from multiple attacks by the Ottoman Empire.
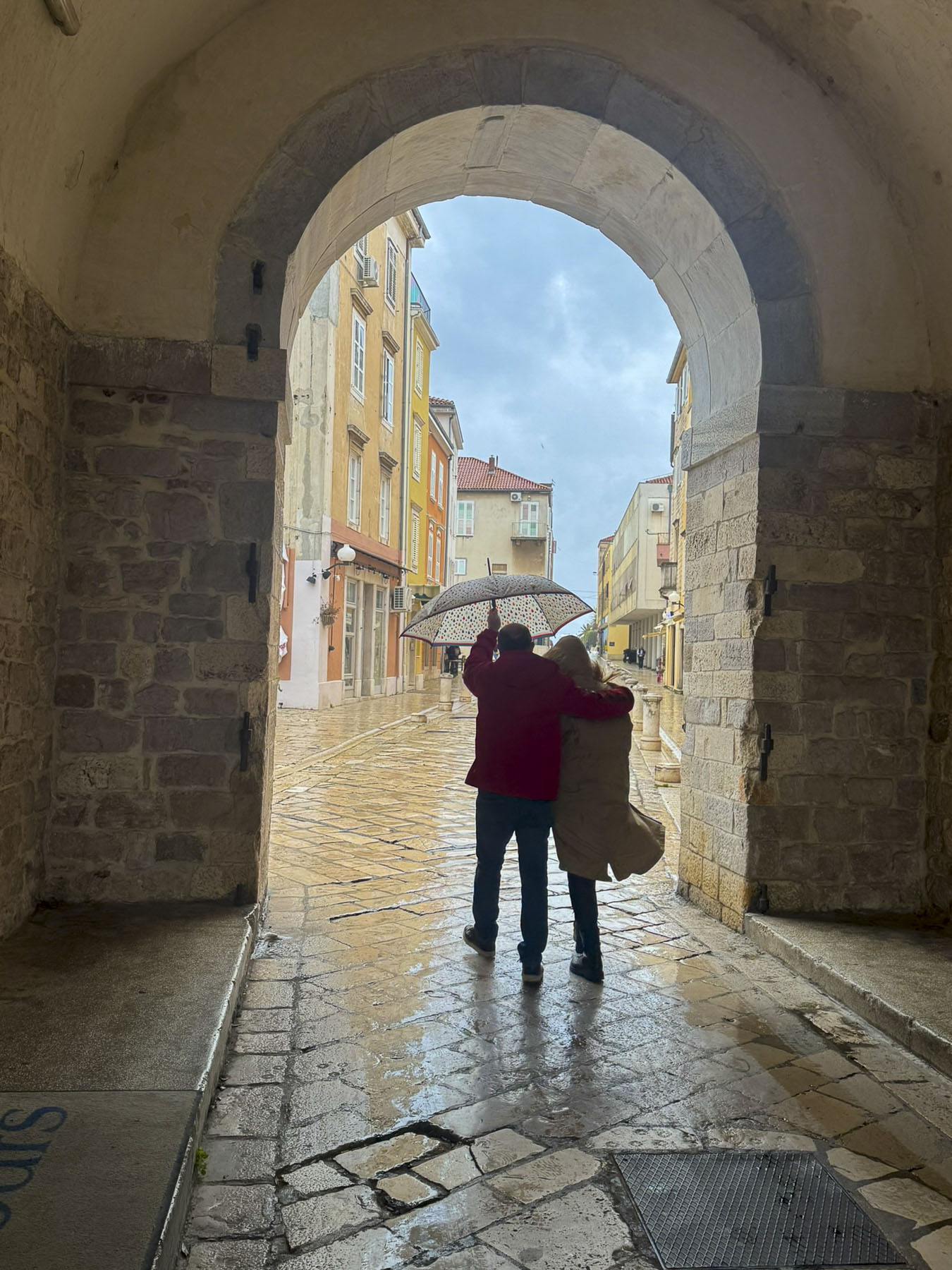


Several of the ancient gates still stand and allow passage from the old town to the ferry harbor. The top of the ramparts over the gates have been incorporated into a scenic walkway that parallels the waterfront and provides a pretty vantage point to view all the maritime activity, and some vignettes of old town Zadar.
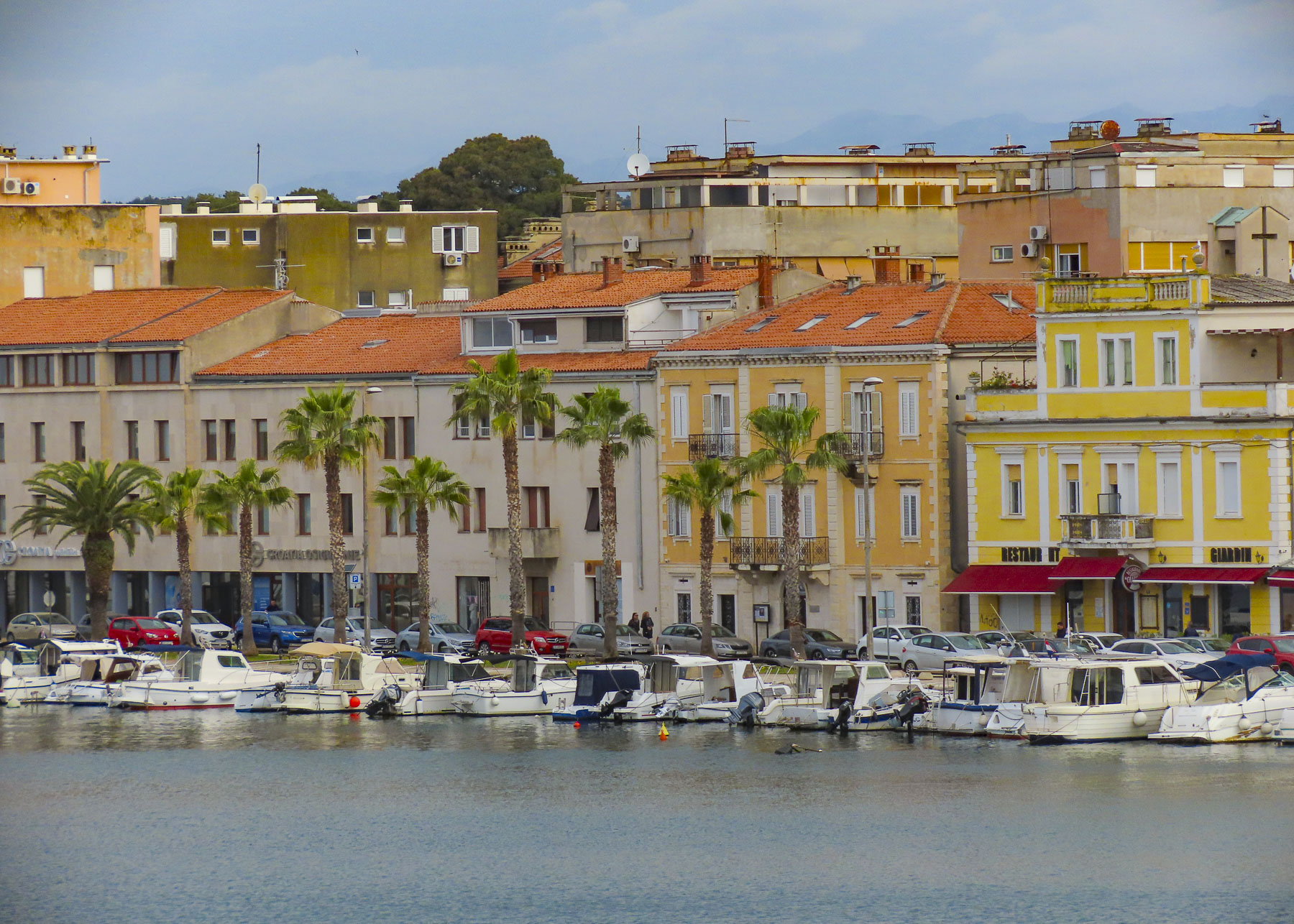





Along this walk we spotted a younger man rowing a small boat with passengers across the narrow harbor, from a small lighthouse to a staired landing on the quay. Apparently, they were on the way to work and his service, like the traghetto in Venice, provided a shortcut. A sign we discovered the next day listed the fee as 2€.

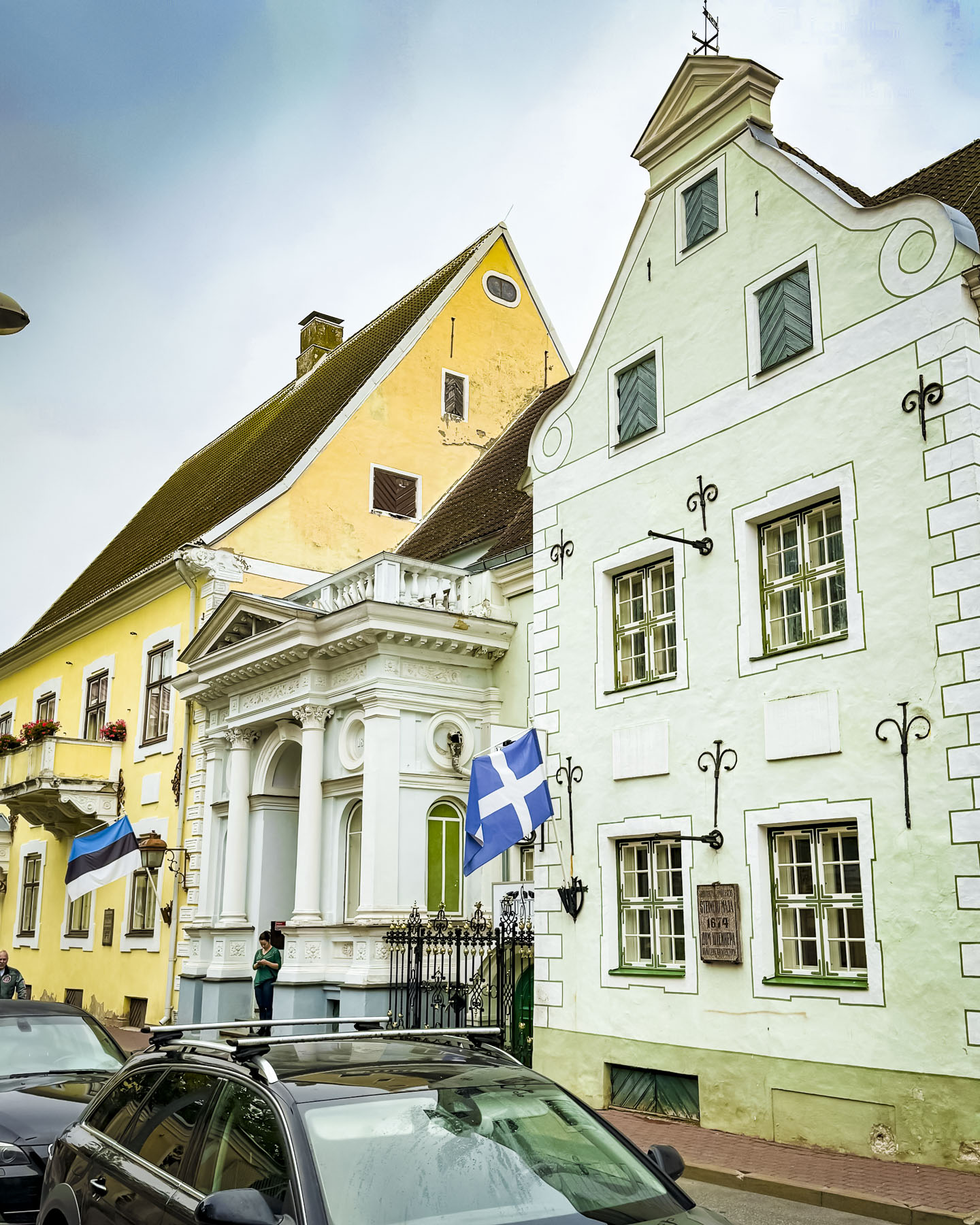
Over the years the population of Zadar has sprawled into new buildings on the mainland, unlike Dubrovnik, which has been gentrified into a theme park. Old Town Zadar, on the other hand, has some newer buildings on its peninsula, but also has many that show the patina of age, and give the town an authenticity and delightful ambience.



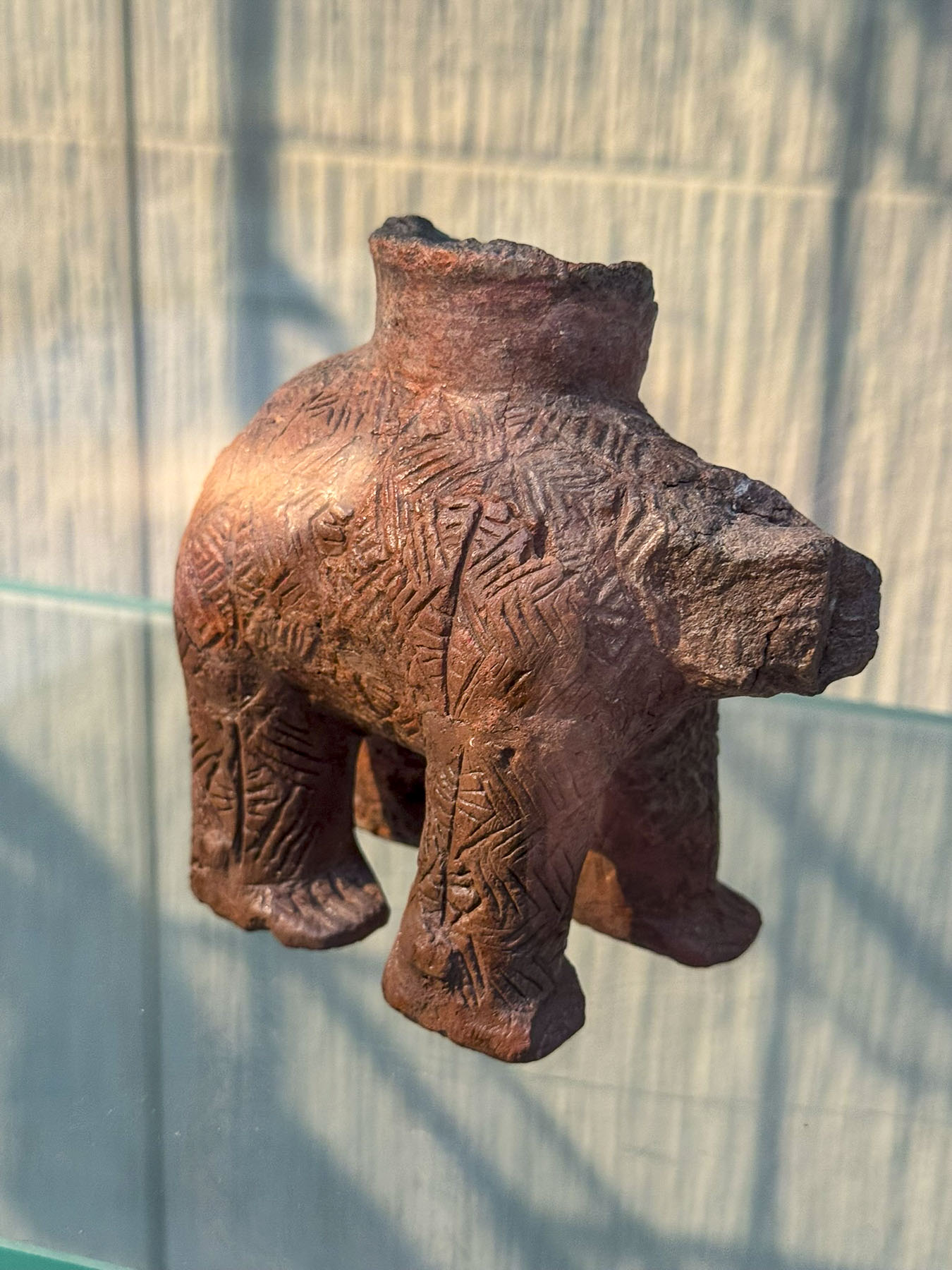
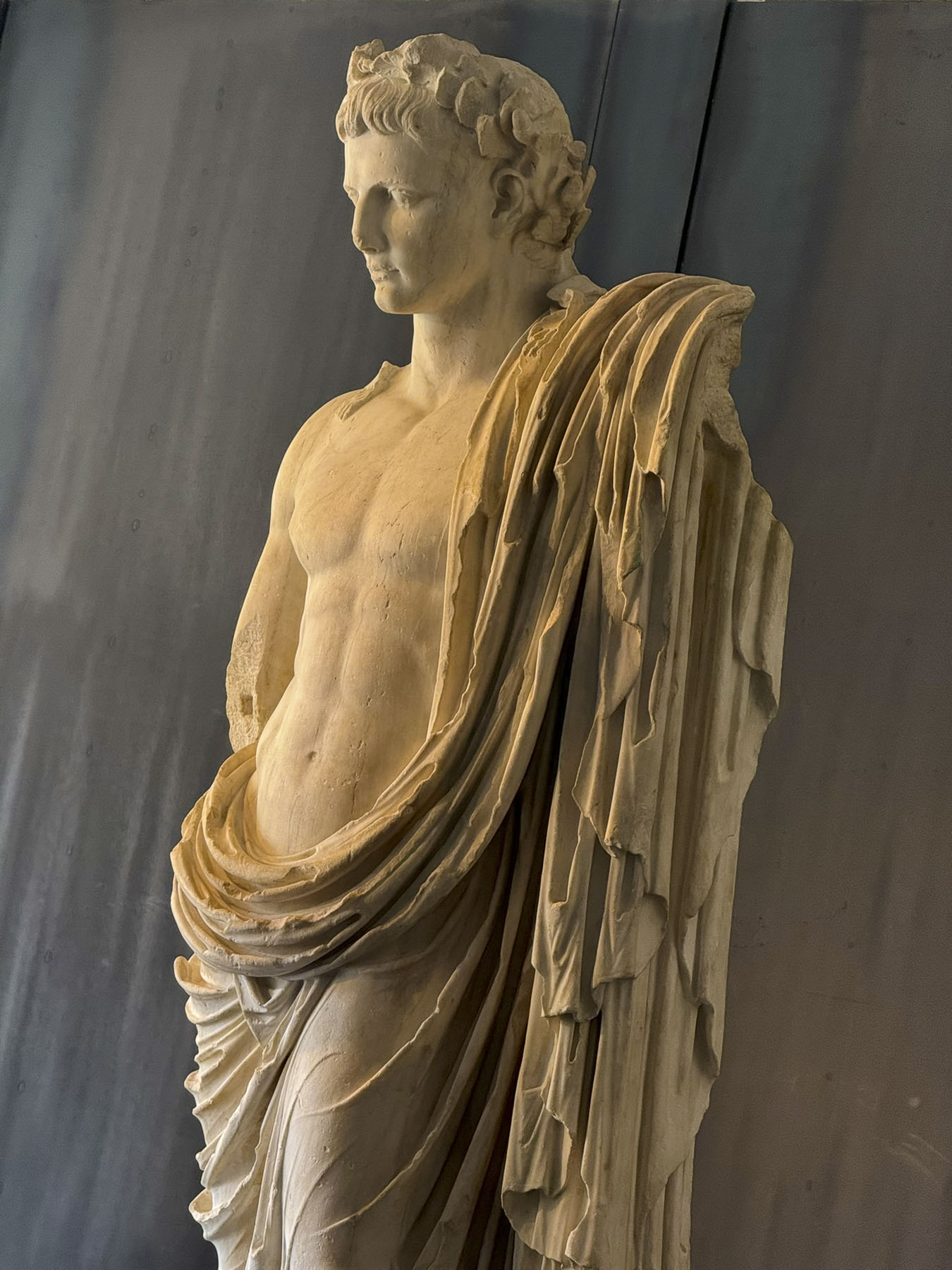
Our sunny morning was threatened with rain by noon, so we headed into the Archaeological Museum, where they have an interesting and diverse collection of ancient artifacts, statuary, and busts unearthed in Zadar, from its pre-history through the Roman Era and Venetian times. Especially unusual was the collection of Neolithic Rhytons, a four-legged ceramic ritual vessel, from the Impresso and Danilo cultures.









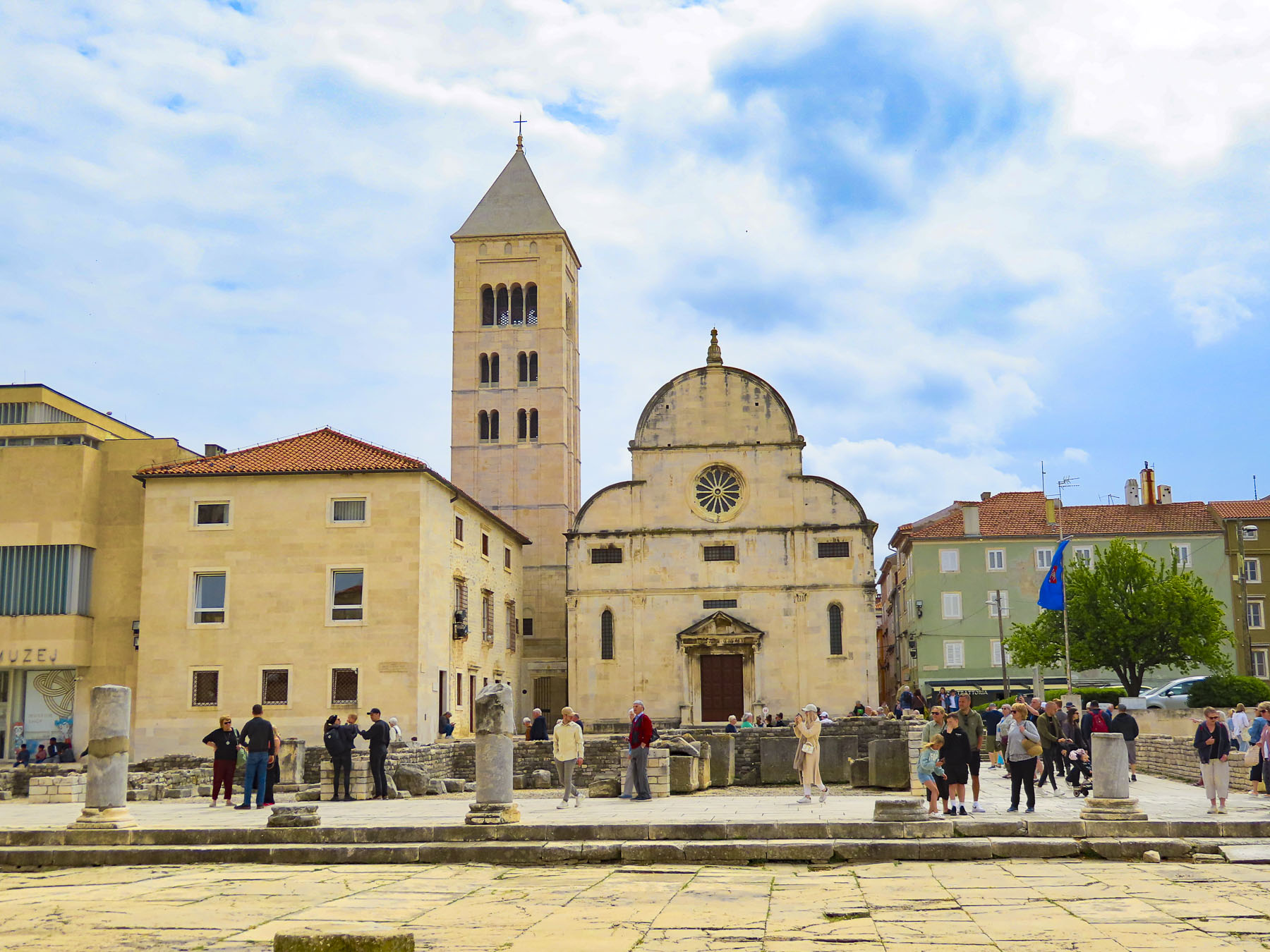
From the museum there is a good view of the Church of St. Donatus, and the belltower of Sainte Anastasie across from the ruins of the Roman forum. We’d pass these landmarks multiple times during our stay.

Fortunately, we did have good raincoats, and we scurried to Kavana Centar, a very nice café several blocks away that had some indoor tables still available and offered a reprieve from the rain. Located away from the main square, its menu was very budget friendly.

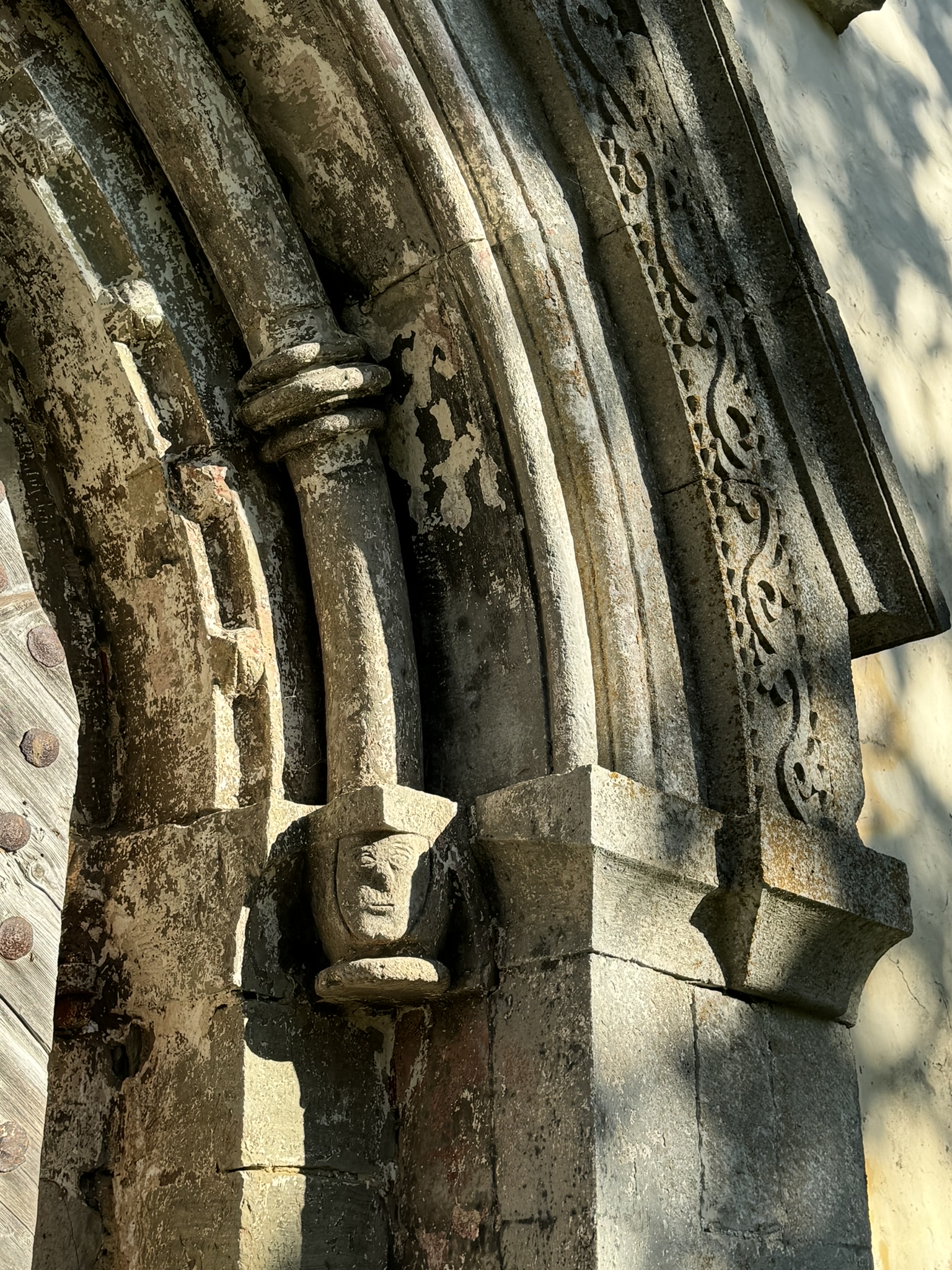
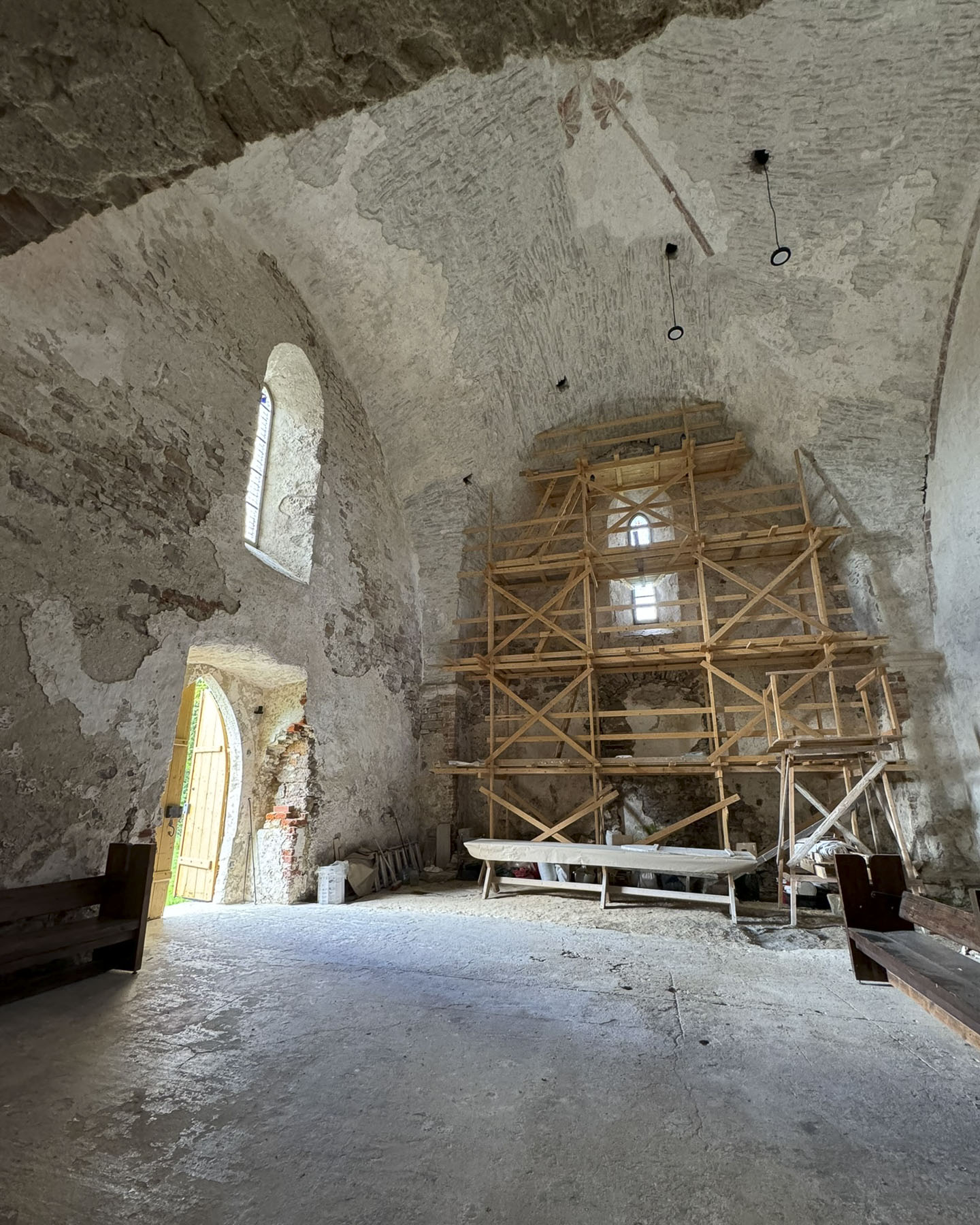
Though the rain had not stopped, folks continued on with their plans, and soon umbrellas were out everywhere. After lunch, we headed back to St. Donatus, an unusual tall round cylinder-shaped church built during the 9th century in a pre-Romanesque style. Much of its construction utilized the ruins of the old Roman Forum, upon which it was built.
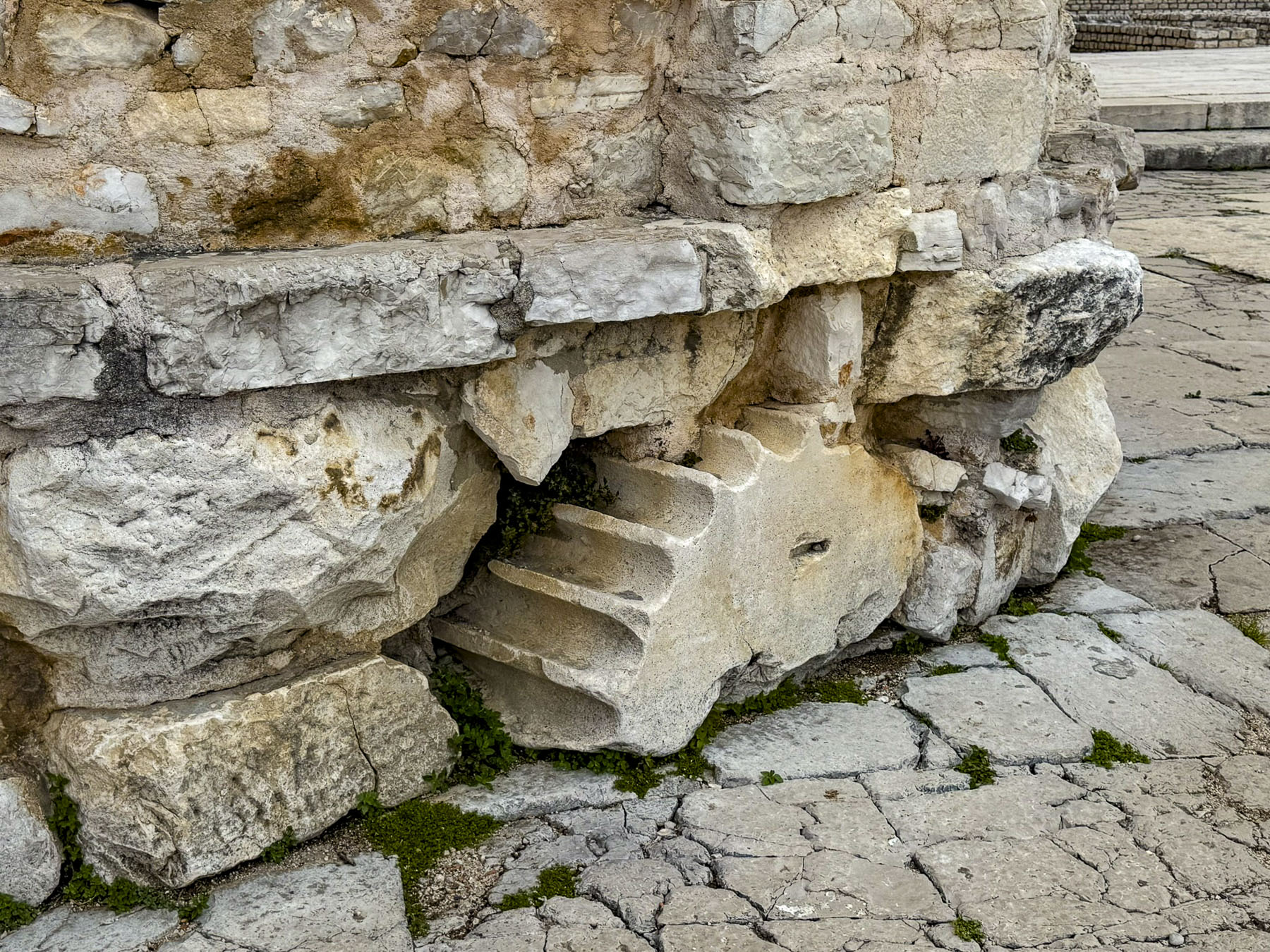

The fragments of reused columns, capitals, plinths, and cornices were used as fill, and can be seen in several exposed spots along the church’s foundation and interior. Its mammoth interior is 27m (89ft) tall, and at the top is a gallery that overlooks the space below.
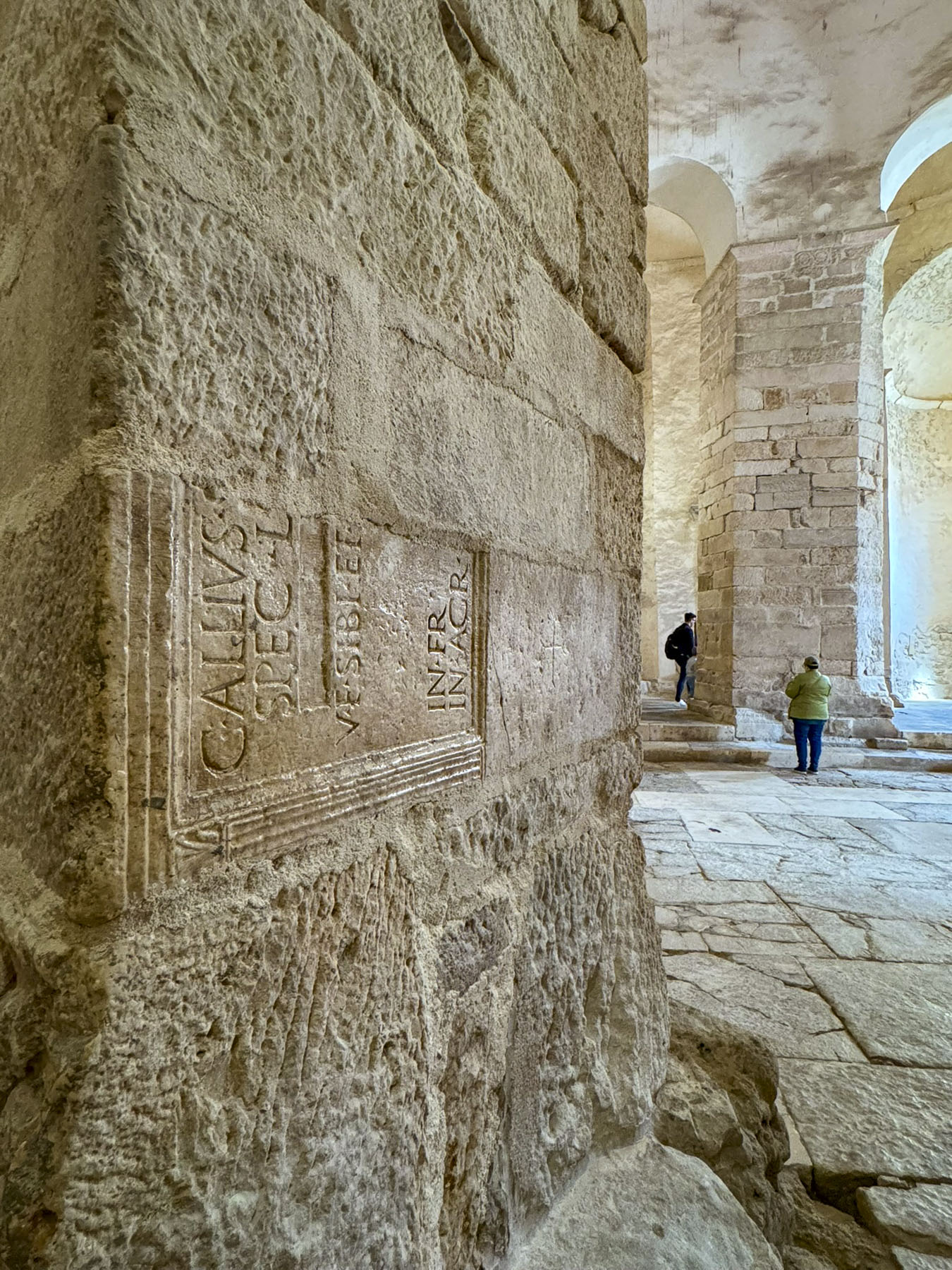

The church was deconsecrated in the early 1700s, after which it was unceremoniously used as a wine cellar, warehouse, and Zadar’s first archaeological museum in the early 1900s. Nowadays, along with being a tourist site, it hosts theMusical Evenings at St Donatus, a concert series that utilizes the church’s excellent acoustics, every July.
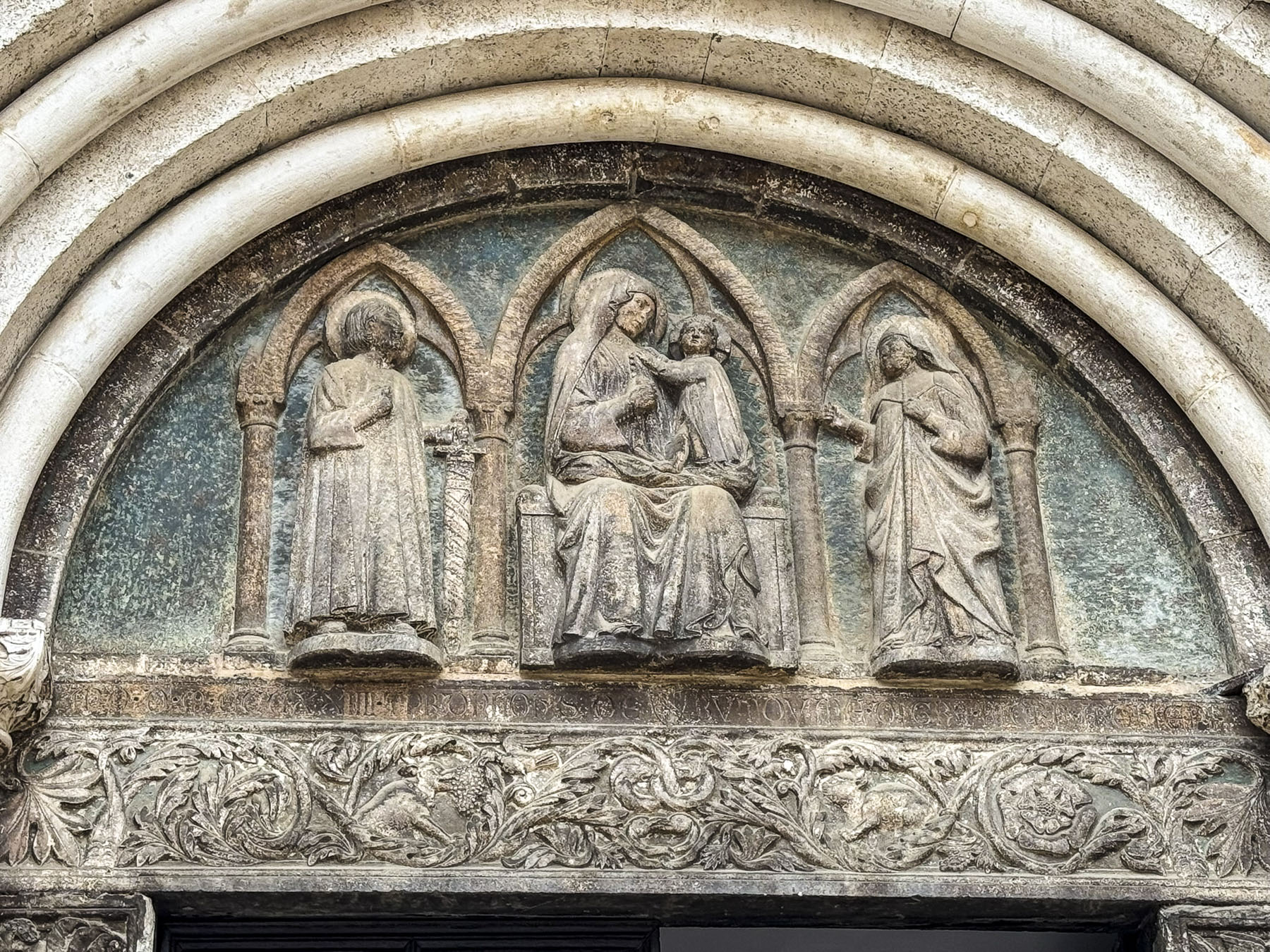


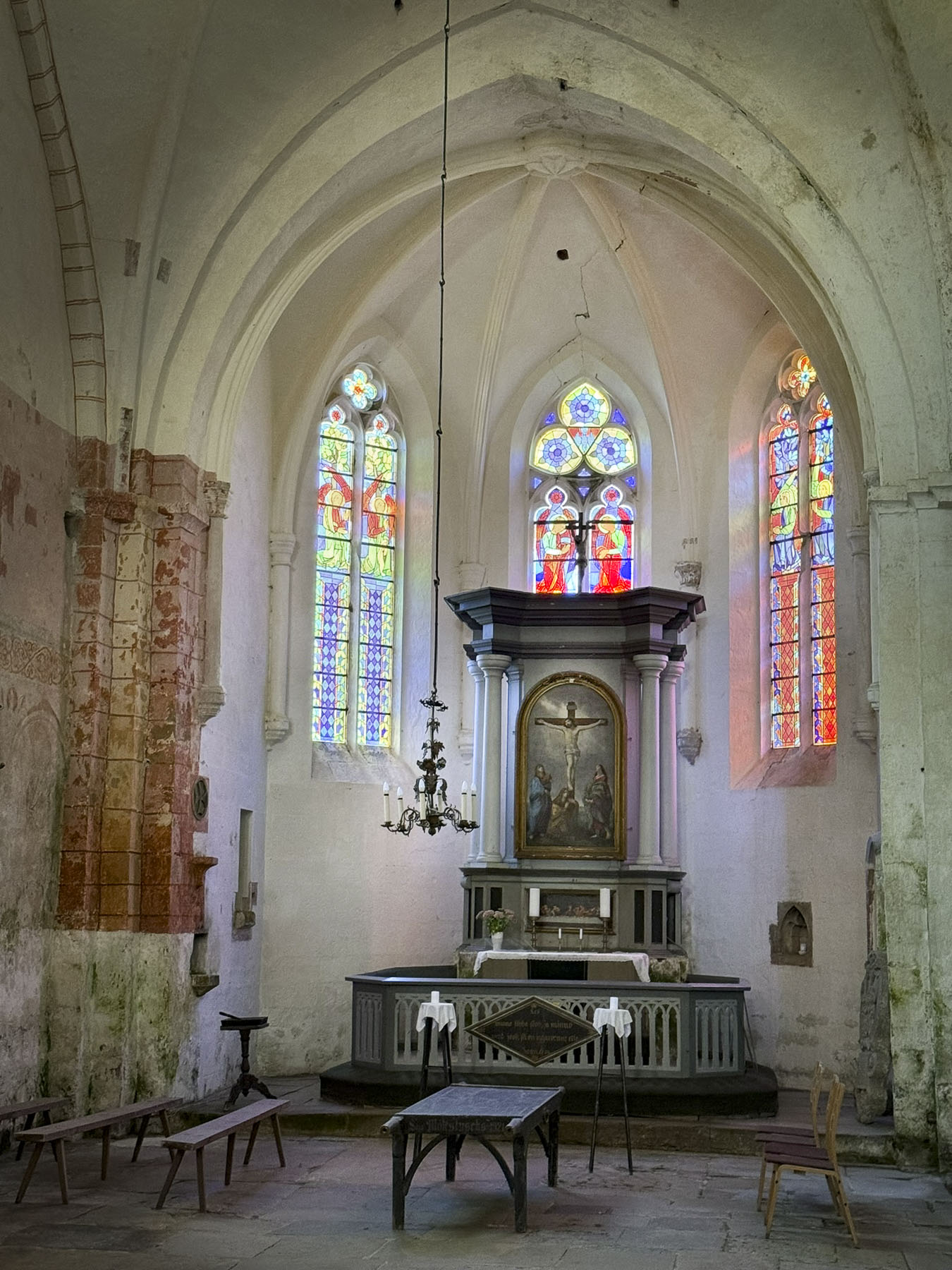
The Campanile di Sant’Anastasia, the belltower of the Cathedral of St Anastasia and its monastery, is right next to St. Donatus. The campanile was added to the church in the 15th century, four centuries after the church and its monastery were completed. During the high season it’s possible to climb the 186 steps to the top of the 55m (180ft) tall tower for a panoramic view of the city and sea. But unfortunately, in early April it was closed when we visited. Surprisingly, the entrance to the cathedral is on the other end of the building, around the corner from the belltower, and took us a few minutes to figure out its location.

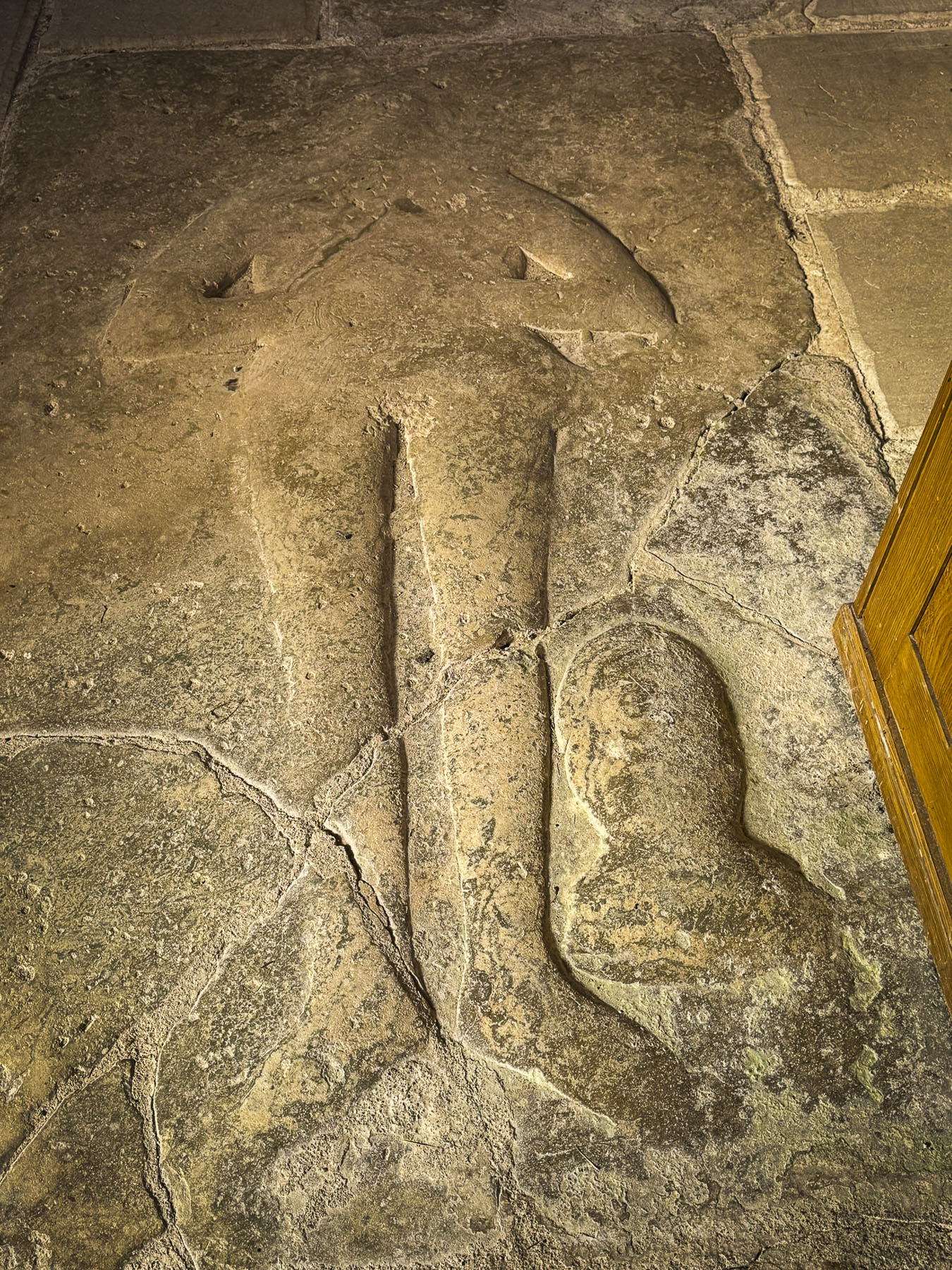
The interior of the Romanesque style church features an open timber truss roof, interesting side altars, an ancient fresco featuring what is believed to be a likeness of the saint, and the remnants of a 13th century mosaic floor, which I almost accidentally fell on, after losing my balance on the uneven stone flooring.
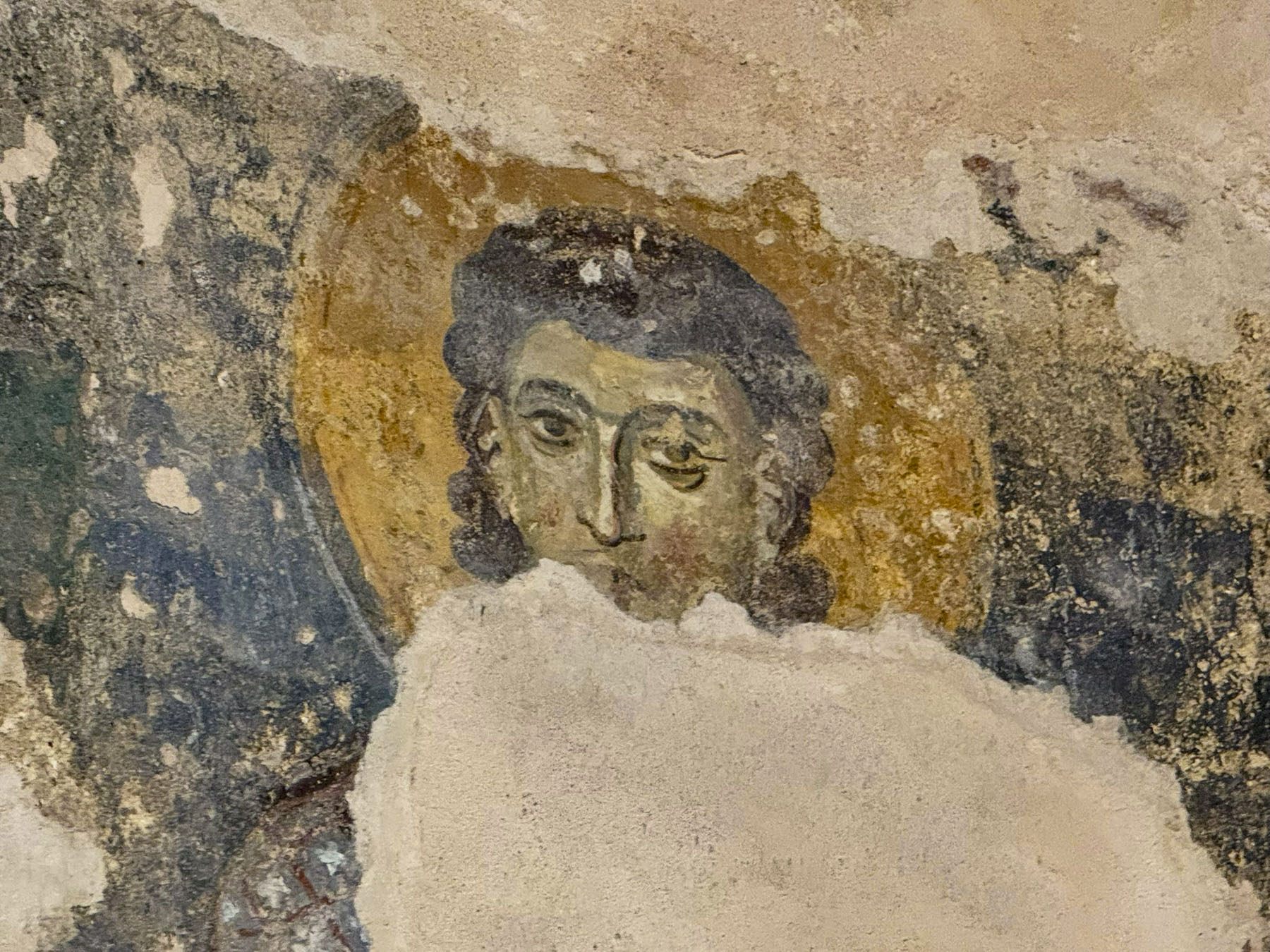




We could only imagine the uproar that would have ensued if I had damaged the antiquity. We wondered if our travel insurance would be of any use in this situation.

There are numerous other churches in old town Zadar. Choosing several churches and connecting the dots between them we found was a good way to see the various neighborhoods on the peninsula.

One of our favorites was the Crkva Gospe od Zdravlja, the Church of Our Lady of Health, set on the edge of a small park. Its small intimate interior was often visited by folks on their way to work in the morning.




Over the course of our wanderings past random buildings, down narrow alleys, and in dim courtyards, we found examples of the many different architectural styles that have graced the city over the centuries.
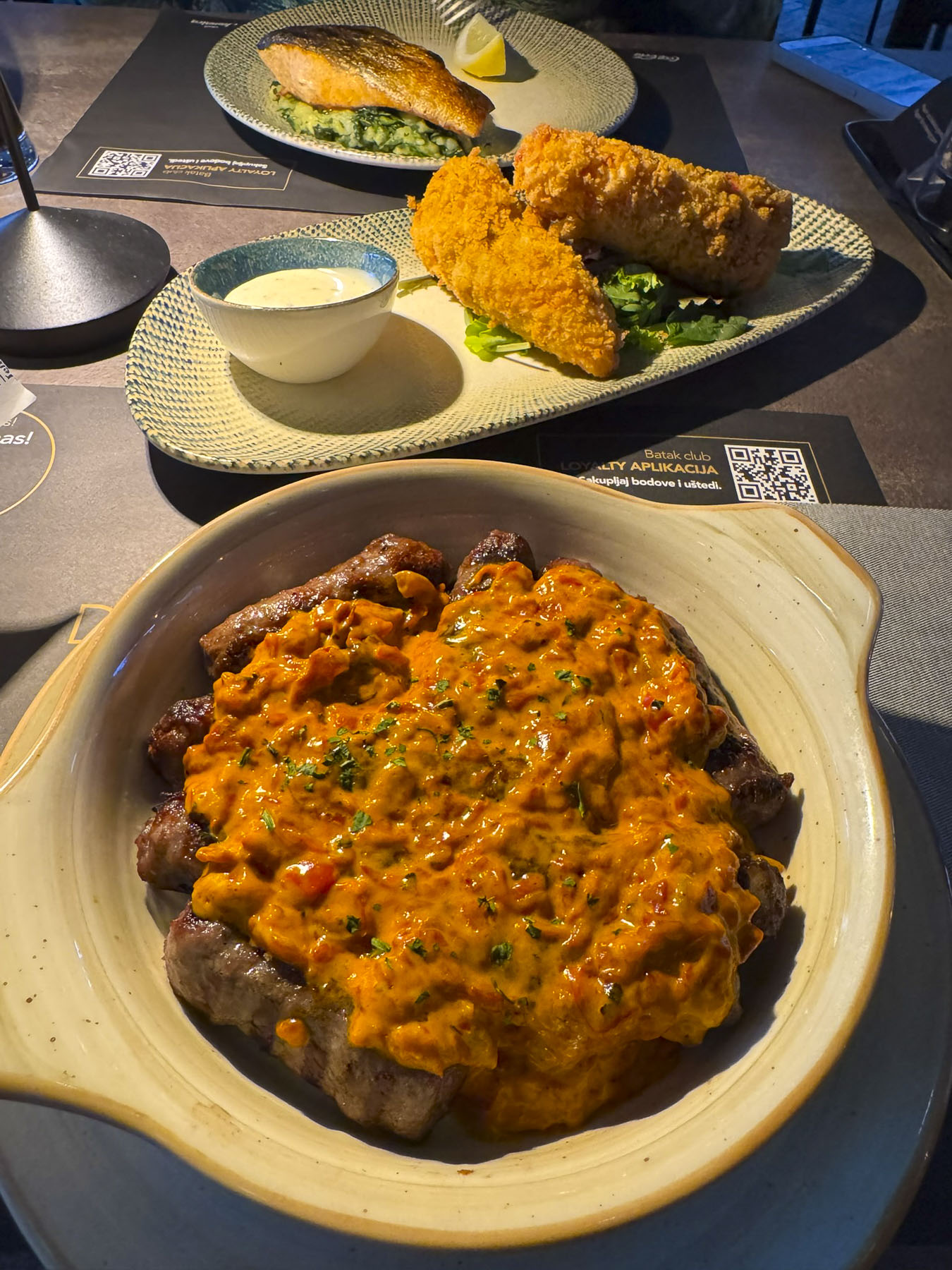
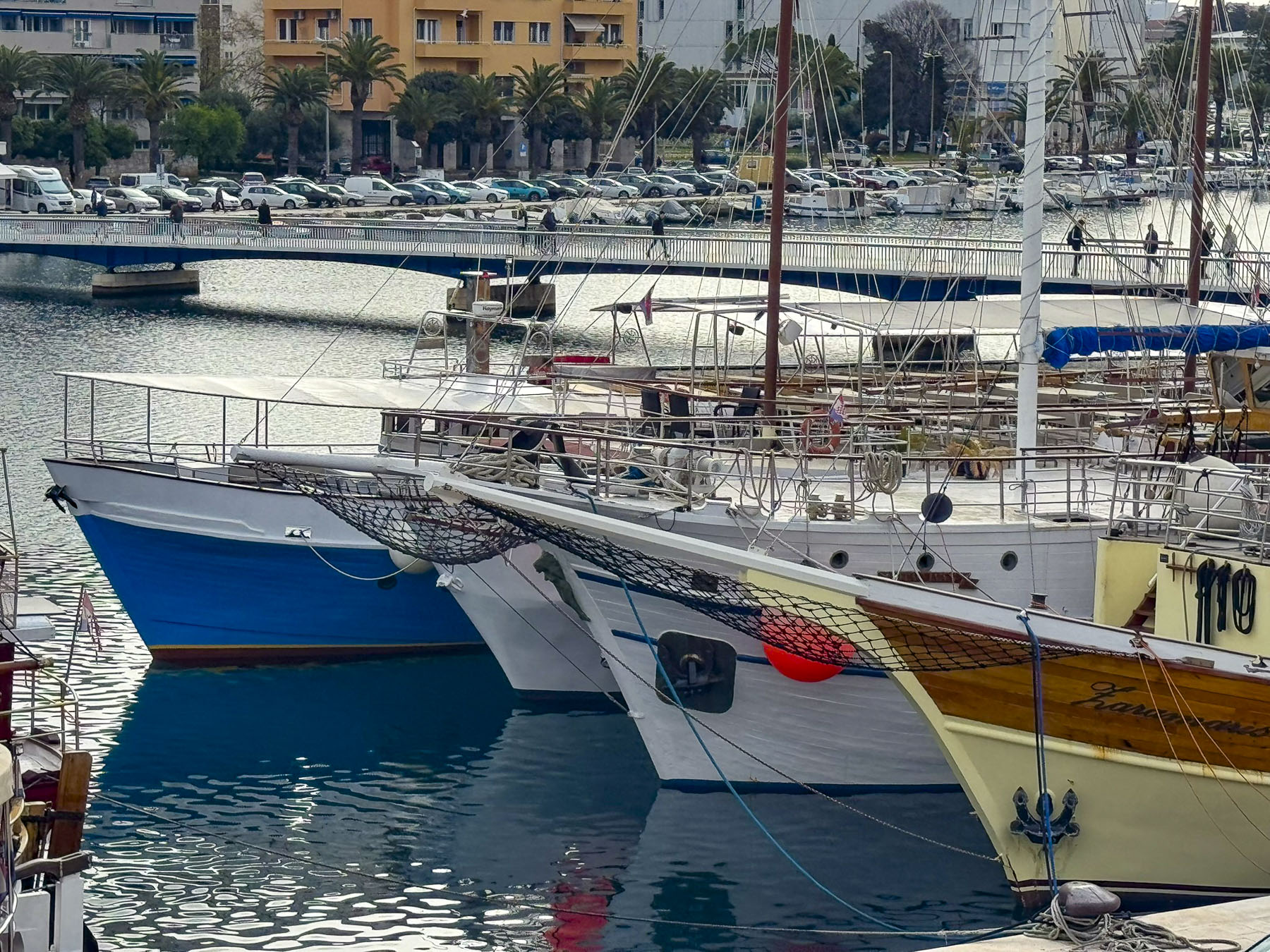


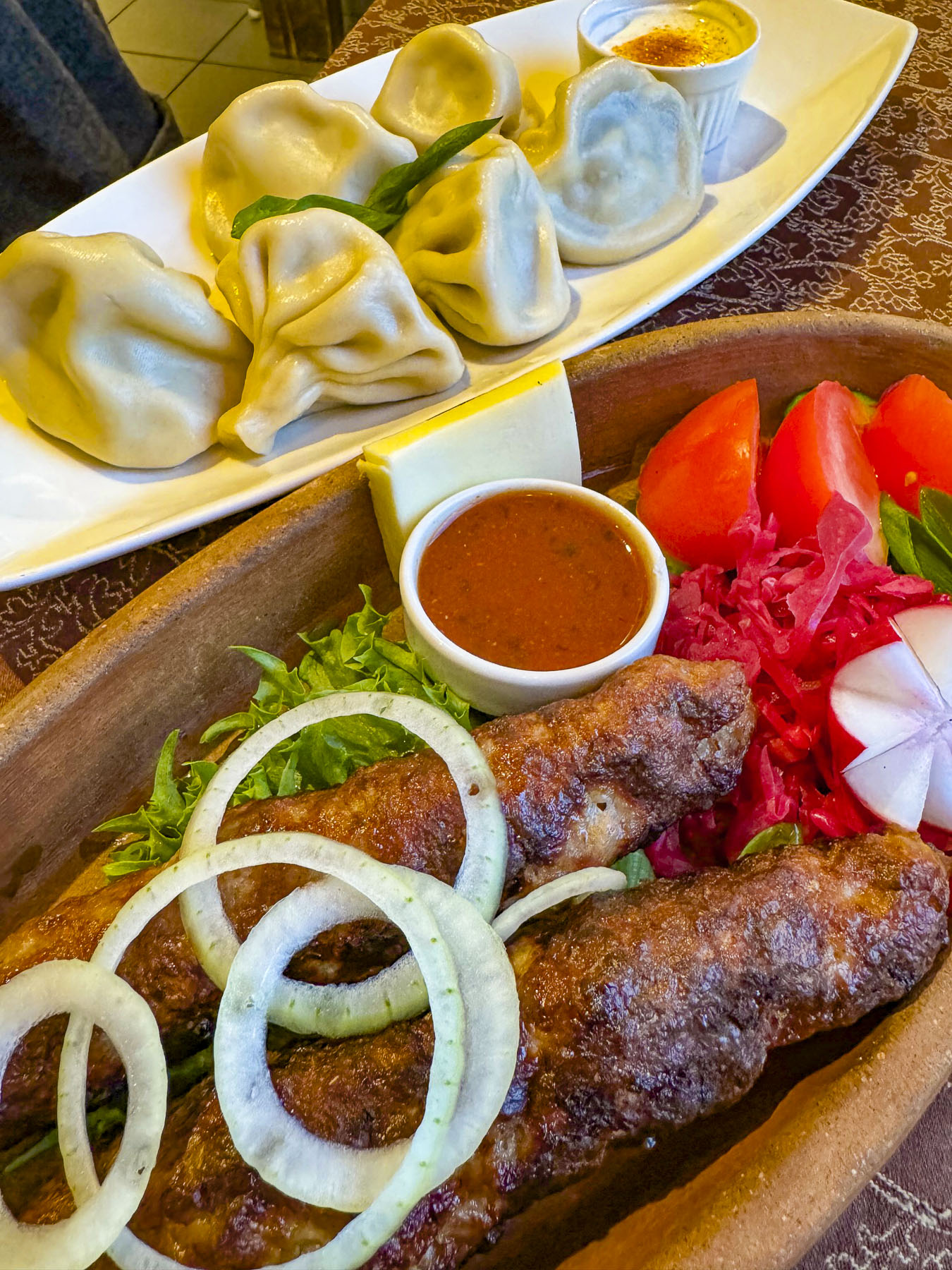
On our last night in Zadar, we drove off the peninsula to another recommended restaurant, Batak Zadar, located in a shopping center, far away from the tourist zone. We ordered several of their Croatian classics, and a local red wine. Everything was very good, and an excellent value compared to the inflated pricing of the restaurants in old town Zadar.
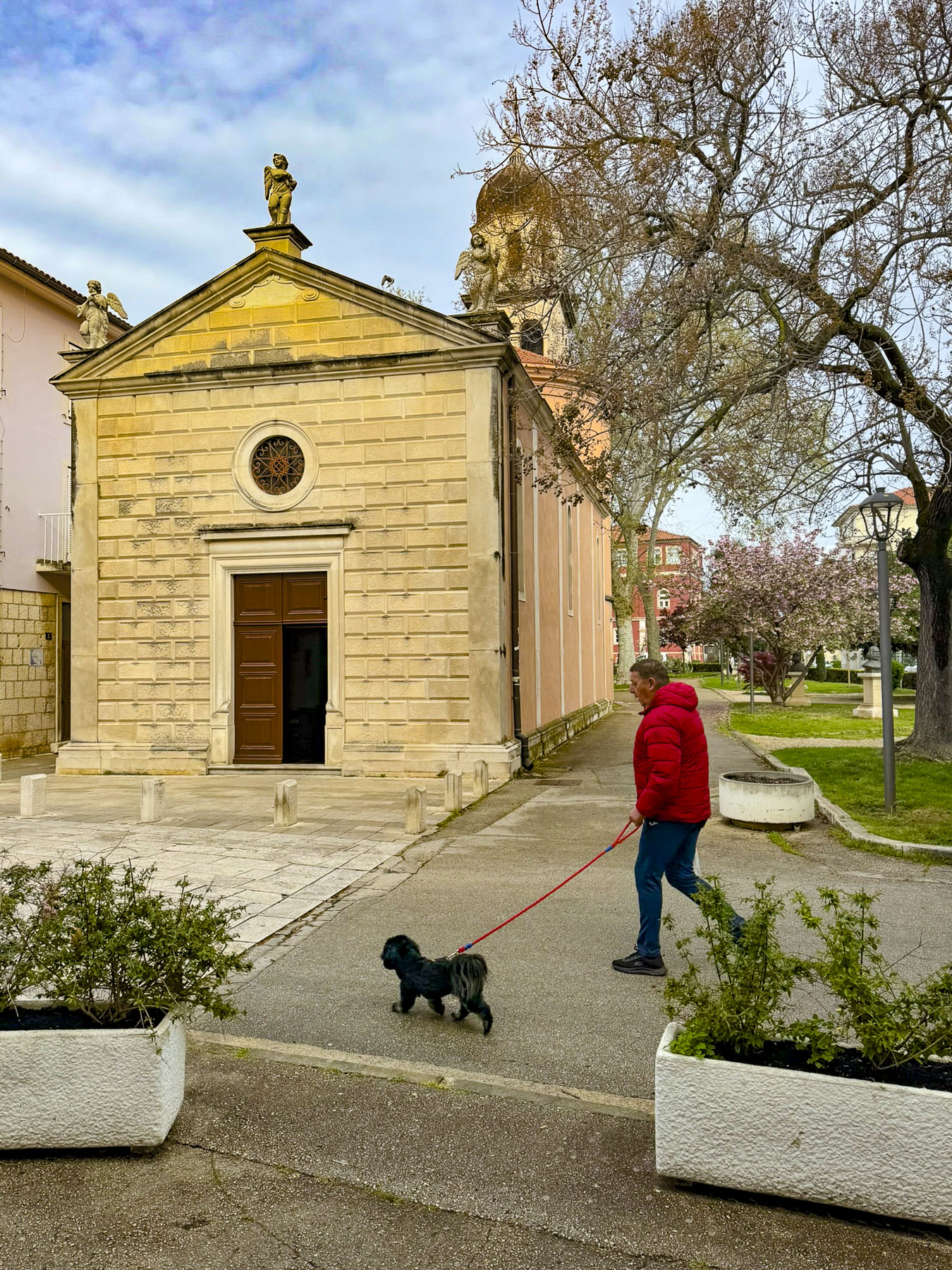





Though the weather could have been more cooperative, we enjoyed our three-night stay in Zadar, and found the size of the charming city just right for a short stay before the start our three-week road trip through Croatia, Slovenia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Till next time,
Craig & Donna